Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8hrb; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- immune system
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.78 Å)
- Summary
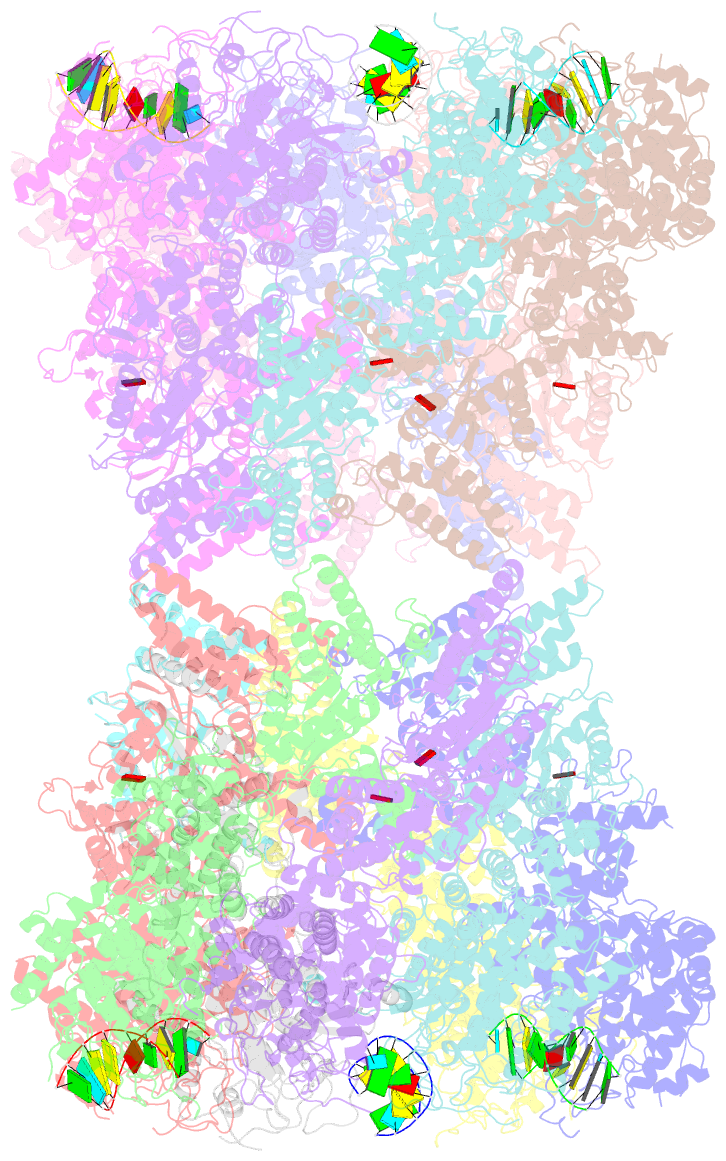
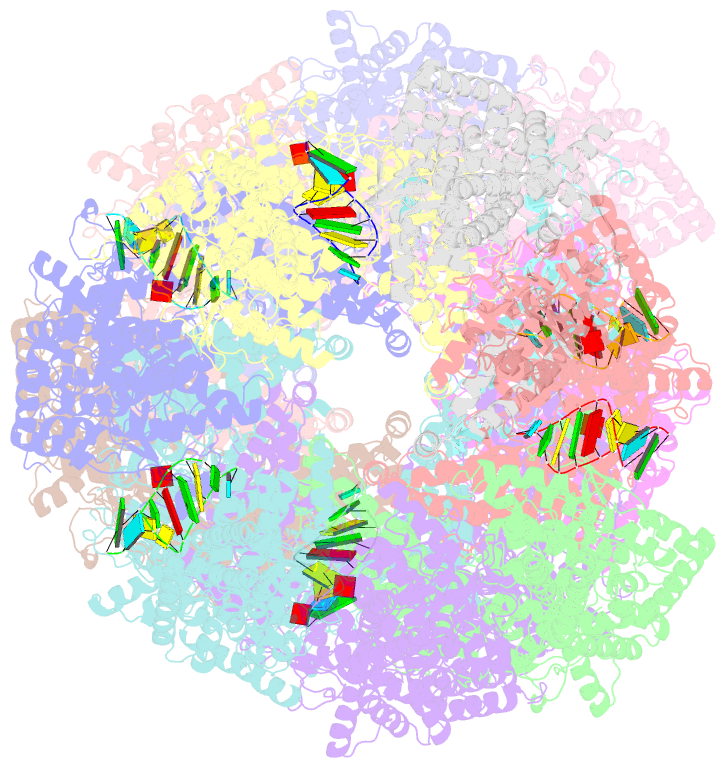
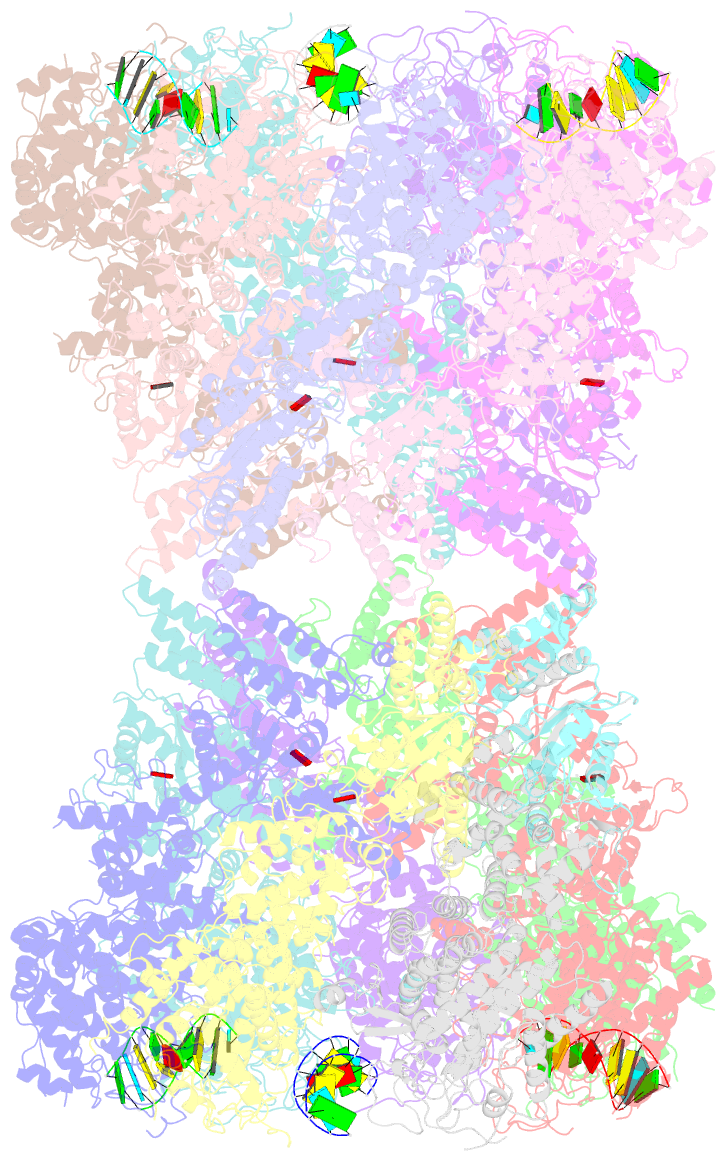
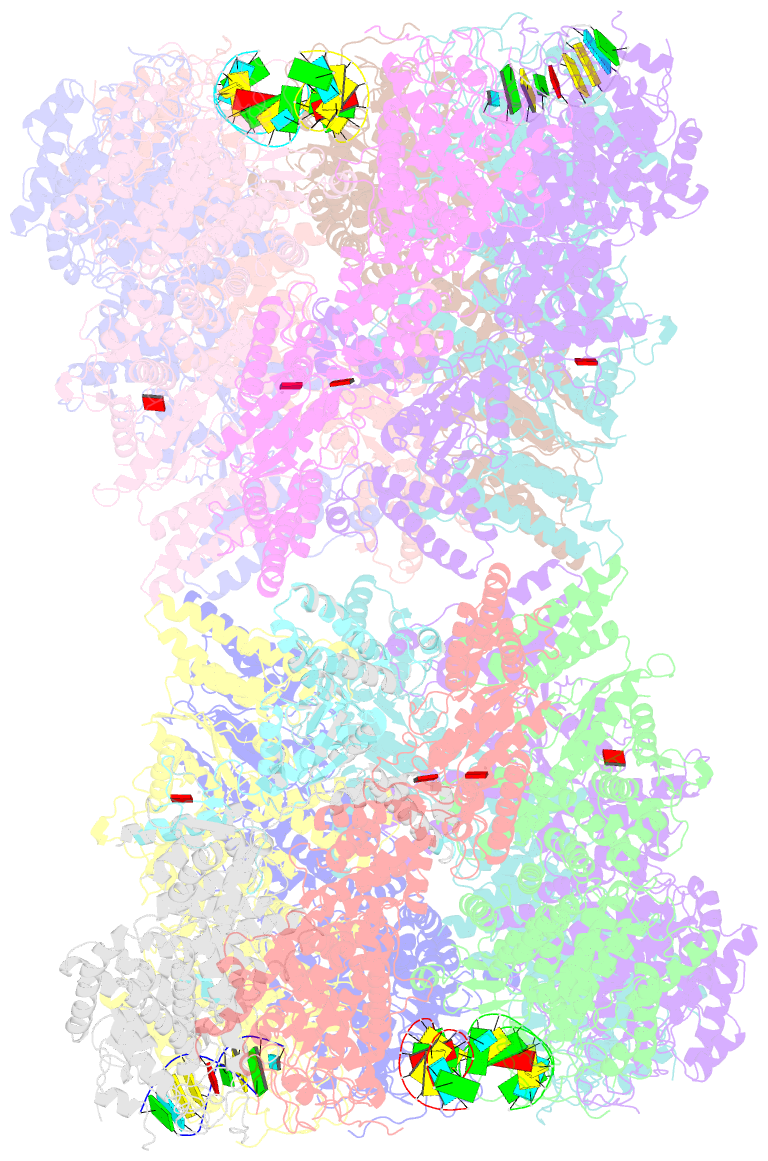
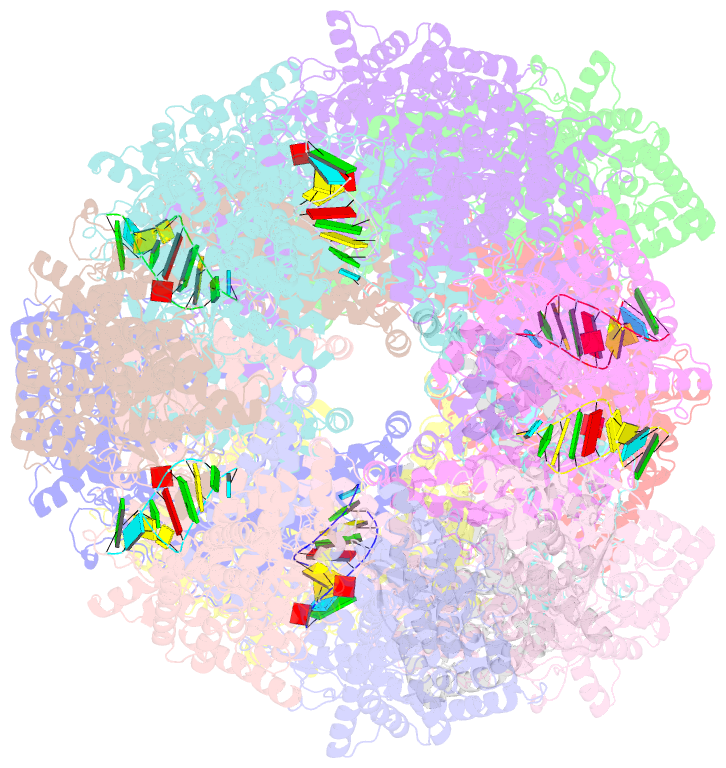
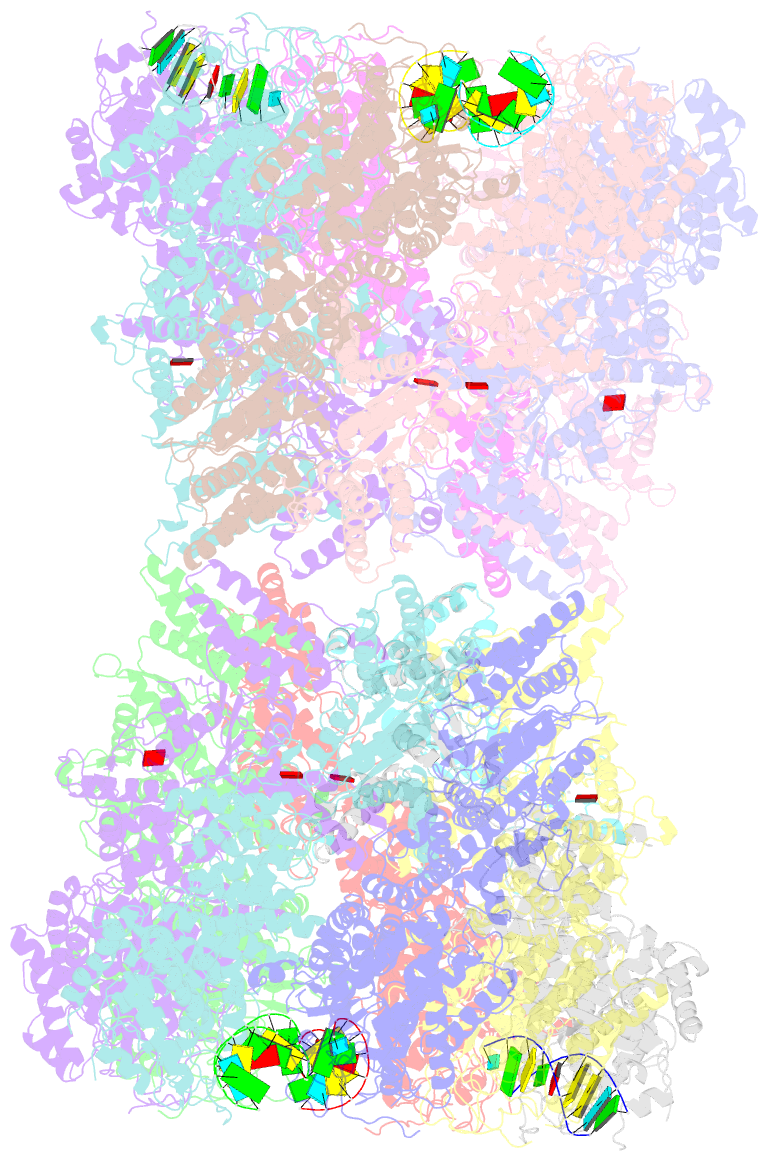
- Structure of tetradecameric rdra ring in RNA-loading state
- Reference
- Gao Y, Luo X, Li P, Li Z, Ye F, Liu S, Gao P (2023): "Molecular basis of RADAR anti-phage supramolecular assemblies." Cell, 186, 999-1012.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.01.026.
- Abstract
- Adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing has been proposed to be involved in a bacterial anti-phage defense system called RADAR. RADAR contains an adenosine triphosphatase (RdrA) and an adenosine deaminase (RdrB). Here, we report cryo-EM structures of RdrA, RdrB, and currently identified RdrA-RdrB complexes in the presence or absence of RNA and ATP. RdrB assembles into a dodecameric cage with catalytic pockets facing outward, while RdrA adopts both autoinhibited tetradecameric and activation-competent heptameric rings. Structural and functional data suggest a model in which RNA is loaded through the bottom section of the RdrA ring and translocated along its inner channel, a process likely coupled with ATP-binding status. Intriguingly, up to twelve RdrA rings can dock one RdrB cage with precise alignments between deaminase catalytic pockets and RNA-translocation channels, indicative of enzymatic coupling of RNA translocation and deamination. Our data uncover an interesting mechanism of enzymatic coupling and anti-phage defense through supramolecular assemblies.