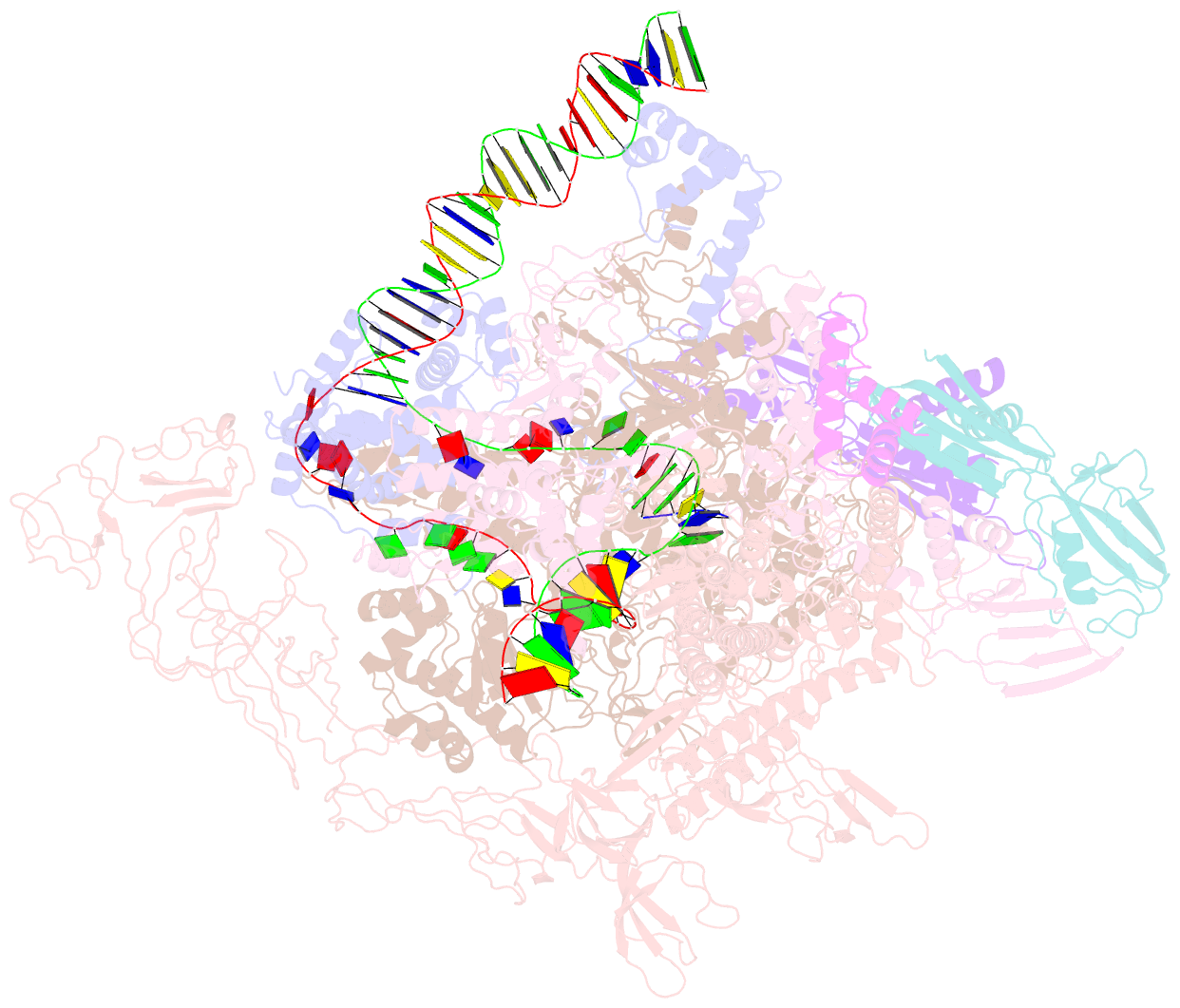
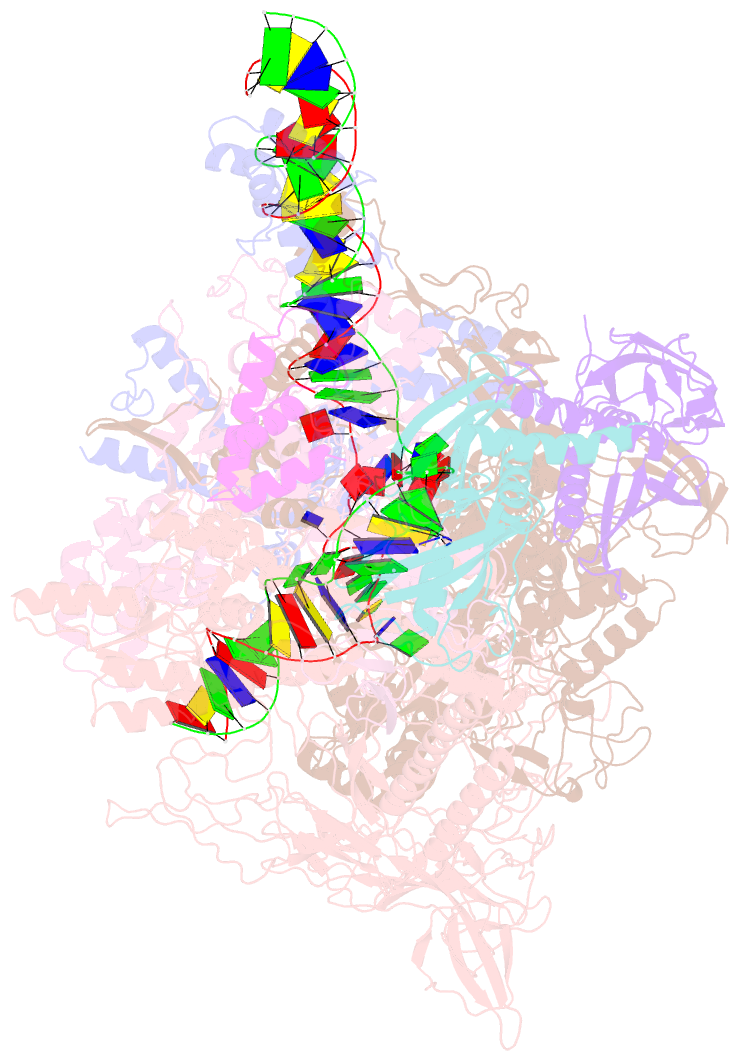
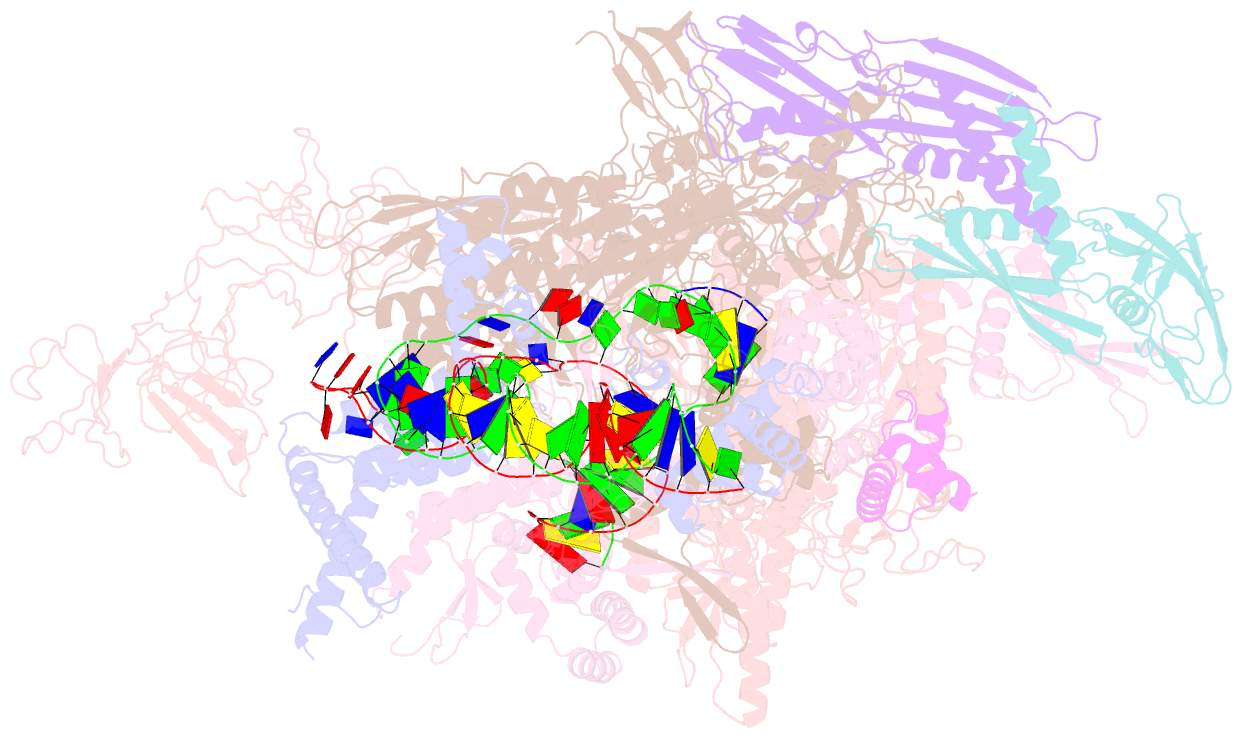
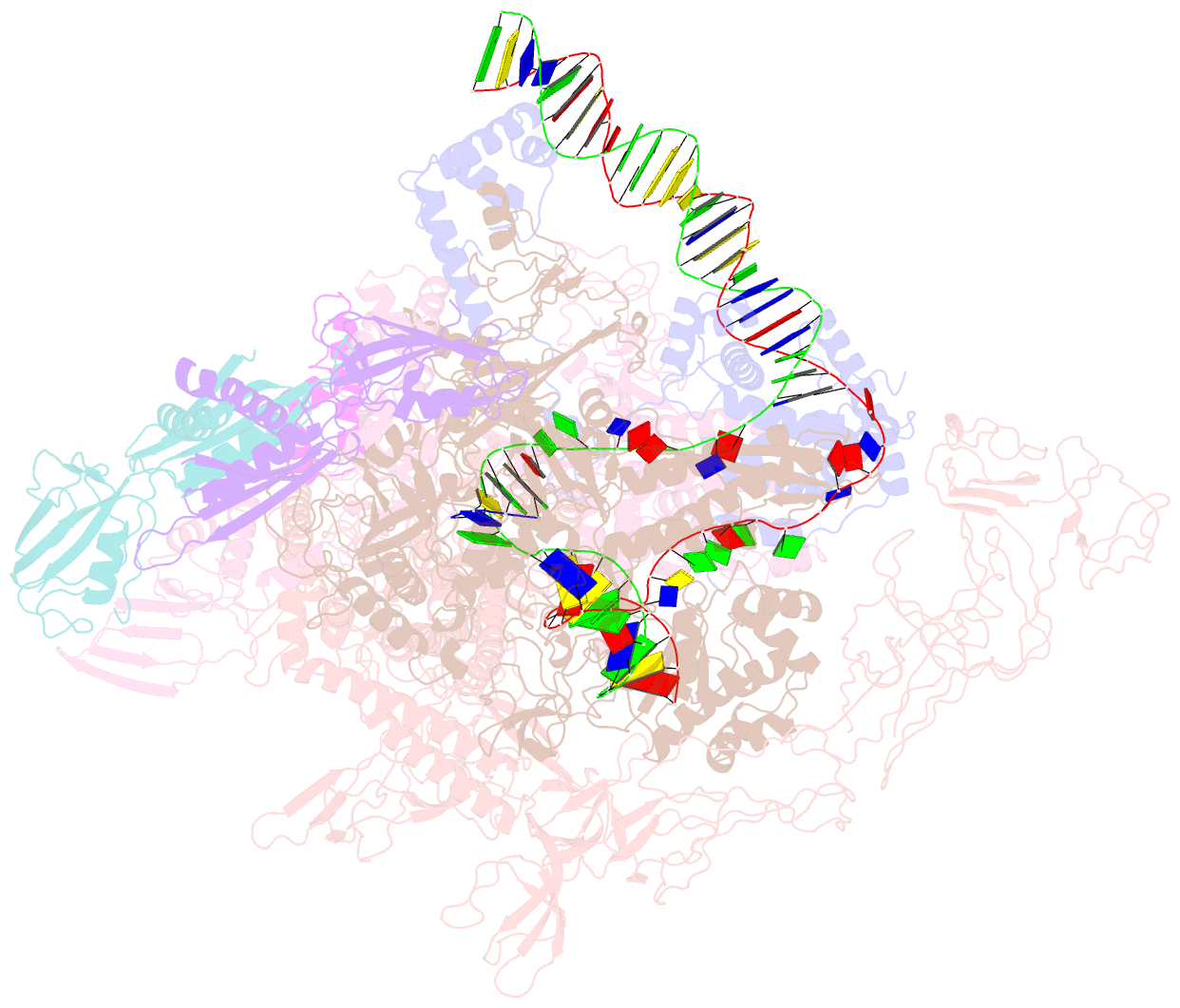
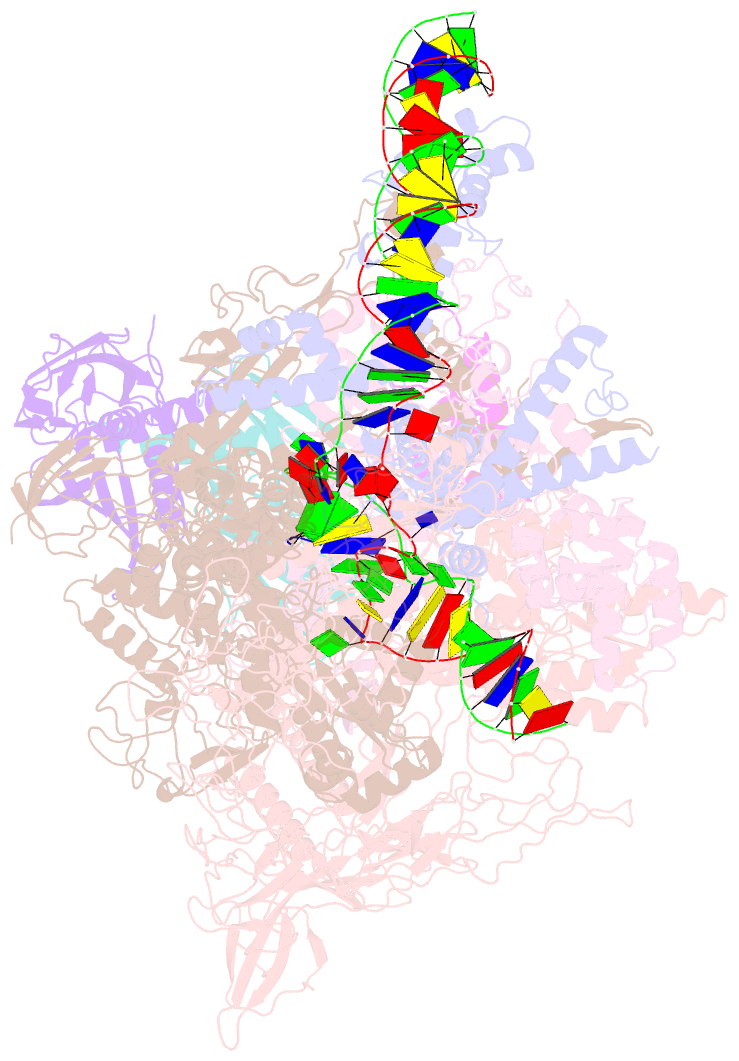
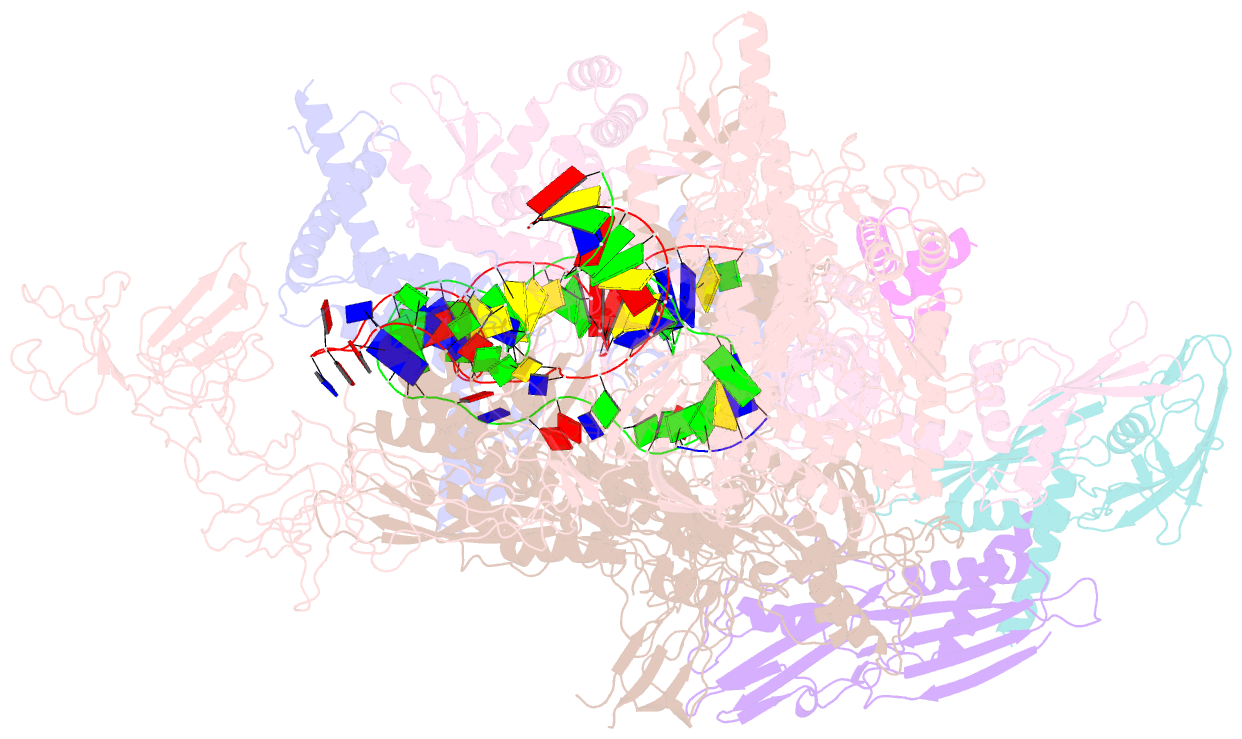
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8gzh; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA-RNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.96 Å)
- Summary
- cryo-EM structure of synechocystis sp. pcc 6803 ctp-bound rpitc
- Reference
- Shen L, Lai G, You L, Shi J, Wu X, Puiu M, Gu Z, Feng Y, Yuzenkova Y, Zhang Y (2023): "An SI3-sigma arch stabilizes cyanobacteria transcription initiation complex." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 120, e2219290120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2219290120.
- Abstract
- Multisubunit RNA polymerases (RNAPs) associate with initiation factors (σ in bacteria) to start transcription. The σ factors are responsible for recognizing and unwinding promoter DNA in all bacterial RNAPs. Here, we report two cryo-EM structures of cyanobacterial transcription initiation complexes at near-atomic resolutions. The structures show that cyanobacterial RNAP forms an "SI3-σ" arch interaction between domain 2 of σA (σ2) and sequence insertion 3 (SI3) in the mobile catalytic domain Trigger Loop (TL). The "SI3-σ" arch facilitates transcription initiation from promoters of different classes through sealing the main cleft and thereby stabilizing the RNAP-promoter DNA open complex. Disruption of the "SI3-σ" arch disturbs cyanobacteria growth and stress response. Our study reports the structure of cyanobacterial RNAP and a unique mechanism for its transcription initiation. Our data suggest functional plasticity of SI3 and provide the foundation for further research into cyanobacterial and chloroplast transcription.