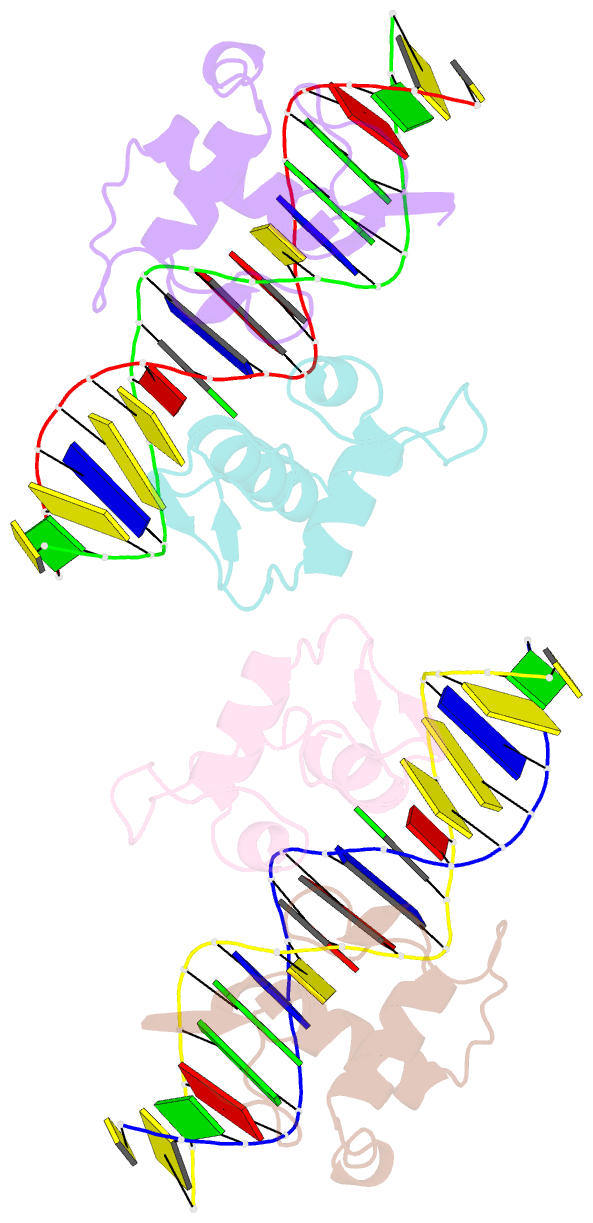
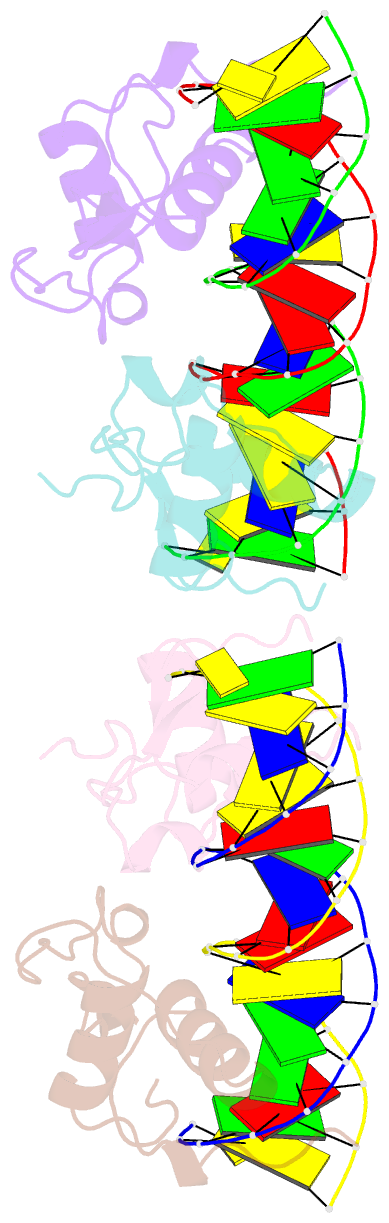
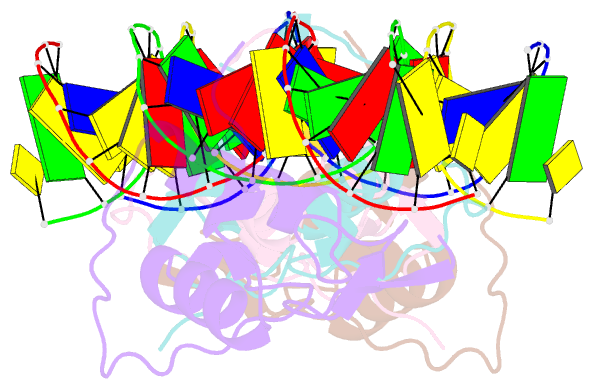
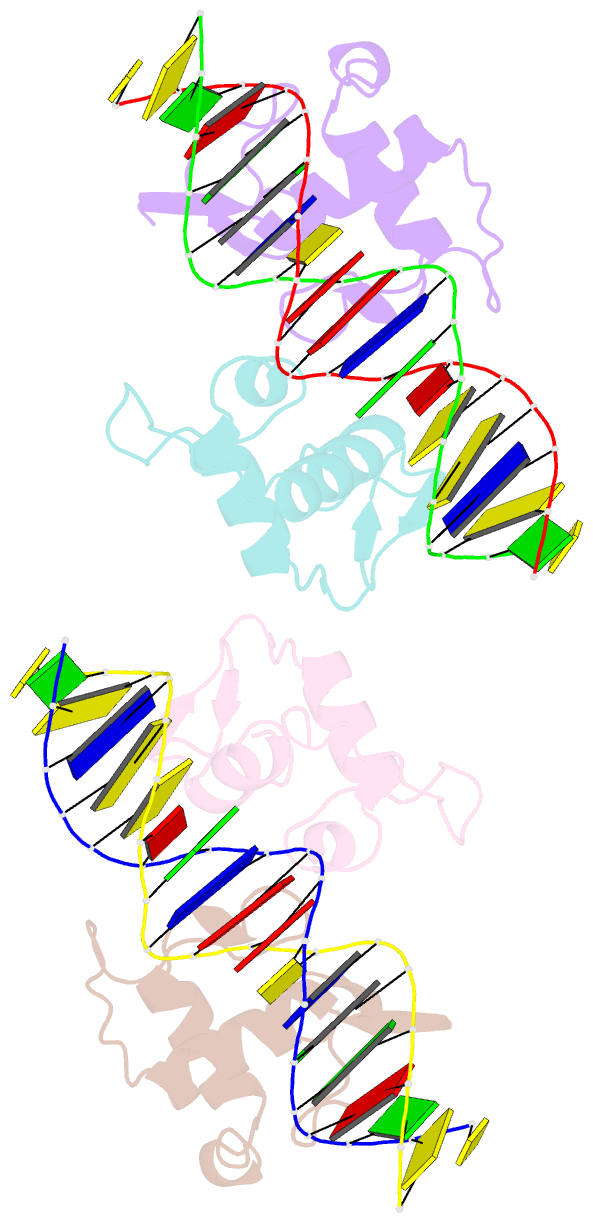
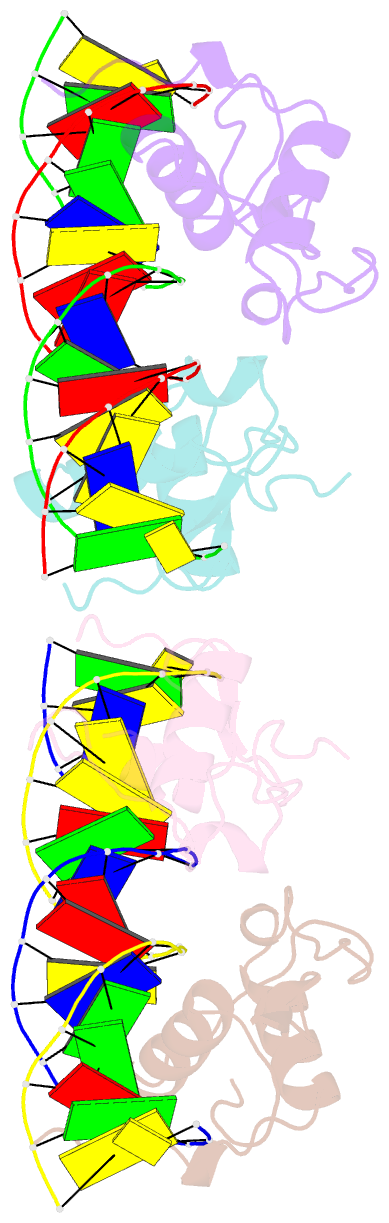
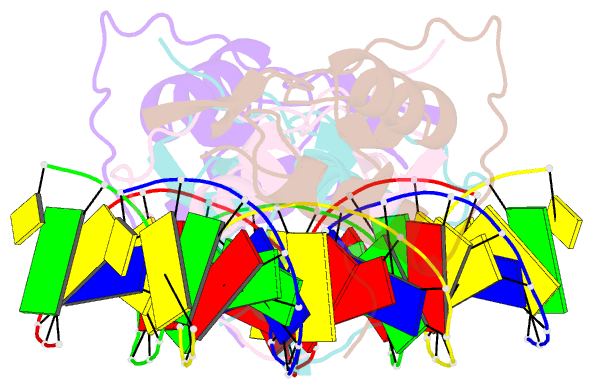
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8hbm; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.3 Å)
- Summary
- Structural basis of the farnesoid x receptor-retinoid x receptor heterodimer on inverted repeat DNA
- Reference
- Jiang L, Liu X, Liang X, Dai S, Wei H, Guo M, Chen Z, Xiao D, Chen Y (2023): "Structural basis of the farnesoid X receptor/retinoid X receptor heterodimer on inverted repeat DNA." Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 21, 3149-3157. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.05.026.
- Abstract
- Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor known as bile acid receptor (BAR). FXR plays critical roles in various biological processes, including metabolism, immune inflammation, liver regeneration and liver carcinogenesis. FXR forms a heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor (RXR) and binds to diverse FXR response elements (FXREs) to exert its various biological functions. However, the mechanism by which the FXR/RXR heterodimer binds the DNA elements remains unclear. In this study, we aimed to use structural, biochemical and bioinformatics analyses to study the mechanism of FXR binding to the typical FXRE, such as the IR1 site, and the heterodimer interactions in the FXR-DBD/RXR-DBD complex. Further biochemical assays showed that RAR, THR and NR4A2 do not form heterodimers with RXR when bound to the IR1 sites, which indicates that IR1 may be a unique binding site for the FXR/RXR heterodimer. Our studies may provide a further understanding of the dimerization specificity of nuclear receptors.