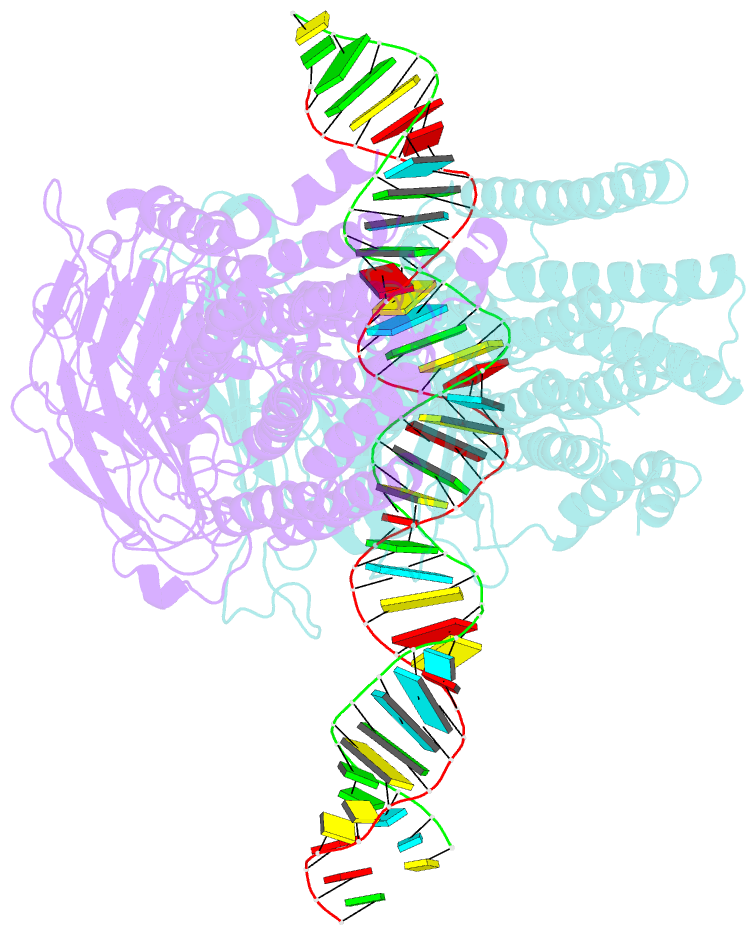
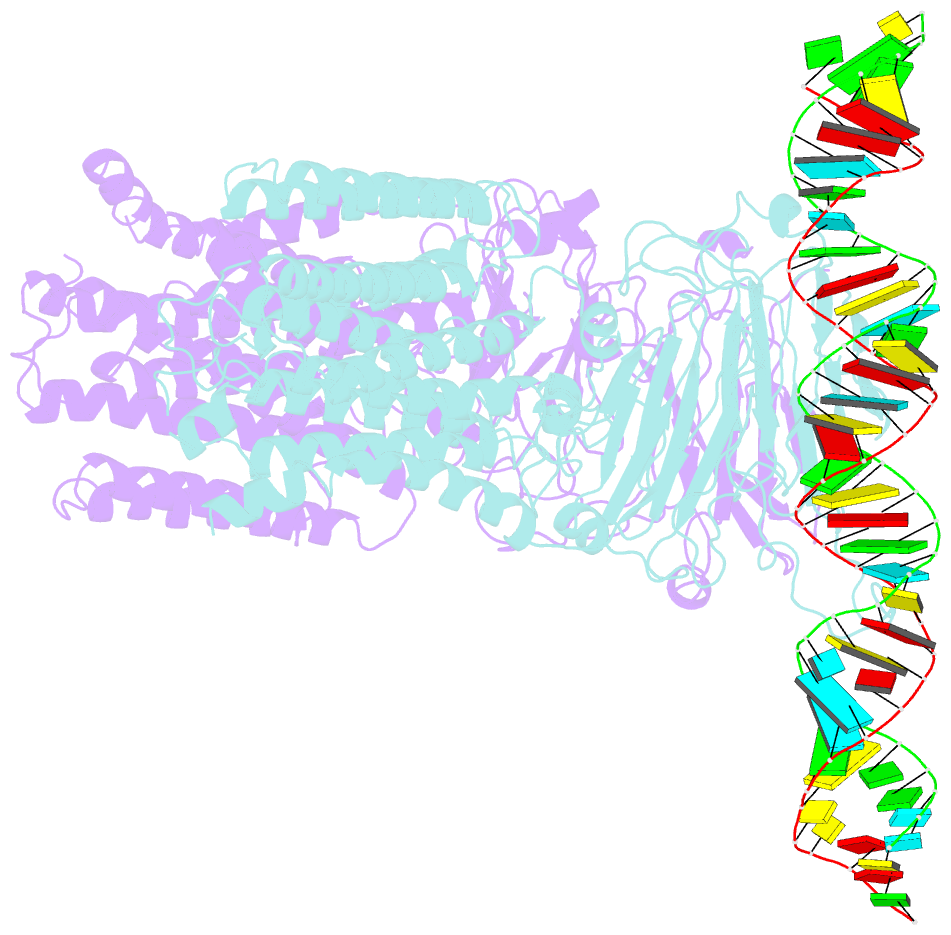
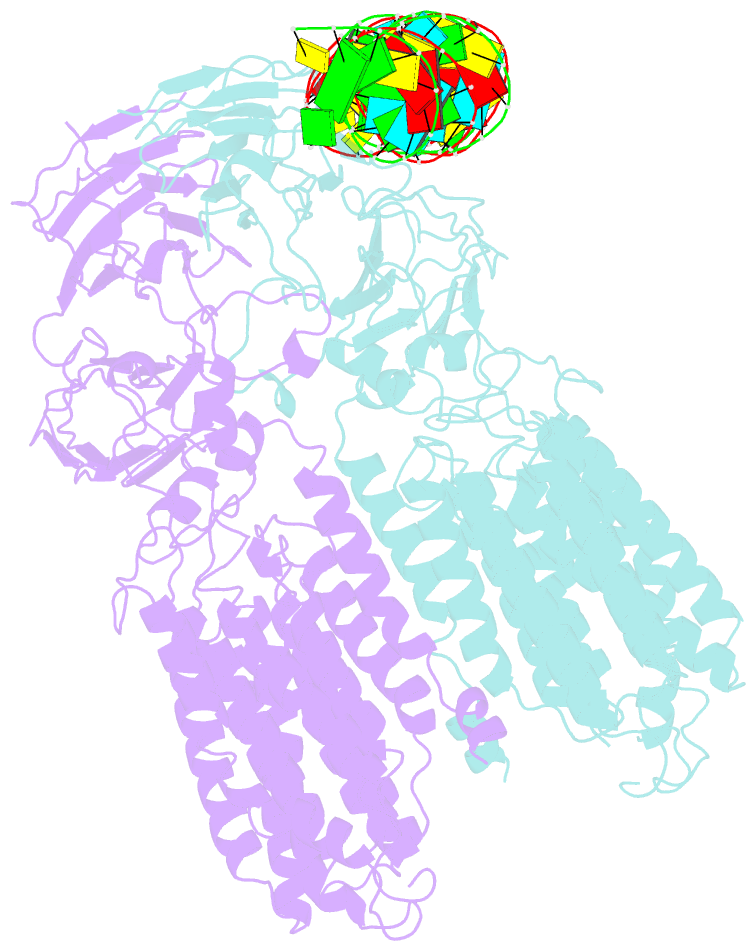
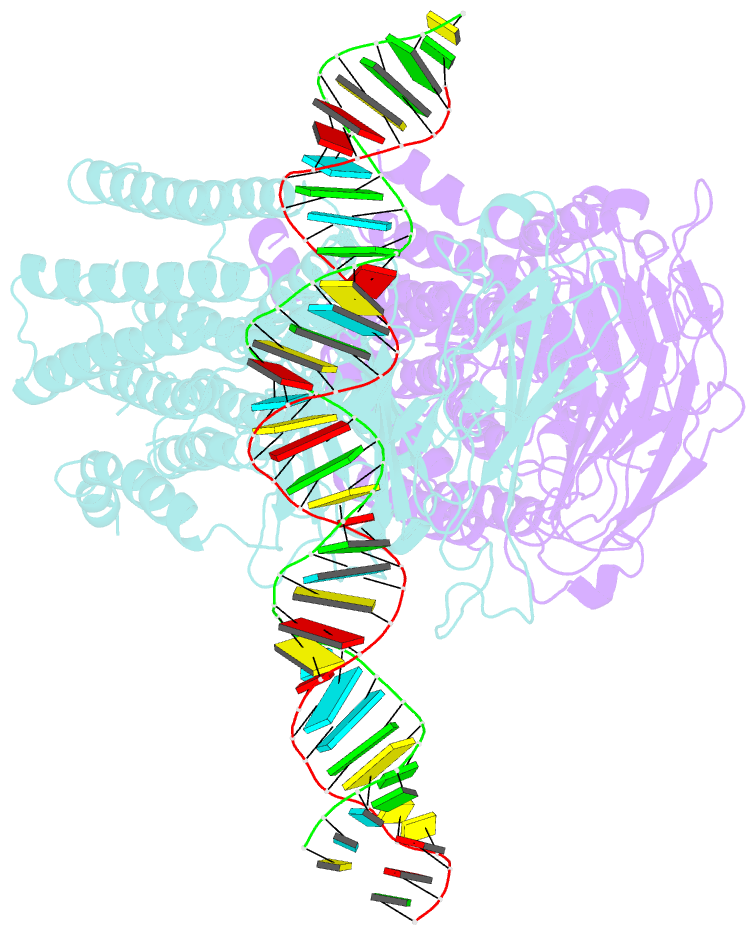
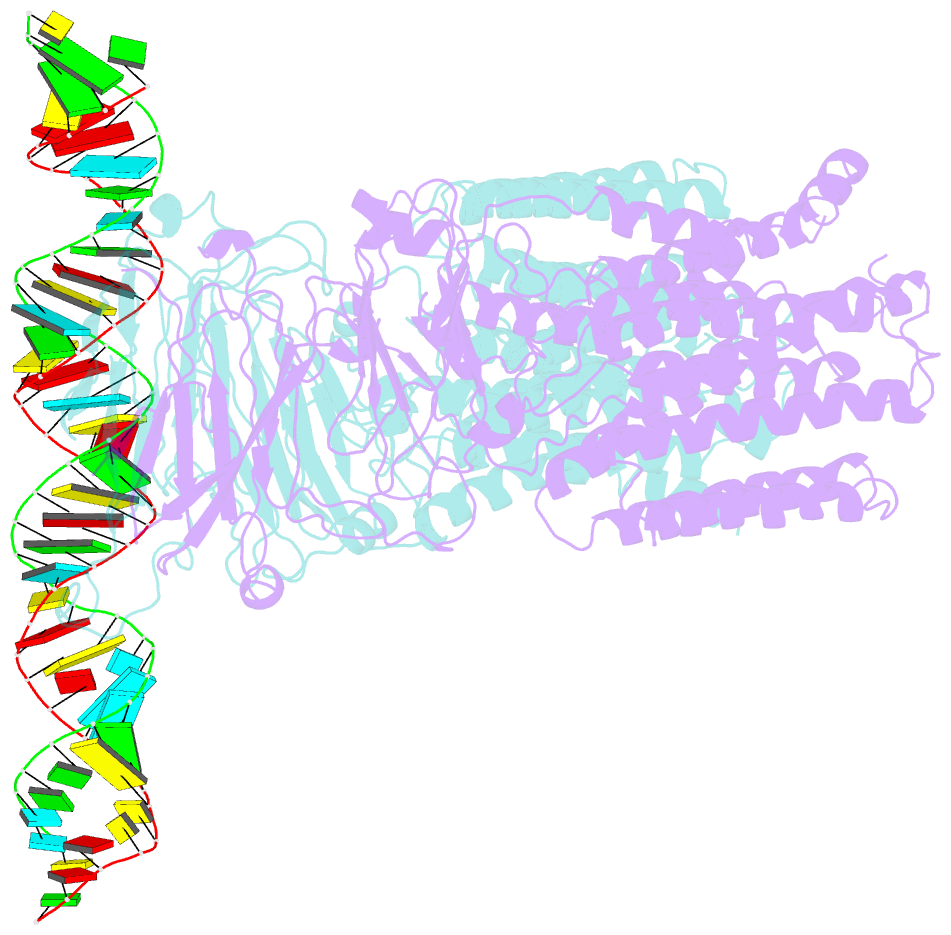
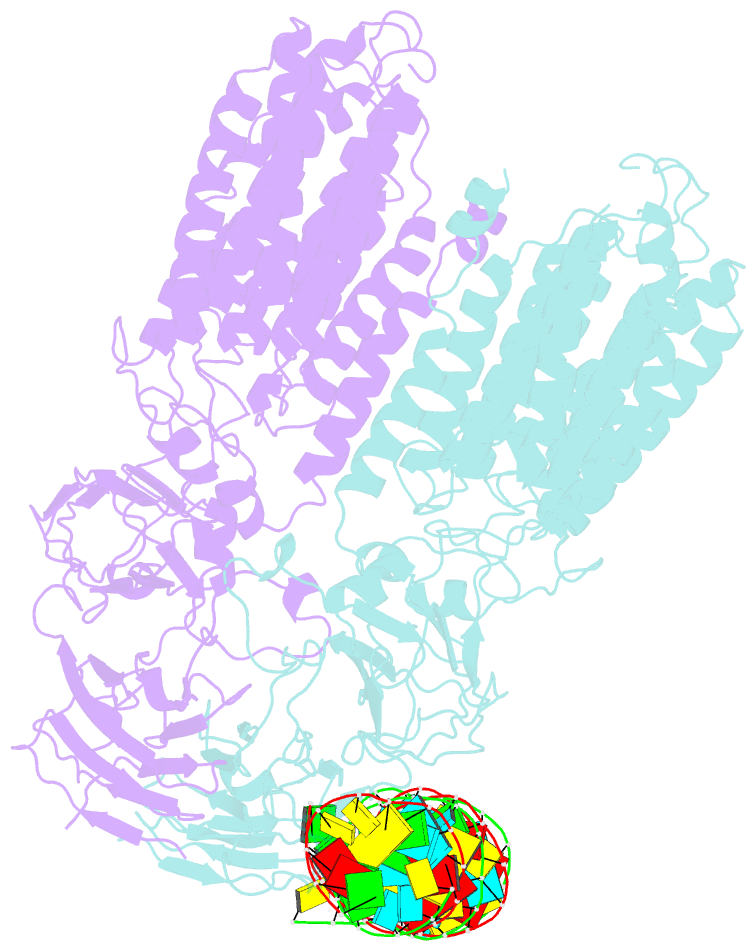
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8hke; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.71 Å)
- Summary
- Dsrna transporter
- Reference
- Zhang J, Zhan C, Fan J, Wu D, Zhang R, Wu D, Chen X, Lu Y, Li M, Lin M, Gong J, Jiang D (2024): "Structural insights into double-stranded RNA recognition and transport by SID-1." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 31, 1095-1104. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01276-9.
- Abstract
- RNA uptake by cells is critical for RNA-mediated gene interference (RNAi) and RNA-based therapeutics. In Caenorhabditis elegans, RNAi is systemic as a result of SID-1-mediated double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) across cells. Despite the functional importance, the underlying mechanisms of dsRNA internalization by SID-1 remain elusive. Here we describe cryogenic electron microscopy structures of SID-1, SID-1-dsRNA complex and human SID-1 homologs SIDT1 and SIDT2, elucidating the structural basis of dsRNA recognition and import by SID-1. The homodimeric SID-1 homologs share conserved architecture, but only SID-1 possesses the molecular determinants within its extracellular domains for distinguishing dsRNA from single-stranded RNA and DNA. We show that the removal of the long intracellular loop between transmembrane helix 1 and 2 attenuates dsRNA uptake and systemic RNAi in vivo, suggesting a possible endocytic mechanism of SID-1-mediated dsRNA internalization. Our study provides mechanistic insights into dsRNA internalization by SID-1, which may facilitate the development of dsRNA applications based on SID-1.