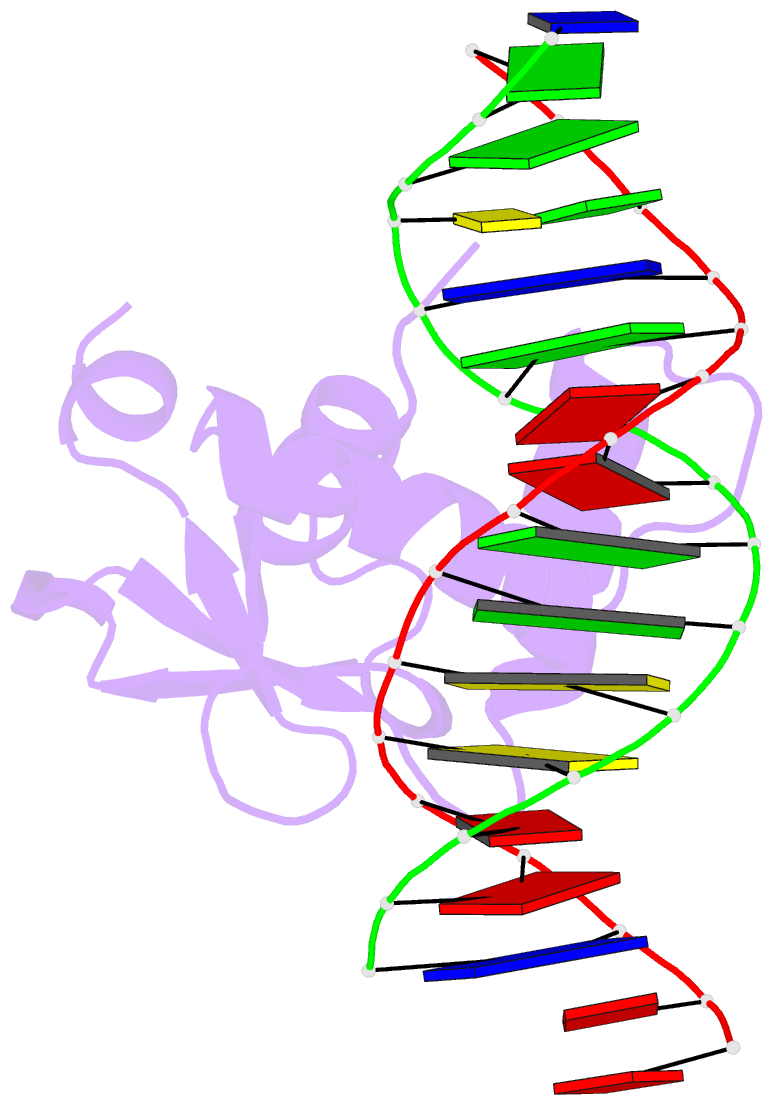
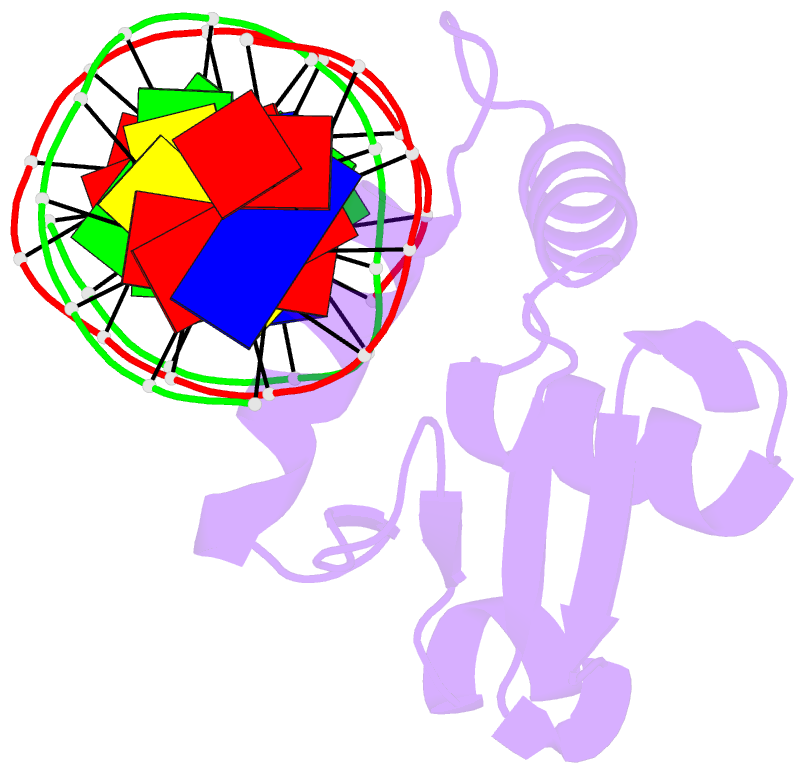
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8eqk; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.45 Å)
- Summary
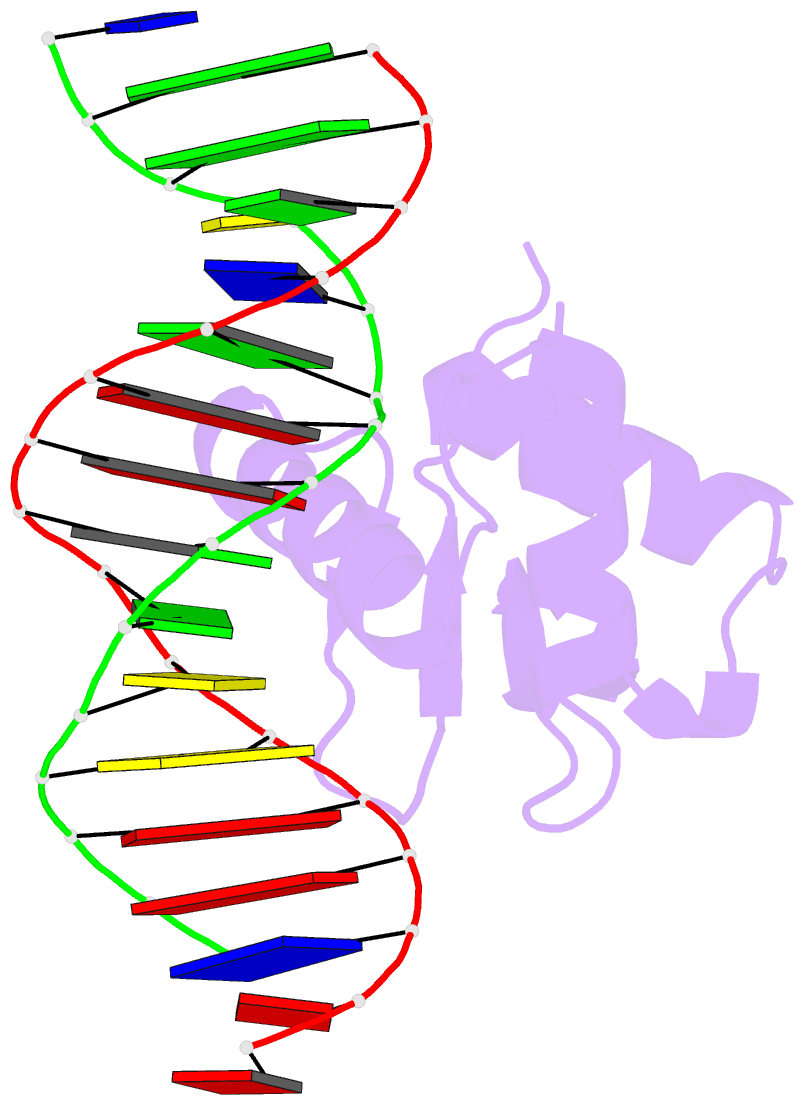
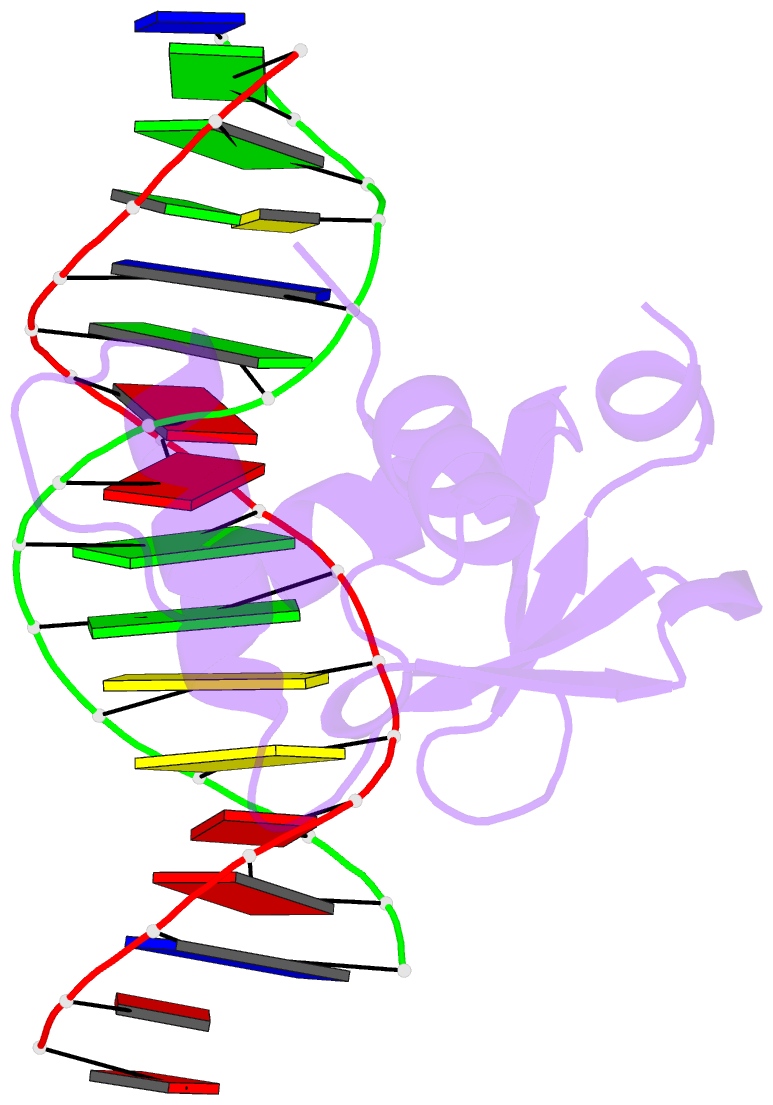
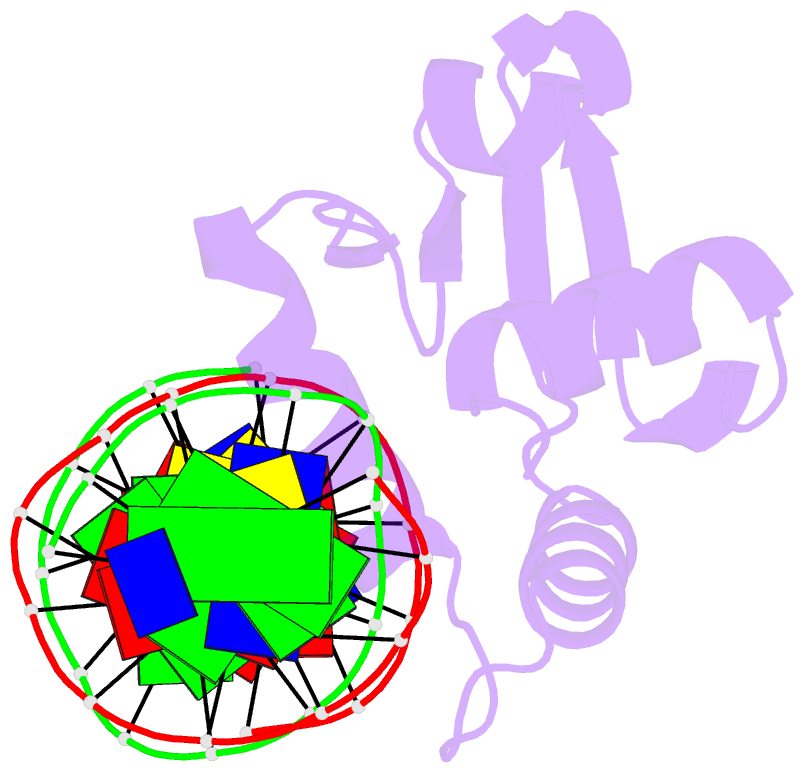
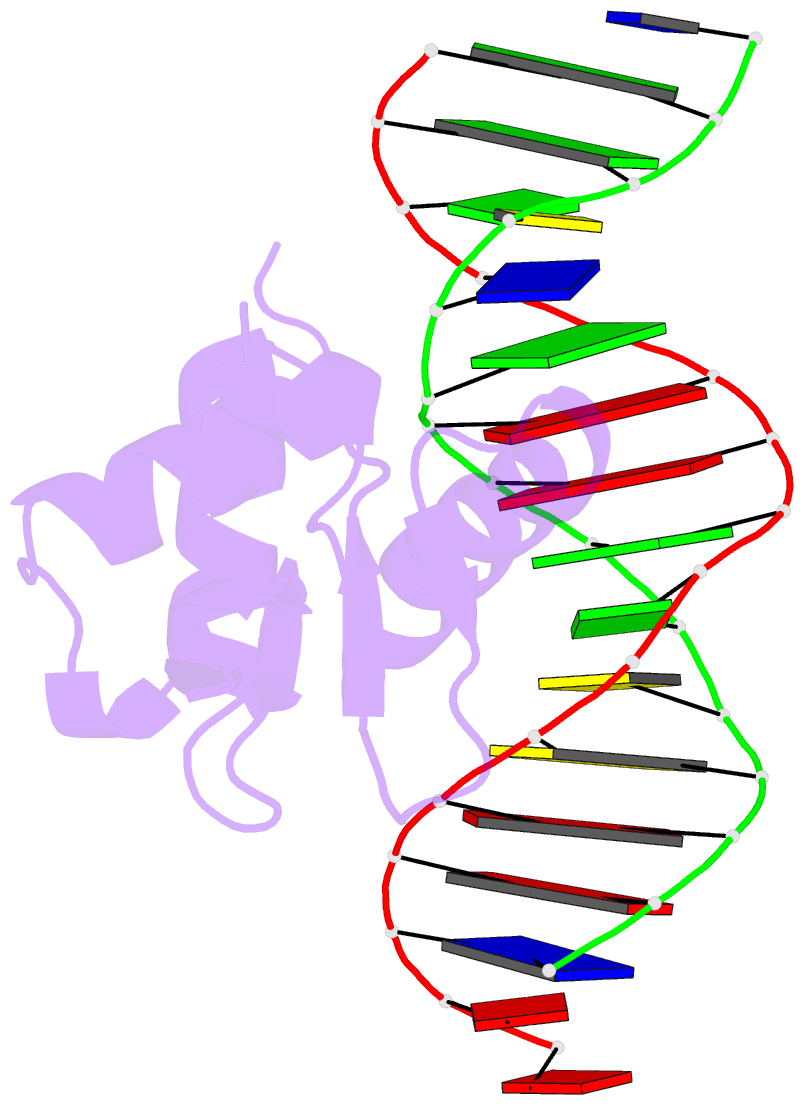
- Human pu.1 ets-domain (165-270) bound to d(aataaccggaagtggg)
- Reference
- Terrell JR, Taylor SJ, Schneider AL, Lu Y, Vernon TN, Xhani S, Gumpper RH, Luo M, Wilson WD, Steidl U, Poon GMK (2023): "DNA selection by the master transcription factor PU.1." Cell Rep, 42, 112671. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112671.
- Abstract
- The master transcriptional regulator PU.1/Spi-1 engages DNA sites with affinities spanning multiple orders of magnitude. To elucidate this remarkable plasticity, we have characterized 22 high-resolution co-crystallographic PU.1/DNA complexes across the addressable affinity range in myeloid gene transactivation. Over a purine-rich core (such as 5'-GGAA-3') flanked by variable sequences, affinity is negotiated by direct readout on the 5' flank via a critical glutamine (Q226) sidechain and by indirect readout on the 3' flank by sequence-dependent helical flexibility. Direct readout by Q226 dynamically specifies PU.1's characteristic preference for purines and explains the pathogenic mutation Q226E in Waldenström macroglobulinemia. The structures also reveal how disruption of Q226 mediates strand-specific inhibition by DNA methylation and the recognition of non-canonical sites, including the authentic binding sequence at the CD11b promoter. A re-synthesis of phylogenetic and structural data on the ETS family, considering the centrality of Q226 in PU.1, unifies the model of DNA selection by ETS proteins.