Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8ftm; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.01 Å)
- Summary
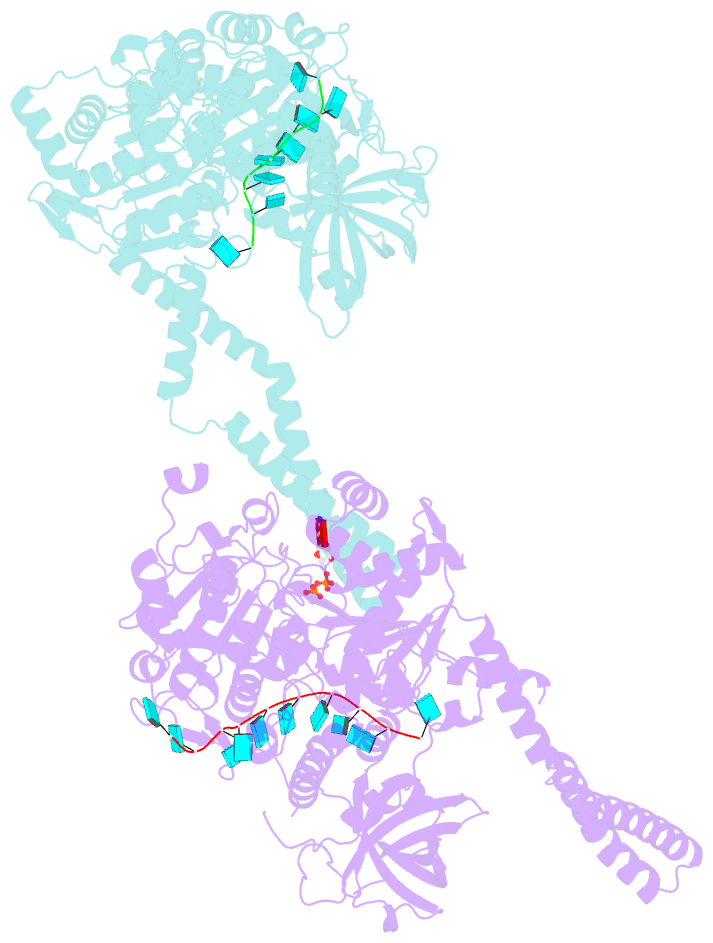
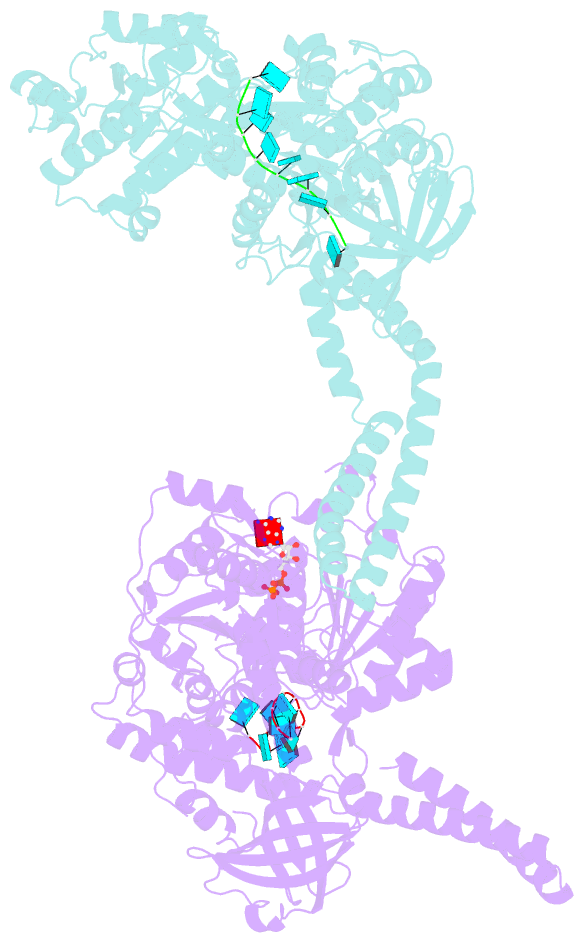
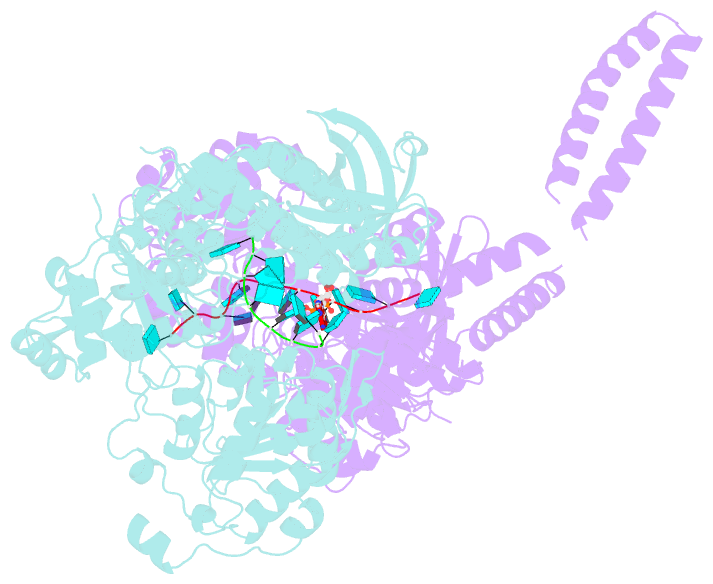
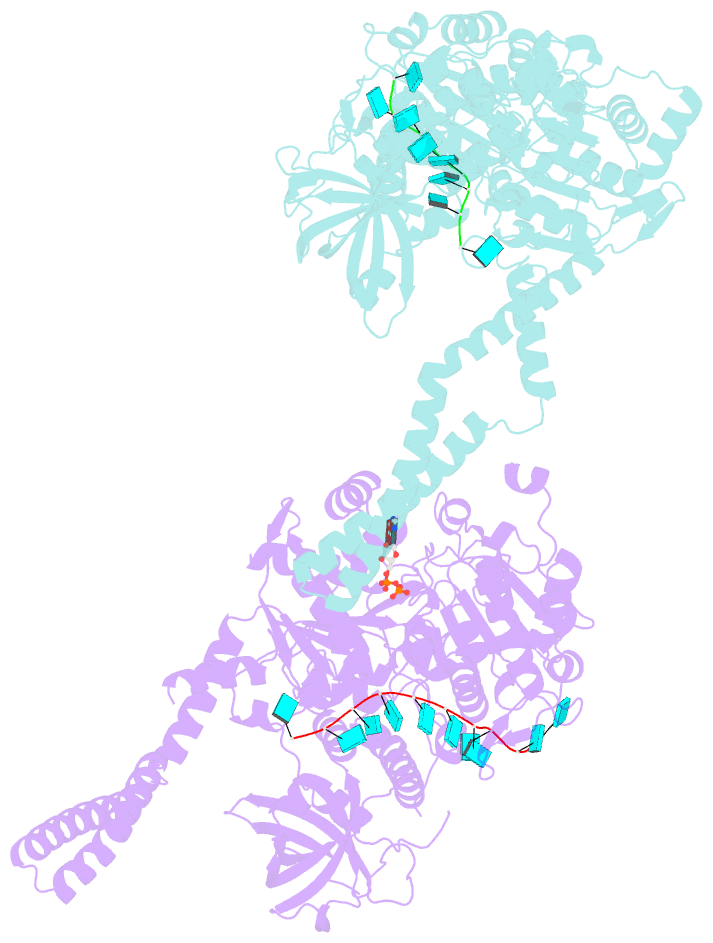
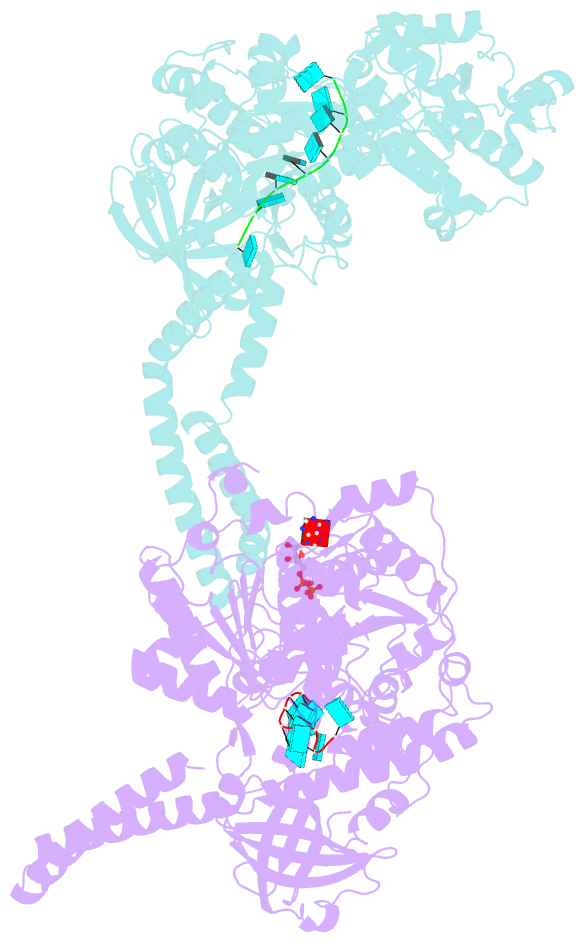
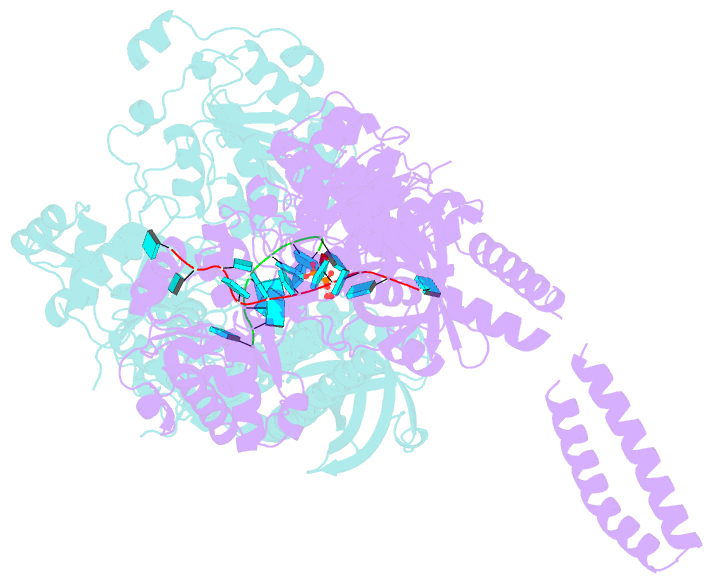
- Setx-ssrna-adp-so4 complex
- Reference
- Appel CD, Bermek O, Dandey VP, Wood M, Viverette E, Williams JG, Bouvette J, Riccio AA, Krahn JM, Borgnia MJ, Williams RS (2023): "Sen1 architecture: RNA-DNA hybrid resolution, autoregulation, and insights into SETX inactivation in AOA2." Mol.Cell, 83, 3692. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.09.024.
- Abstract
- The senataxin (SETX, Sen1 in yeasts) RNA-DNA hybrid resolving helicase regulates multiple nuclear transactions, including DNA replication, transcription, and DNA repair, but the molecular basis for Sen1 activities is ill defined. Here, Sen1 cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) reconstructions reveal an elongated inchworm-like architecture. Sen1 is composed of an amino terminal helical repeat Sen1 N-terminal (Sen1N) regulatory domain that is flexibly linked to its C-terminal SF1B helicase motor core (Sen1Hel) via an intrinsically disordered tether. In an autoinhibited state, the Sen1Sen1N domain regulates substrate engagement by promoting occlusion of the RNA substrate-binding cleft. The X-ray structure of an activated Sen1Hel engaging single-stranded RNA and ADP-SO4 shows that the enzyme encircles RNA and implicates a single-nucleotide power stroke in the Sen1 RNA translocation mechanism. Together, our data unveil dynamic protein-protein and protein-RNA interfaces underpinning helicase regulation and inactivation of human SETX activity by RNA-binding-deficient mutants in ataxia with oculomotor apraxia 2 neurodegenerative disease.