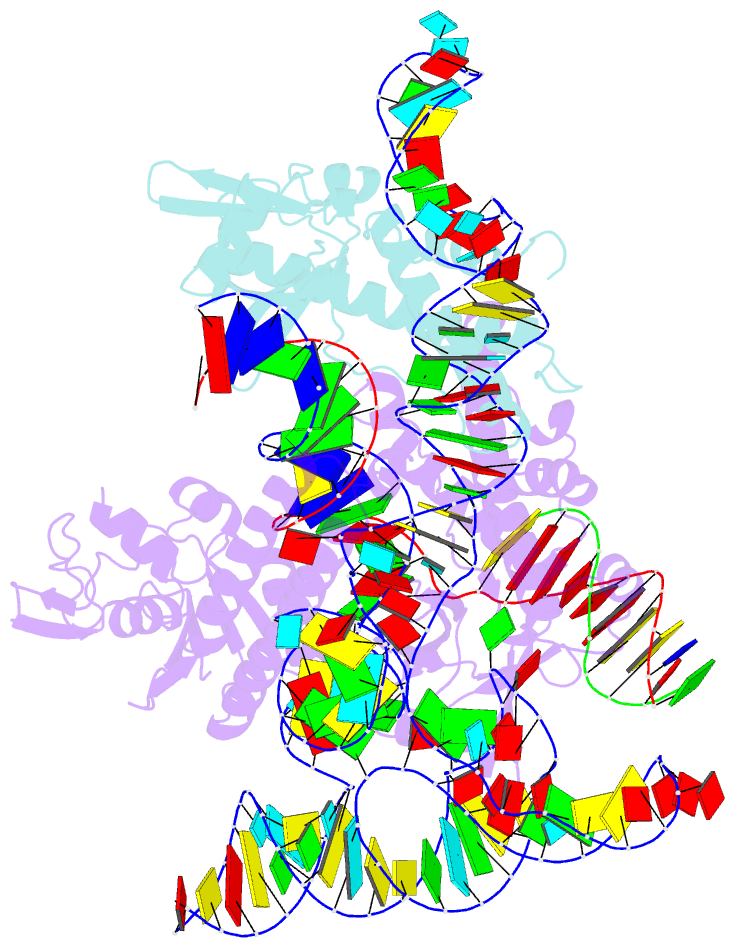
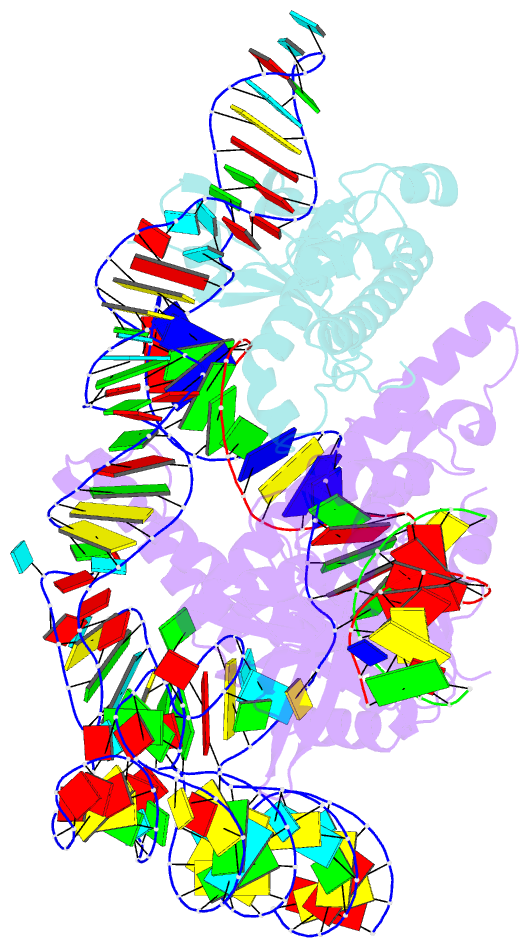
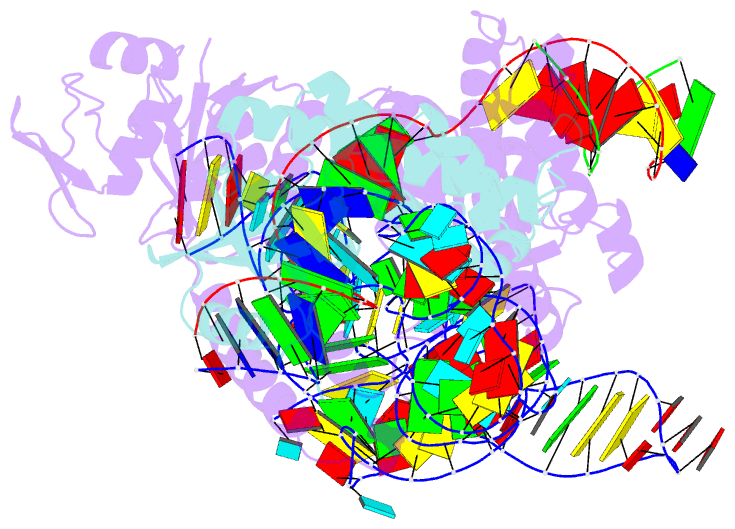
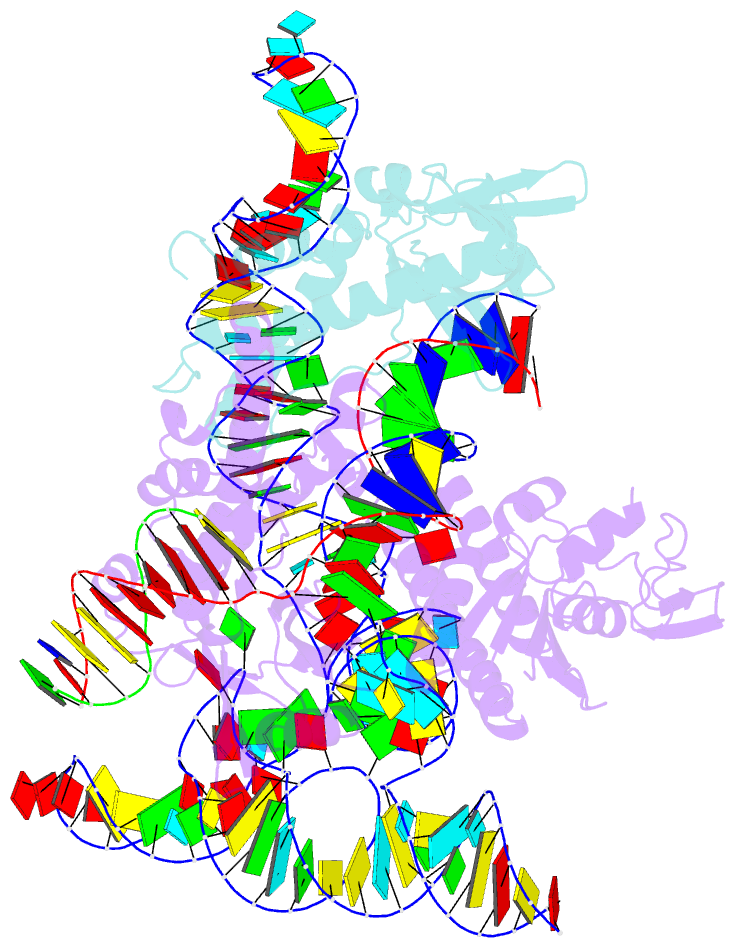
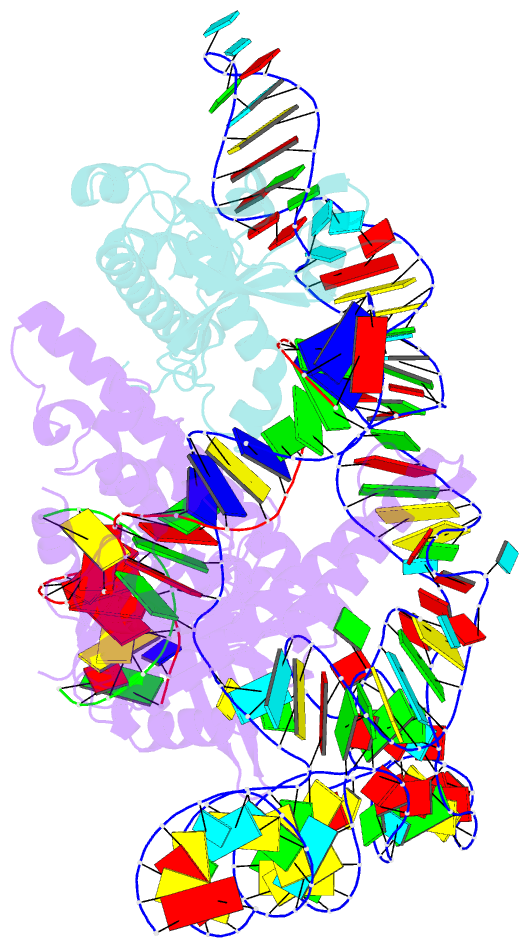
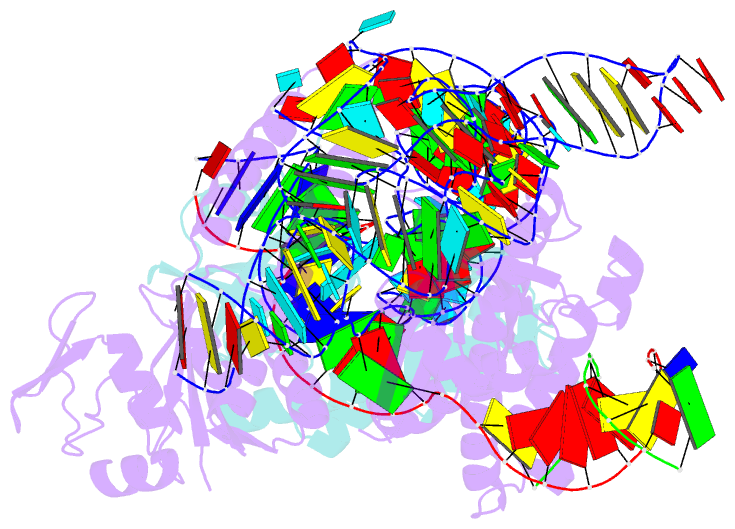
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8dzj; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.9 Å)
- Summary
- cryo-EM structure of acidibacillus sulfuroxidans cas12f in complex with sgrna and target DNA
- Reference
- Wu T, Liu C, Zou S, Lyu R, Yang B, Yan H, Zhao M, Tang W (2023): "An engineered hypercompact CRISPR-Cas12f system with boosted gene-editing activity." Nat.Chem.Biol., 19, 1384-1393. doi: 10.1038/s41589-023-01380-9.
- Abstract
- Compact CRISPR-Cas systems offer versatile treatment options for genetic disorders, but their application is often limited by modest gene-editing activity. Here we present enAsCas12f, an engineered RNA-guided DNA endonuclease up to 11.3-fold more potent than its parent protein, AsCas12f, and one-third of the size of SpCas9. enAsCas12f shows higher DNA cleavage activity than wild-type AsCas12f in vitro and functions broadly in human cells, delivering up to 69.8% insertions and deletions at user-specified genomic loci. Minimal off-target editing is observed with enAsCas12f, suggesting that boosted on-target activity does not impair genome-wide specificity. We determine the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the AsCas12f-sgRNA-DNA complex at a resolution of 2.9 Å, which reveals dimerization-mediated substrate recognition and cleavage. Structure-guided single guide RNA (sgRNA) engineering leads to sgRNA-v2, which is 33% shorter than the full-length sgRNA, but with on par activity. Together, the engineered hypercompact AsCas12f system enables robust and faithful gene editing in mammalian cells.