Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8f1k; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.8 Å)
- Summary
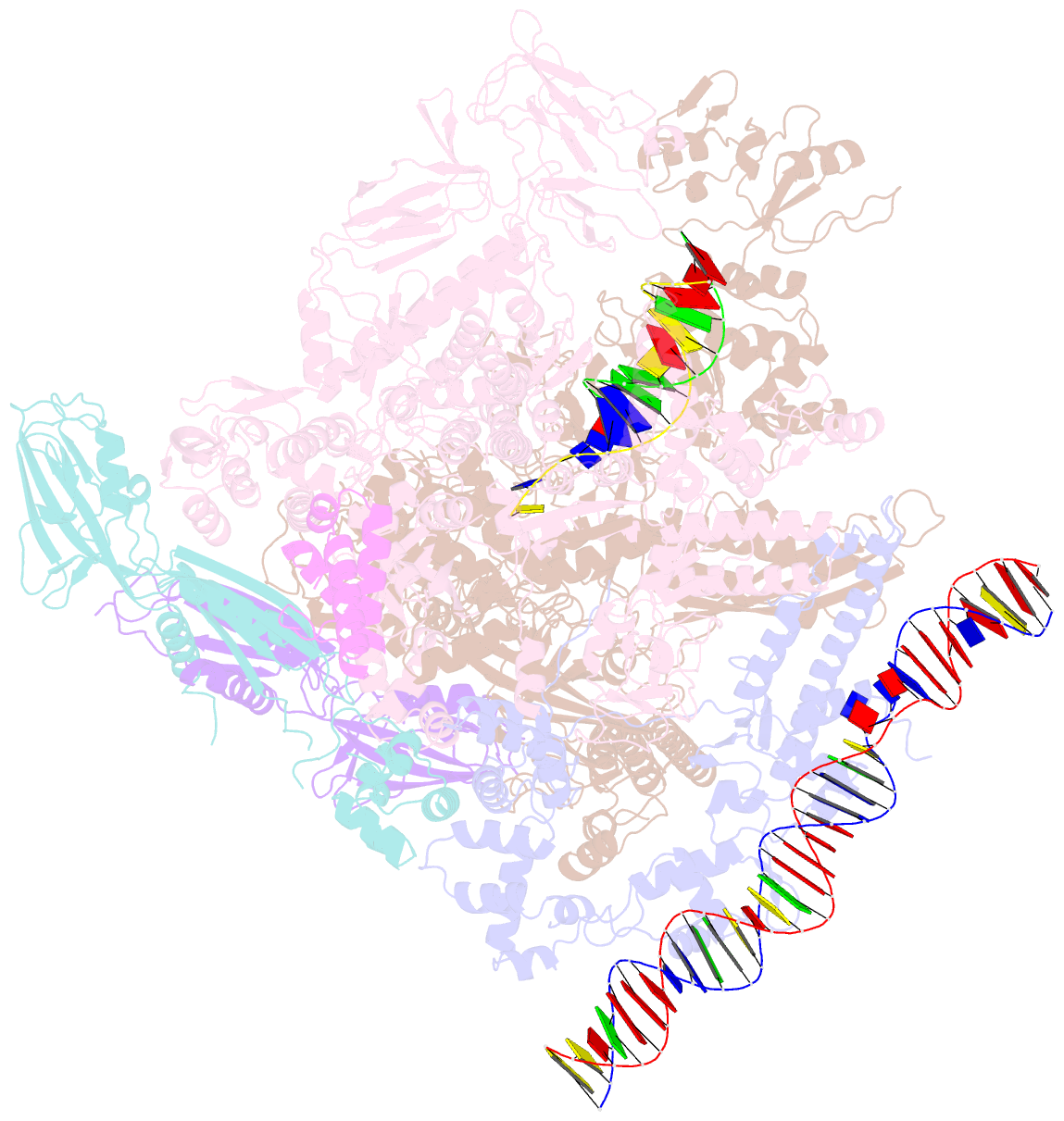
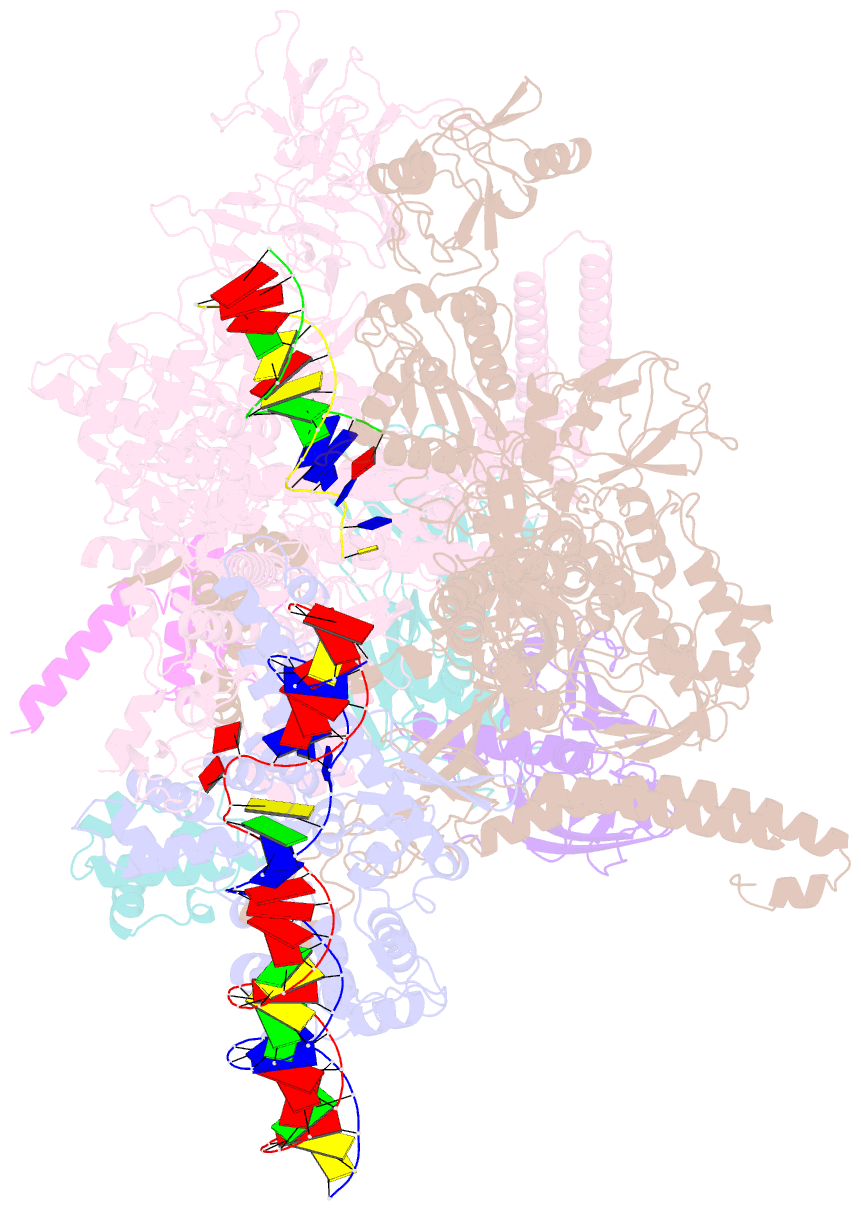
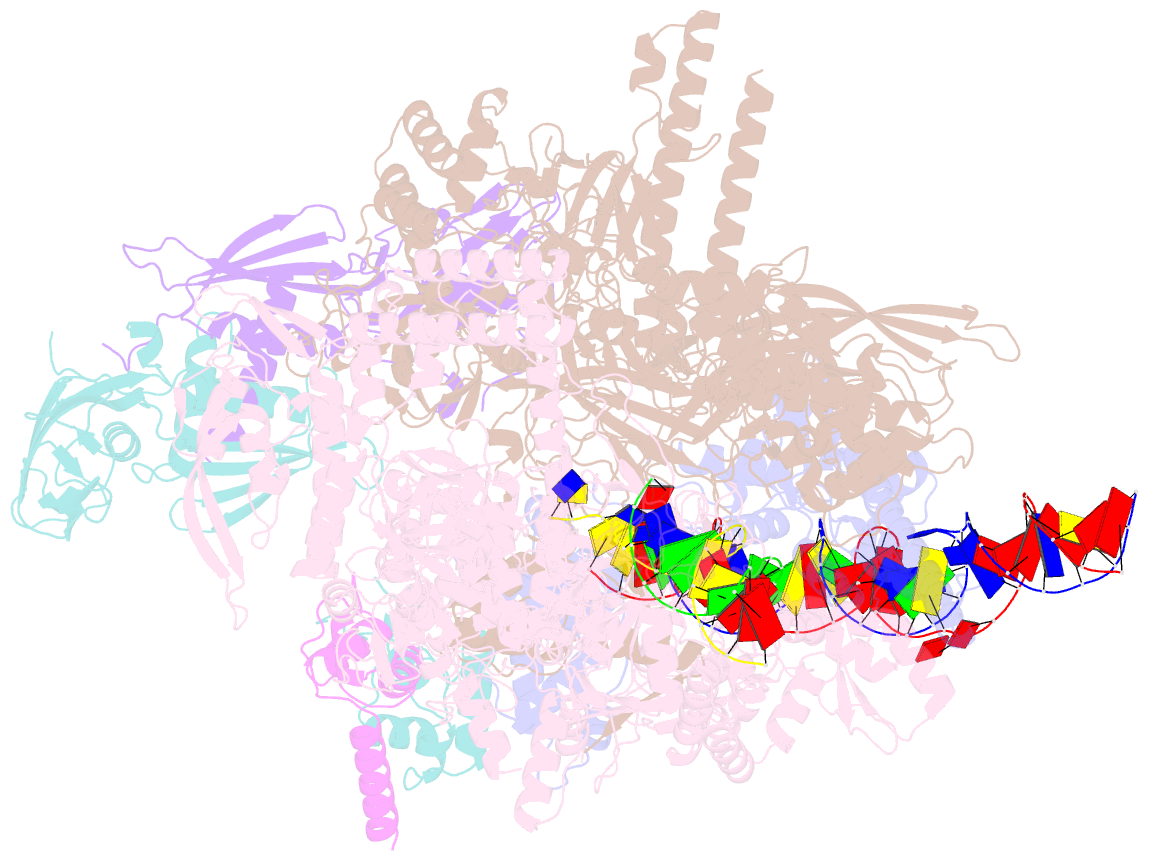
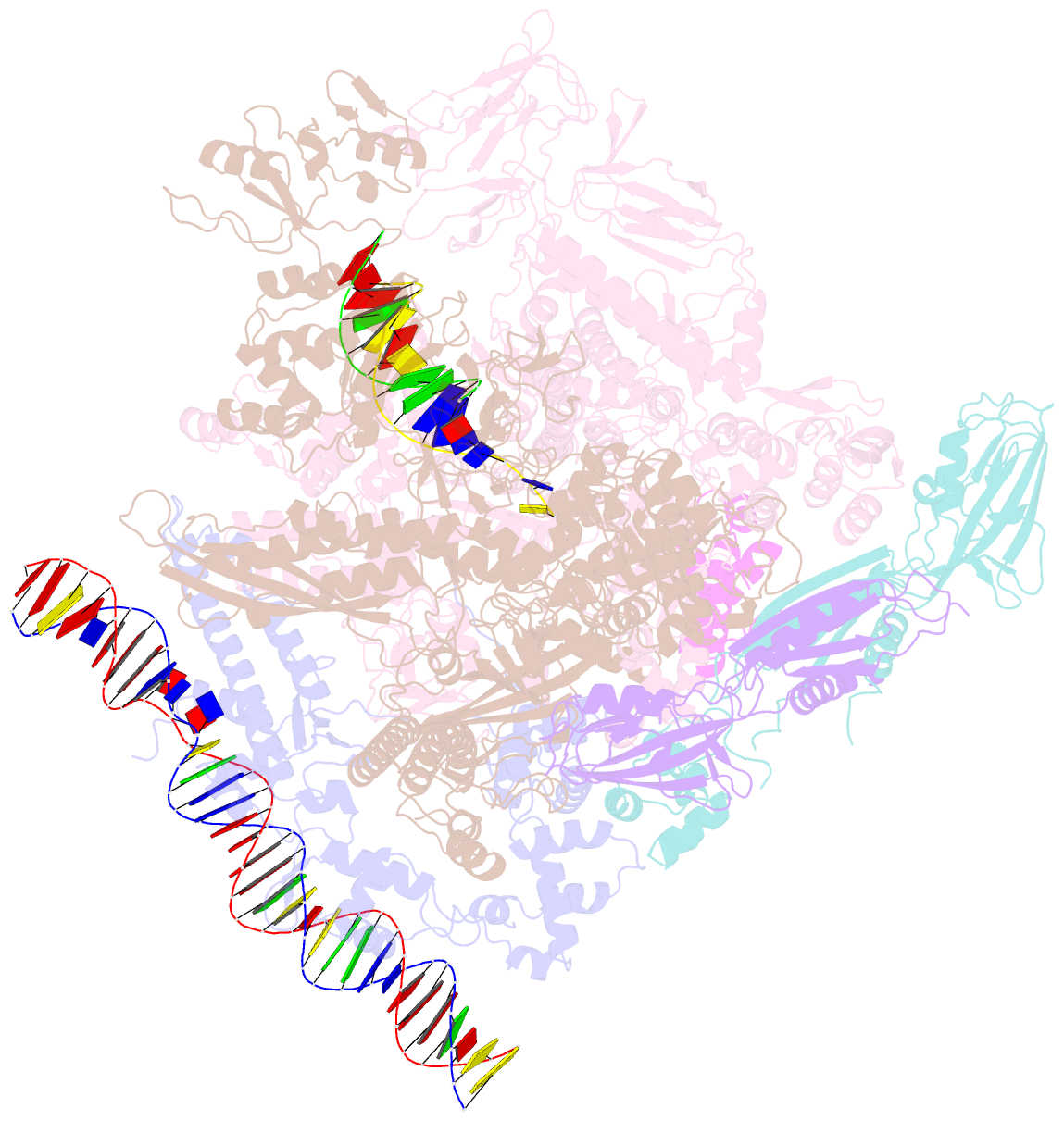
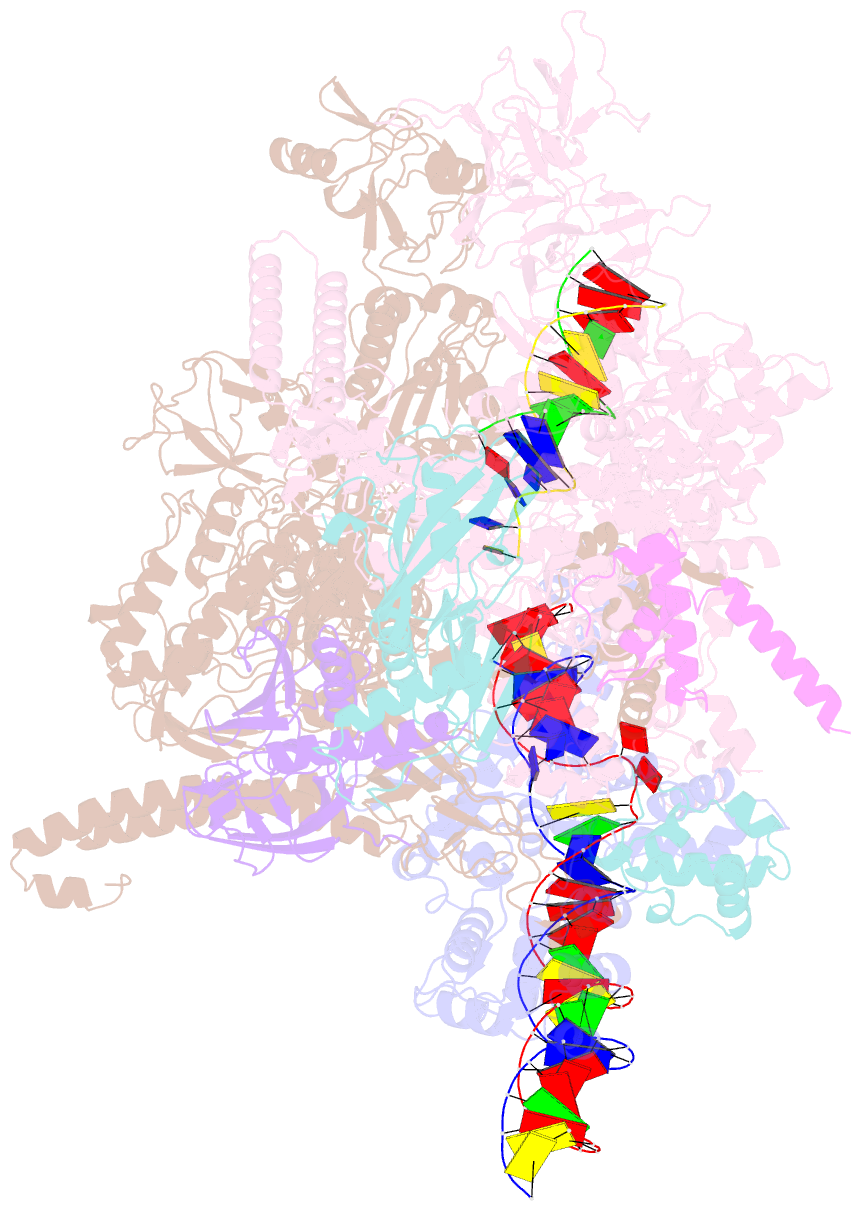
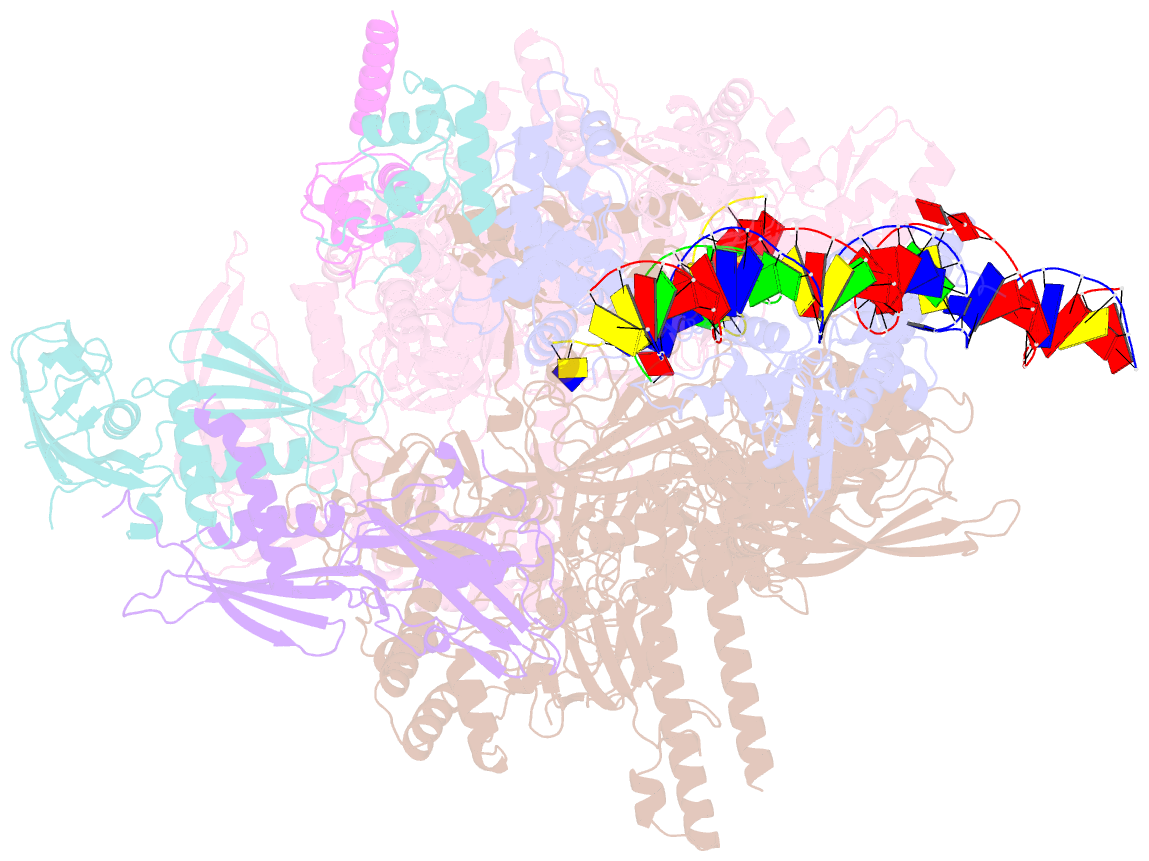
- Sign RNA polymerase early-melted intermediate bound to full duplex DNA fragment dhsu36 (-12t)
- Reference
- Mueller AU, Chen J, Wu M, Chiu C, Nixon BT, Campbell EA, Darst SA (2023): "A general mechanism for transcription bubble nucleation in bacteria." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 120, e2220874120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2220874120.
- Abstract
- Bacterial transcription initiation requires σ factors for nucleation of the transcription bubble. The canonical housekeeping σ factor, σ70, nucleates DNA melting via recognition of conserved bases of the promoter -10 motif, which are unstacked and captured in pockets of σ70. By contrast, the mechanism of transcription bubble nucleation and formation during the unrelated σN-mediated transcription initiation is poorly understood. Herein, we combine structural and biochemical approaches to establish that σN, like σ70, captures a flipped, unstacked base in a pocket formed between its N-terminal region I (RI) and extra-long helix features. Strikingly, RI inserts into the nascent bubble to stabilize the nucleated bubble prior to engagement of the obligate ATPase activator. Our data suggest a general paradigm of transcription initiation that requires σ factors to nucleate an early melted intermediate prior to productive RNA synthesis.