Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8fiy; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA-RNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (7.3 Å)
- Summary
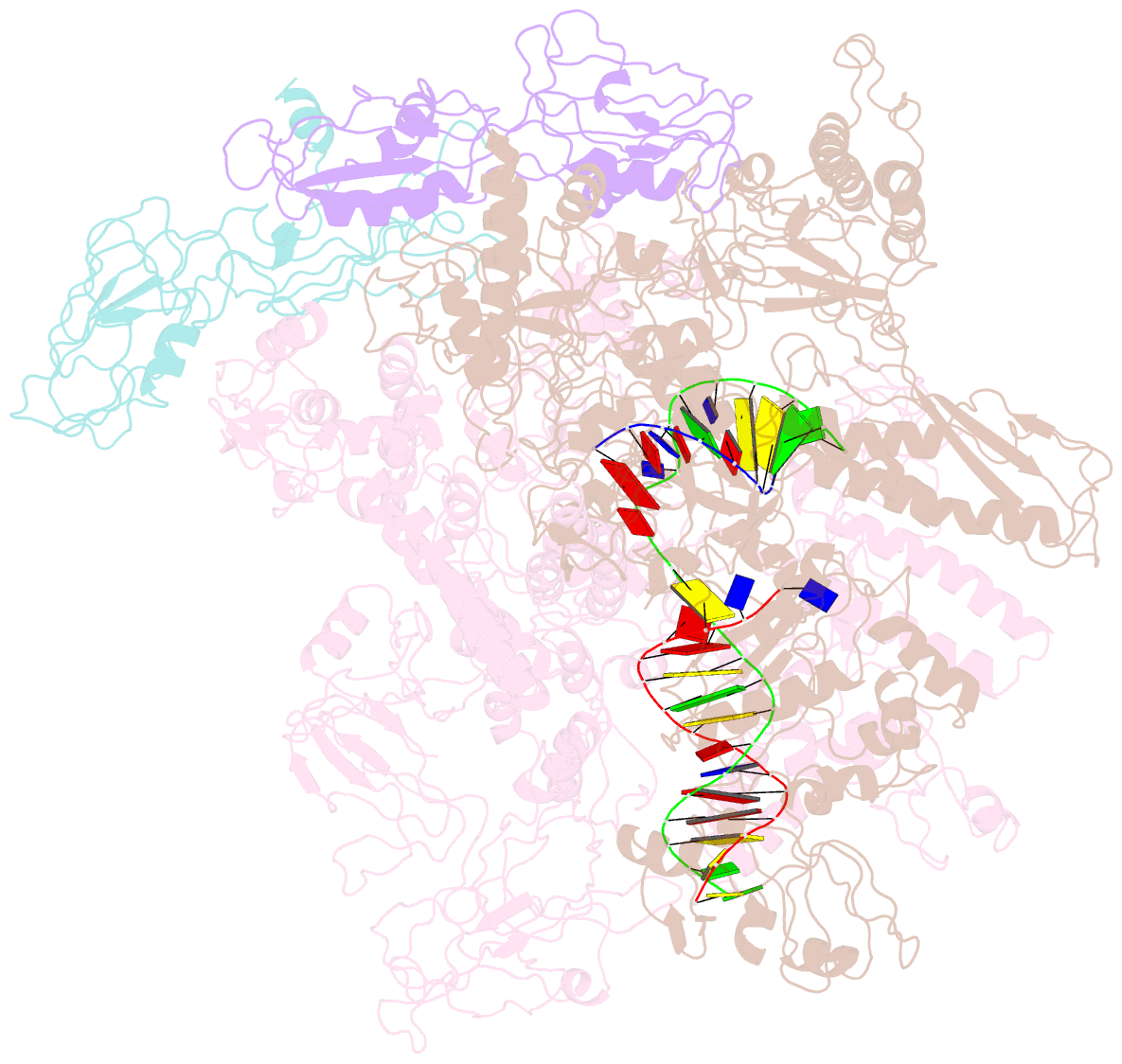
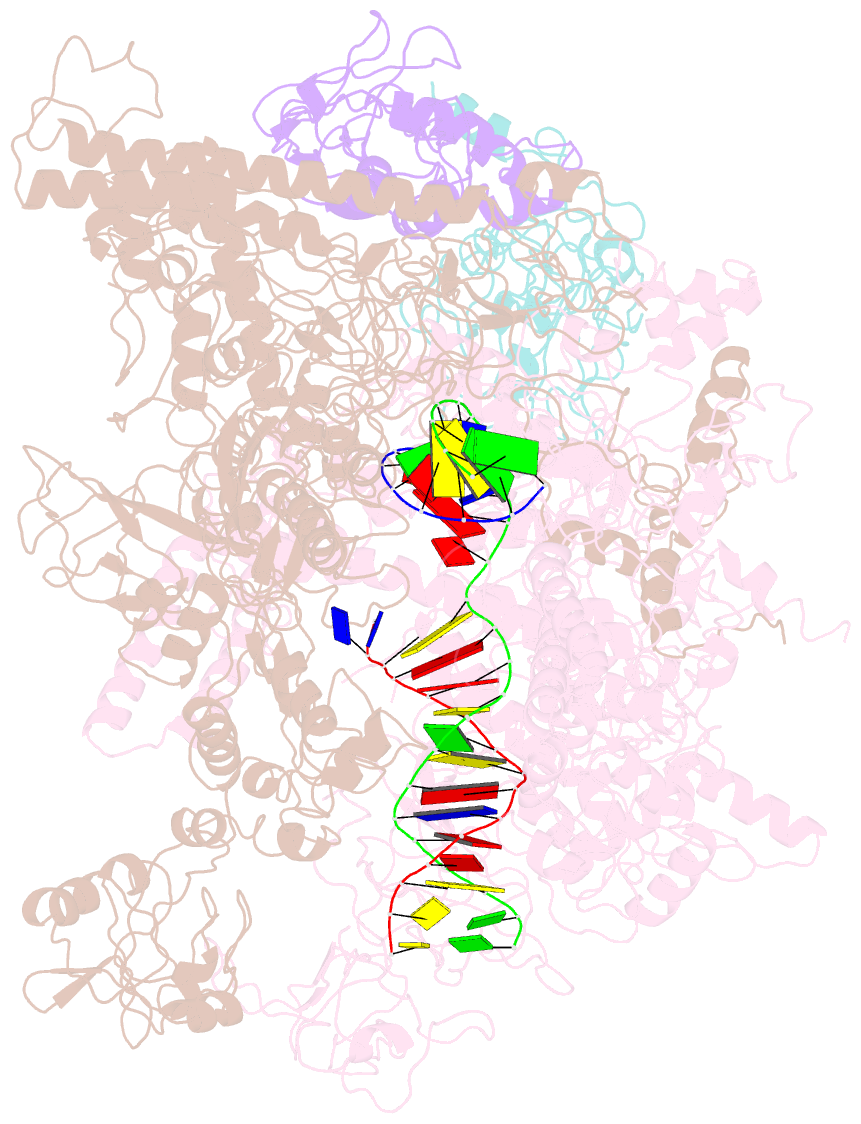
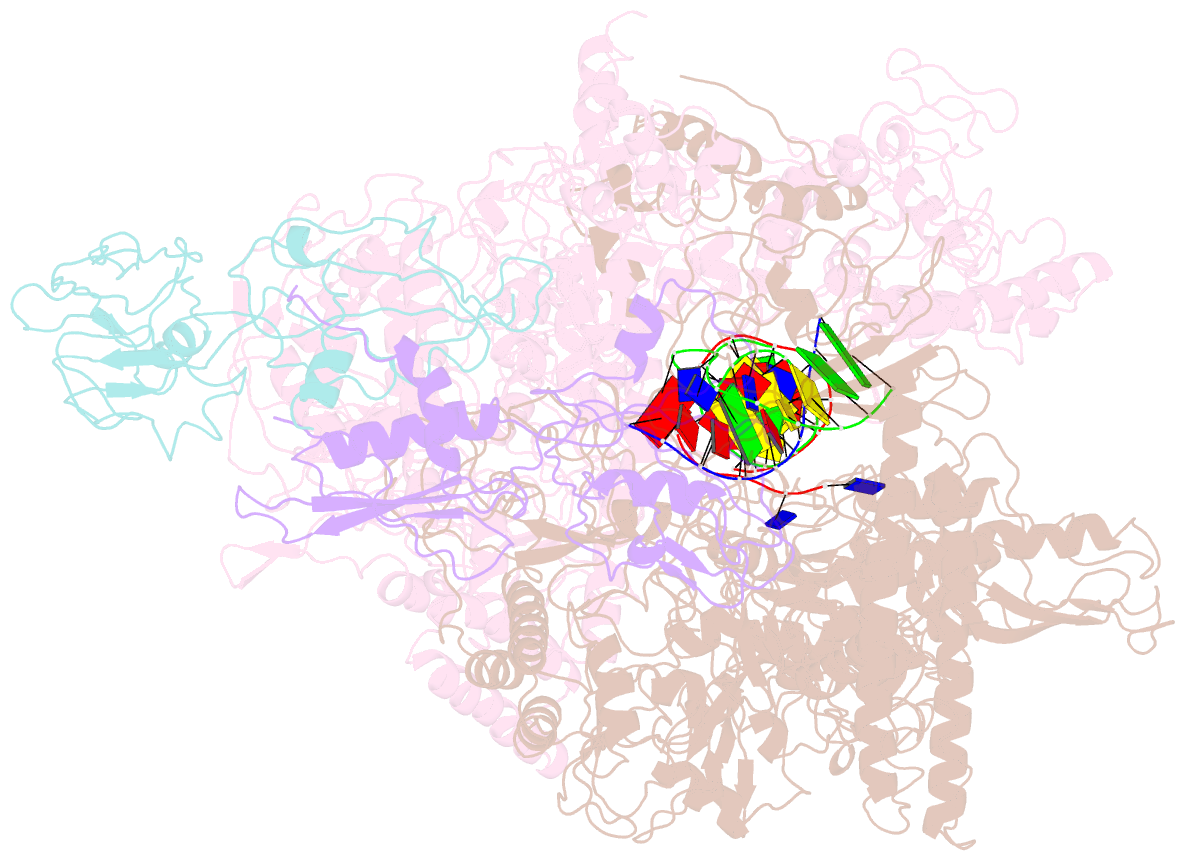
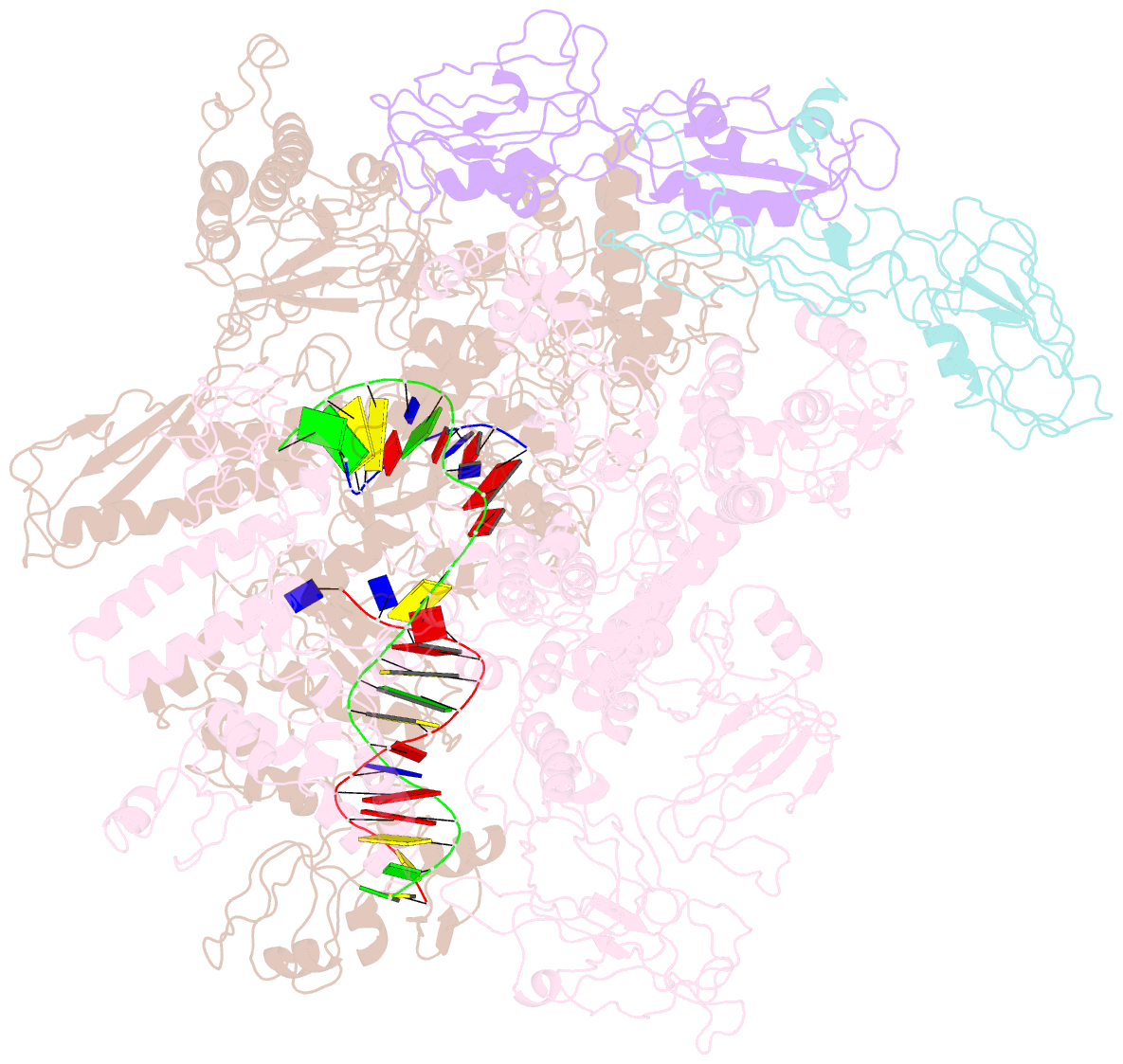
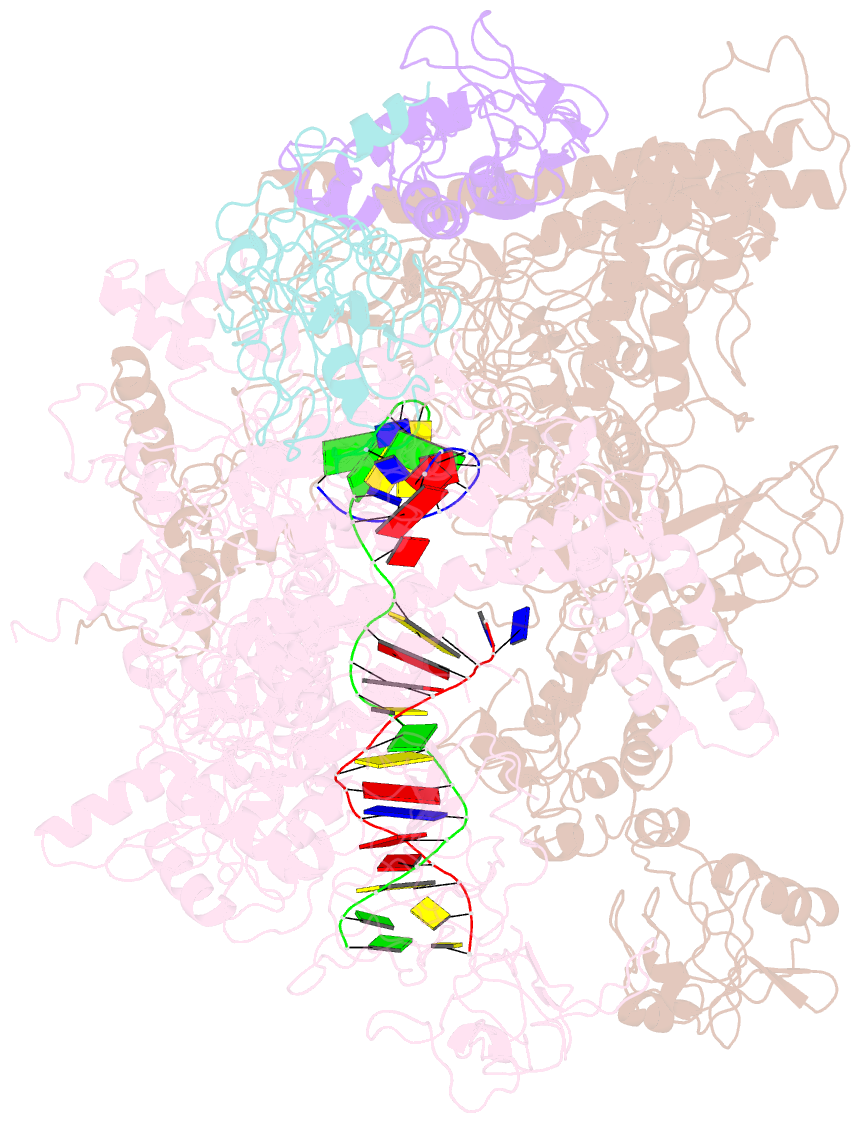
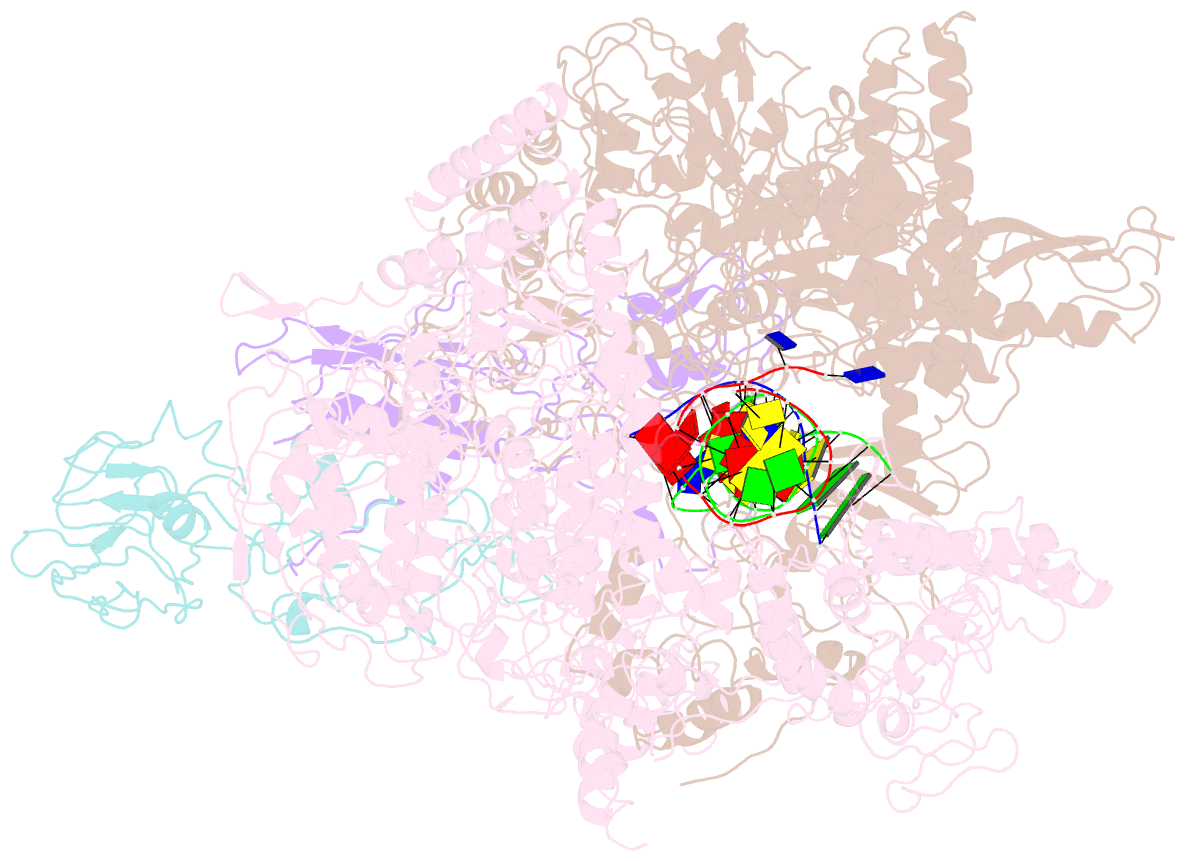
- cryo-EM structure of e. coli RNA polymerase elongation complex in the transcription-translation complex (rnap in an anti-swiveled conformation)
- Reference
- Wee LM, Tong AB, Florez Ariza AJ, Canari-Chumpitaz C, Grob P, Nogales E, Bustamante CJ (2023): "A trailing ribosome speeds up RNA polymerase at the expense of transcript fidelity via force and allostery." Cell, 186, 1244-1262.e34. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.02.008.
- Abstract
- In prokaryotes, translation can occur on mRNA that is being transcribed in a process called coupling. How the ribosome affects the RNA polymerase (RNAP) during coupling is not well understood. Here, we reconstituted the E. coli coupling system and demonstrated that the ribosome can prevent pausing and termination of RNAP and double the overall transcription rate at the expense of fidelity. Moreover, we monitored single RNAPs coupled to ribosomes and show that coupling increases the pause-free velocity of the polymerase and that a mechanical assisting force is sufficient to explain the majority of the effects of coupling. Also, by cryo-EM, we observed that RNAPs with a terminal mismatch adopt a backtracked conformation, while a coupled ribosome allosterically induces these polymerases toward a catalytically active anti-swiveled state. Finally, we demonstrate that prolonged RNAP pausing is detrimental to cell viability, which could be prevented by polymerase reactivation through a coupled ribosome.