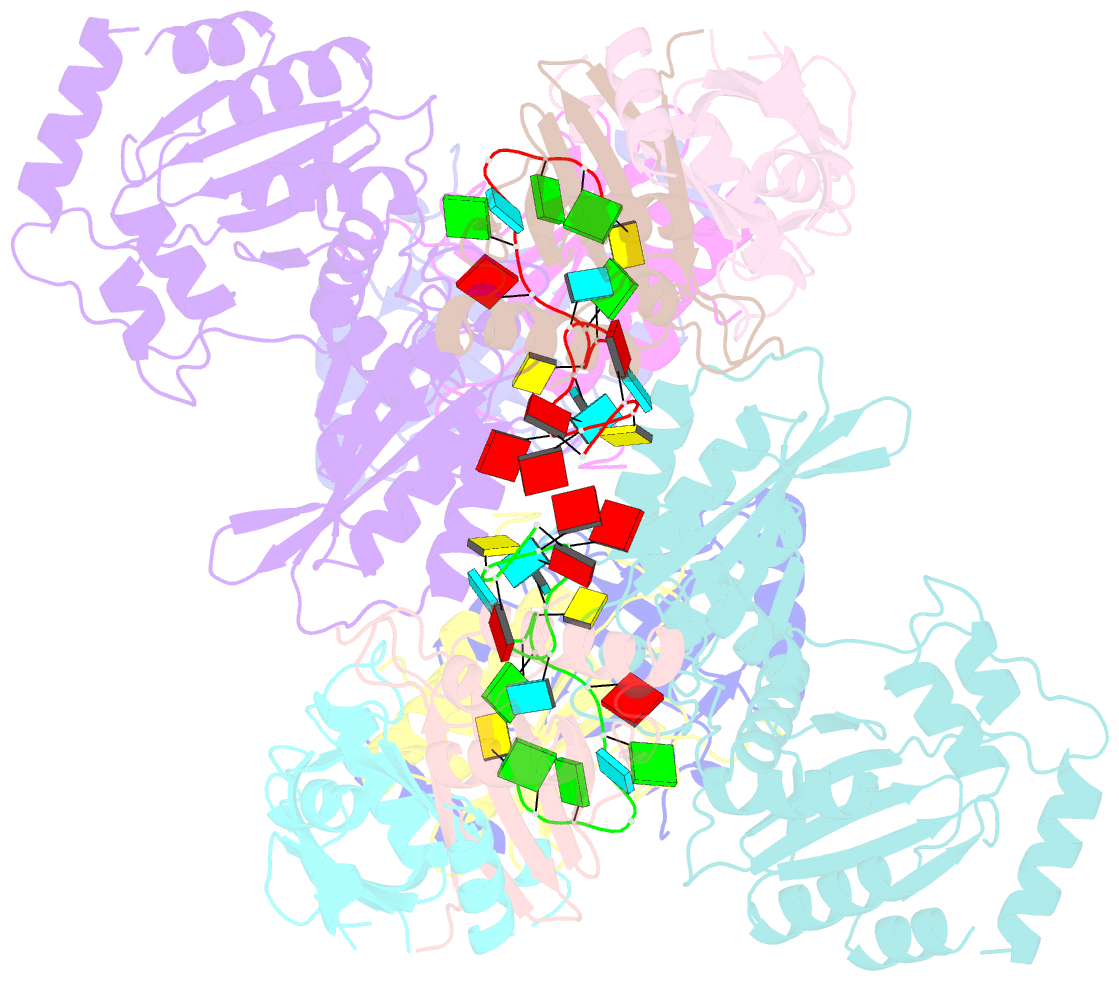
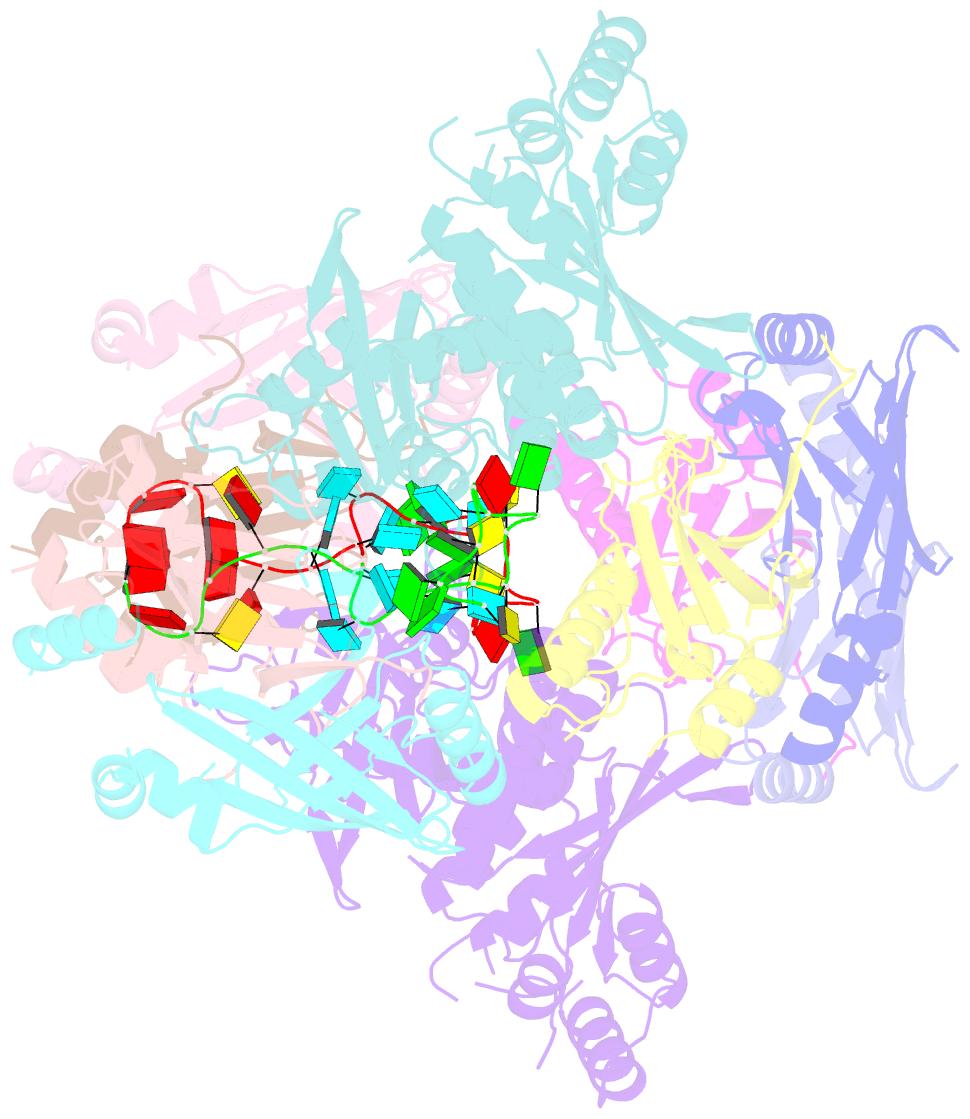
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8h0i; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- antiviral protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.8 Å)
- Summary
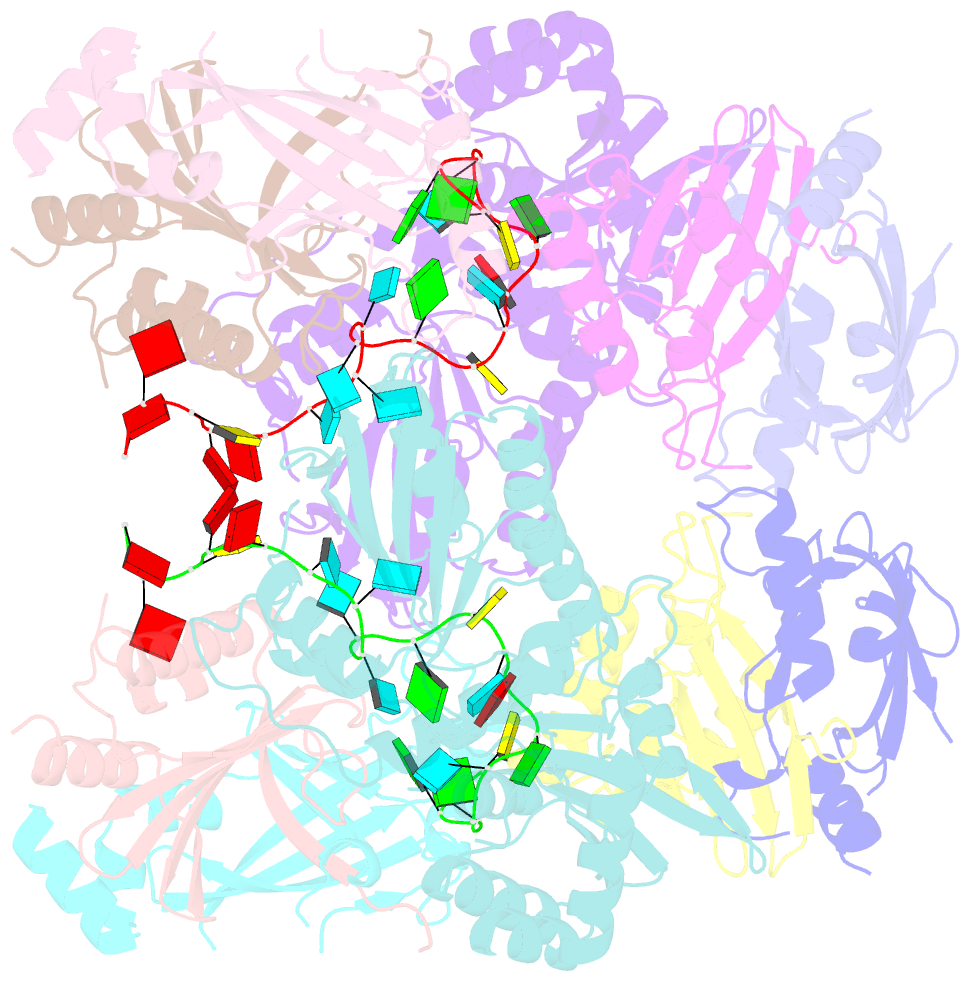
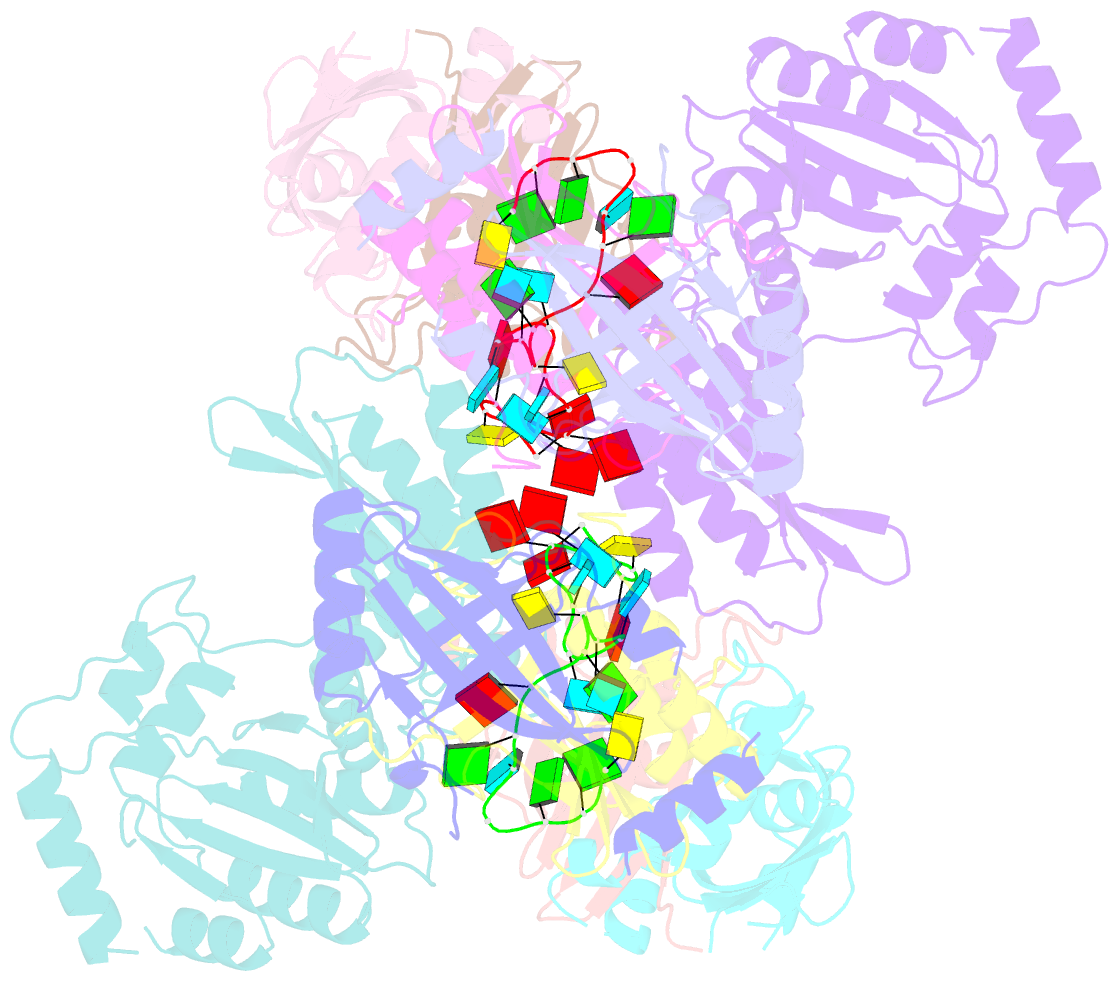
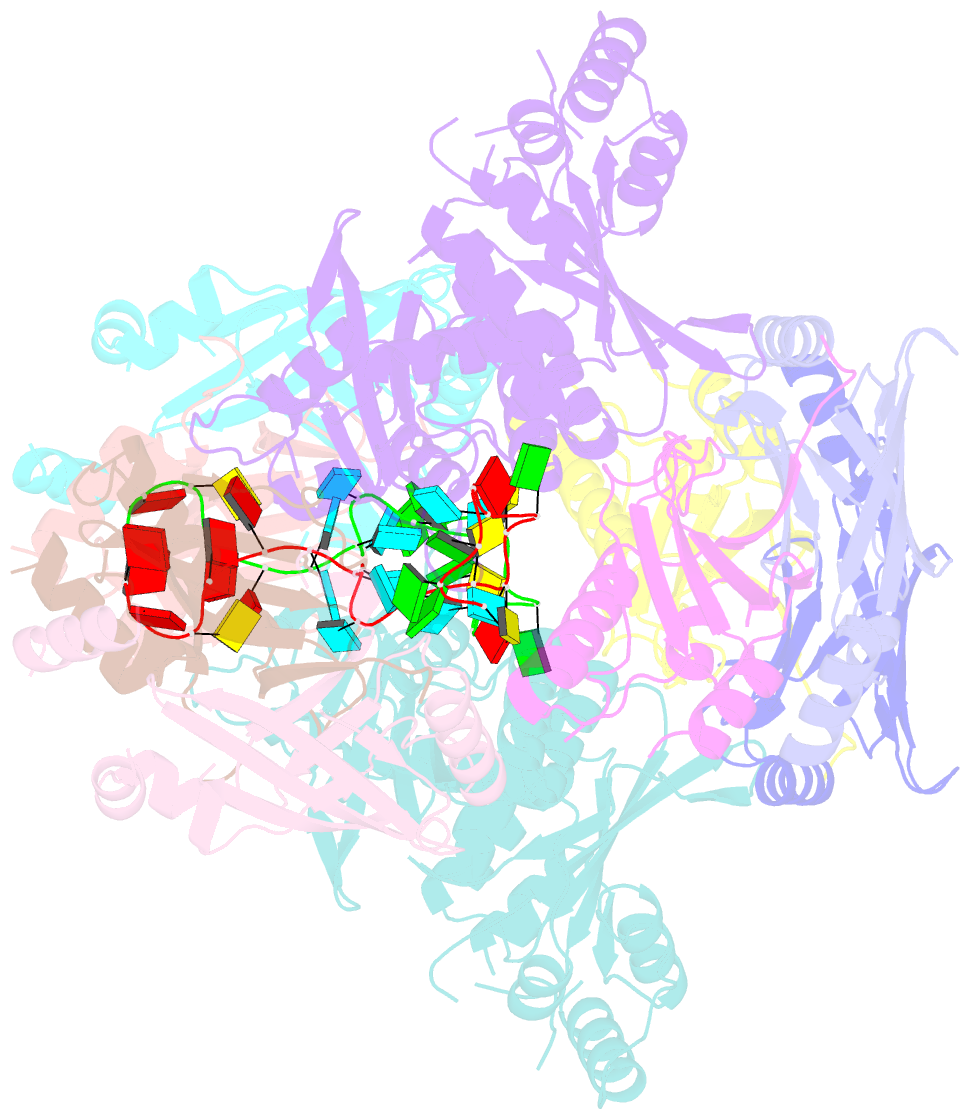
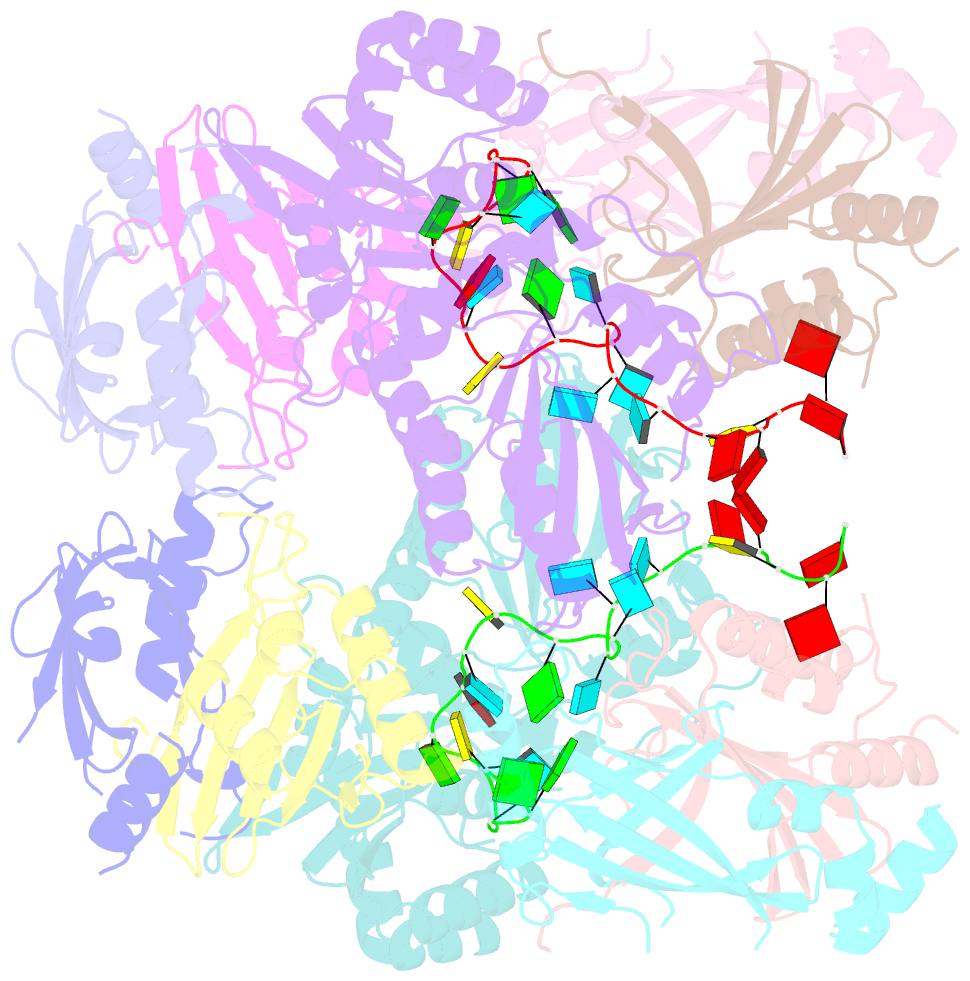
- cryo-EM structure of apobec3g-vif complex
- Reference
- Kouno T, Shibata S, Shigematsu M, Hyun J, Kim TG, Matsuo H, Wolf M (2023): "Structural insights into RNA bridging between HIV-1 Vif and antiviral factor APOBEC3G." Nat Commun, 14, 4037. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39796-5.
- Abstract
- Great effort has been devoted to discovering the basis of A3G-Vif interaction, the key event of HIV's counteraction mechanism to evade antiviral innate immune response. Here we show reconstitution of the A3G-Vif complex and subsequent A3G ubiquitination in vitro and report the cryo-EM structure of the A3G-Vif complex at 2.8 Å resolution using solubility-enhanced variants of A3G and Vif. We present an atomic model of the A3G-Vif interface, which assembles via known amino acid determinants. This assembly is not achieved by protein-protein interaction alone, but also involves RNA. The cryo-EM structure and in vitro ubiquitination assays identify an adenine/guanine base preference for the interaction and a unique Vif-ribose contact. This establishes the biological significance of an RNA ligand. Further assessment of interactions between A3G, Vif, and RNA ligands show that the A3G-Vif assembly and subsequent ubiquitination can be controlled by amino acid mutations at the interface or by polynucleotide modification, suggesting that a specific chemical moiety would be a promising pharmacophore to inhibit the A3G-Vif interaction.