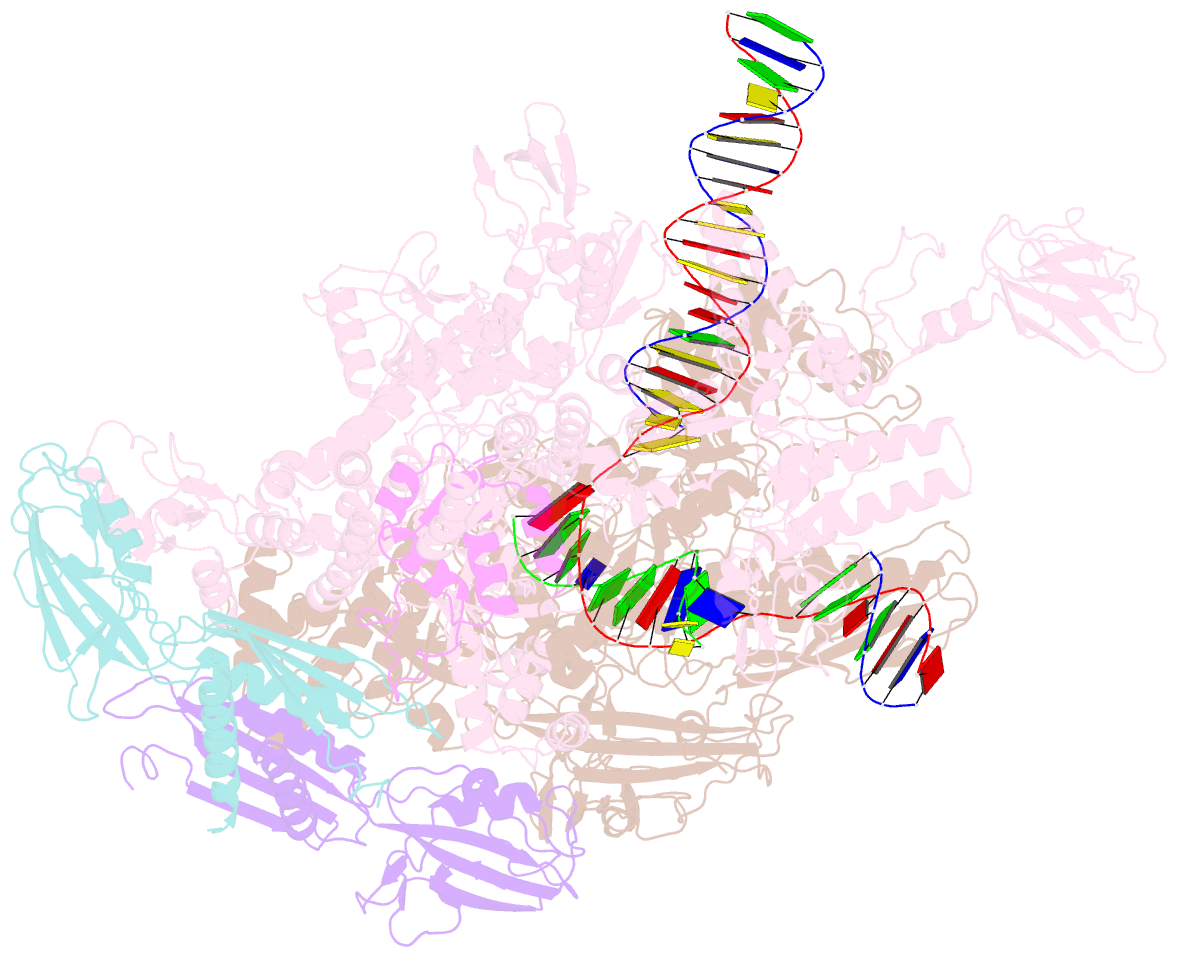
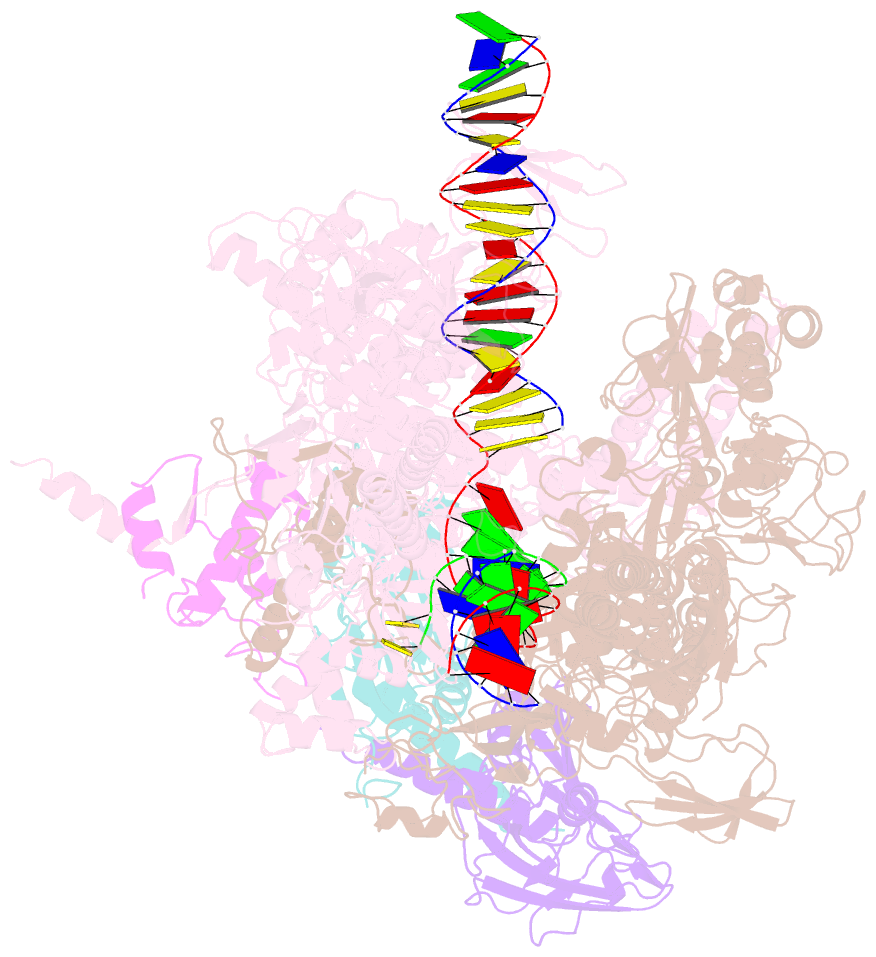
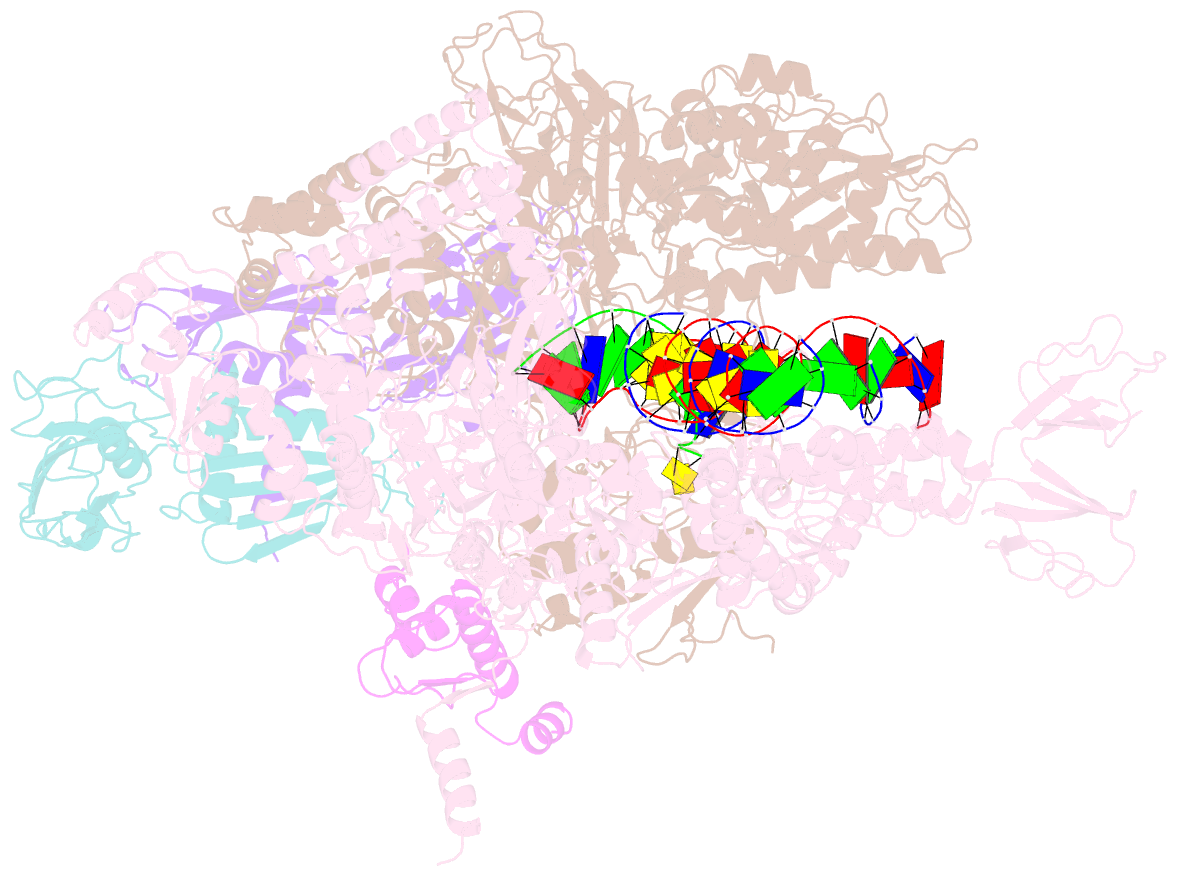
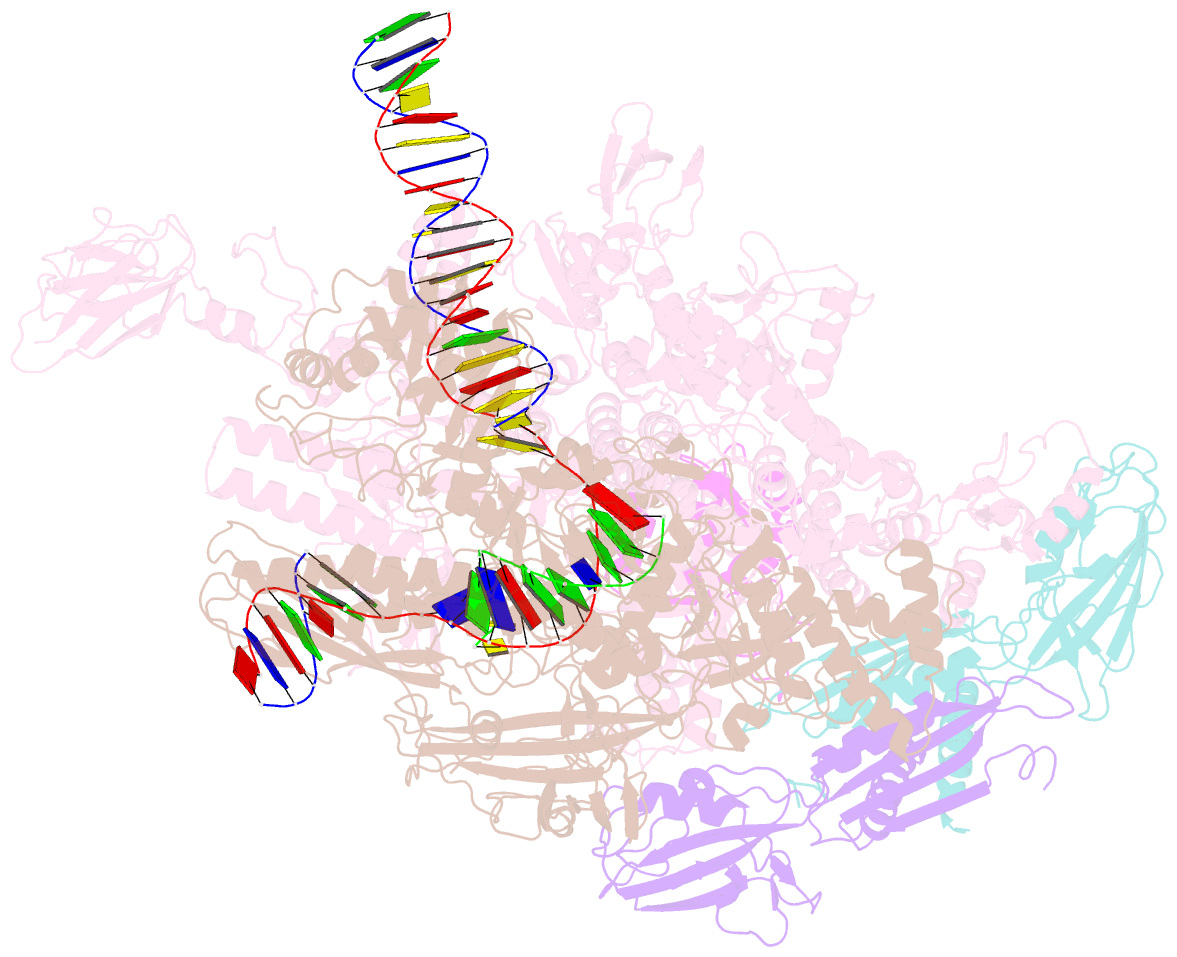
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8hsg; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.2 Å)
- Summary
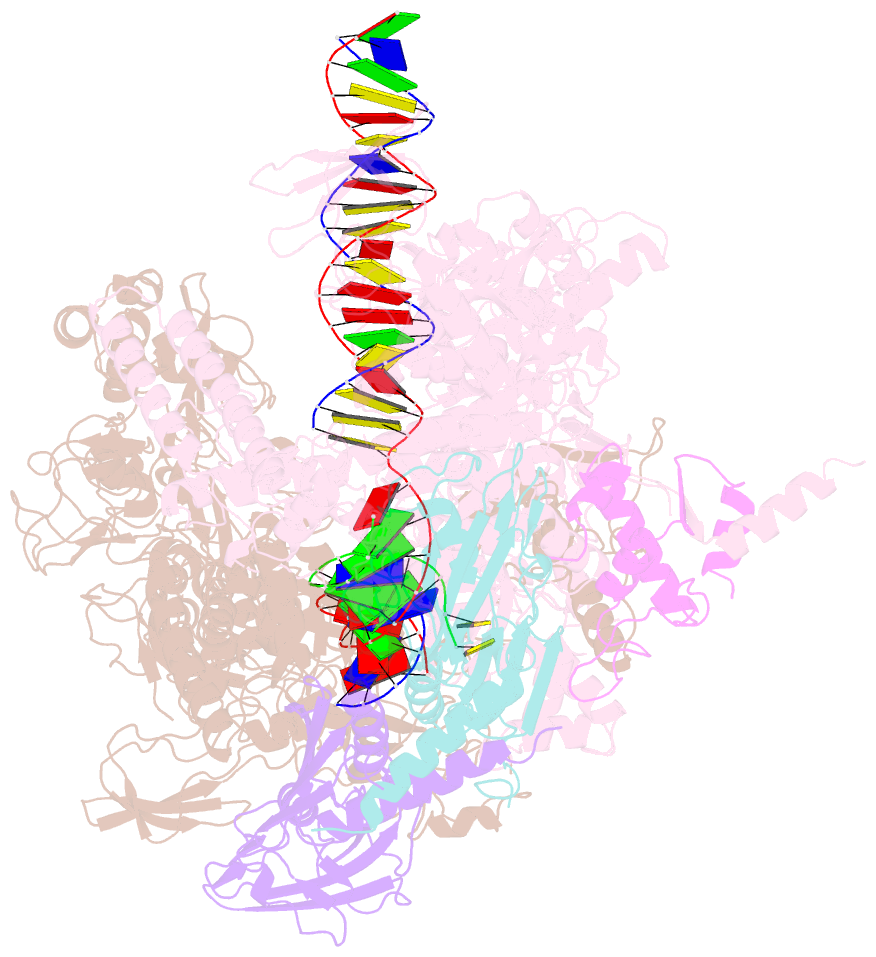
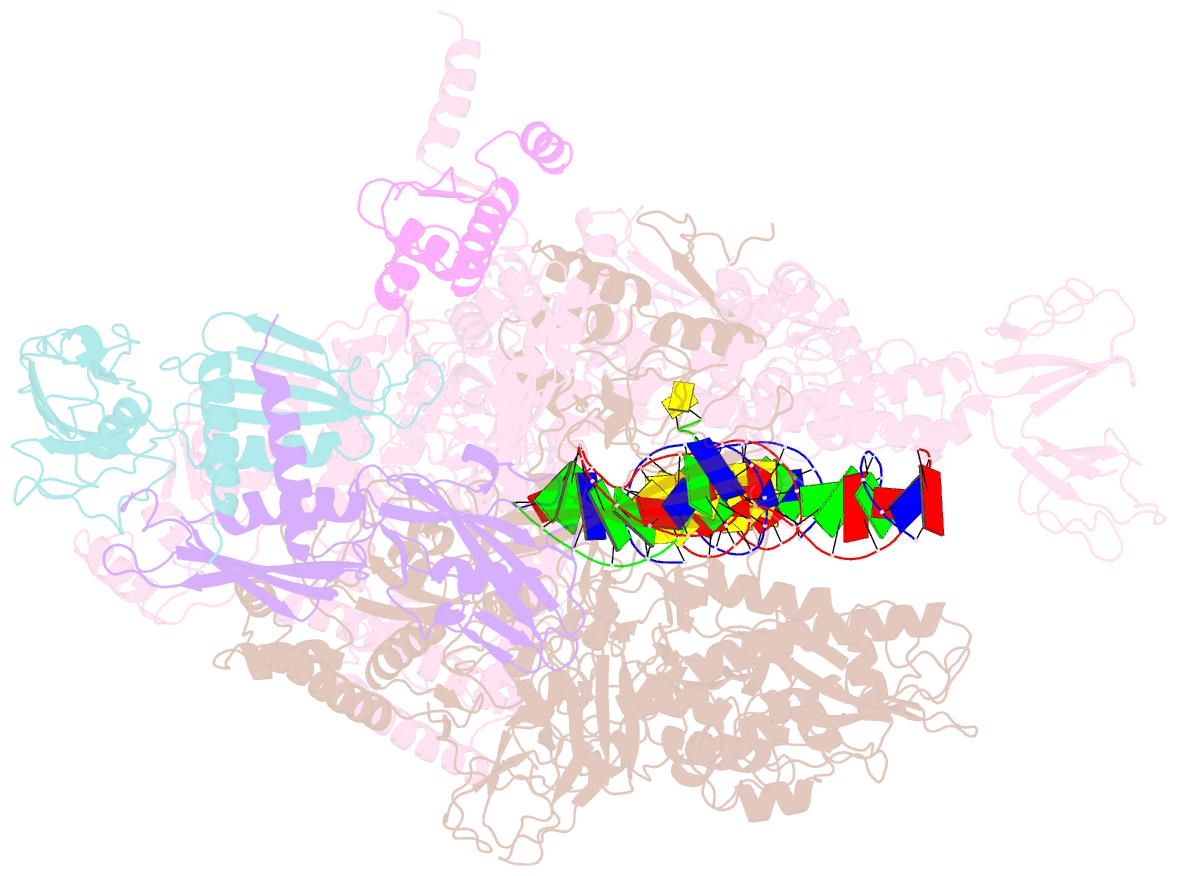
- Thermus thermophilus RNA polymerase elongation complex
- Reference
- Murayama Y, Ehara H, Aoki M, Goto M, Yokoyama T, Sekine SI (2023): "Structural basis of the transcription termination factor Rho engagement with transcribing RNA polymerase from Thermus thermophilus." Sci Adv, 9, eade7093. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ade7093.
- Abstract
- Transcription termination is an essential step in transcription by RNA polymerase (RNAP) and crucial for gene regulation. For many bacterial genes, transcription termination is mediated by the adenosine triphosphate-dependent RNA translocase/helicase Rho, which causes RNA/DNA dissociation from the RNAP elongation complex (EC). However, the structural basis of the interplay between Rho and RNAP remains obscure. Here, we report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the Thermus thermophilus RNAP EC engaged with Rho. The Rho hexamer binds RNAP through the carboxyl-terminal domains, which surround the RNA exit site of RNAP, directing the nascent RNA seamlessly from the RNA exit to its central channel. The β-flap tip at the RNA exit is critical for the Rho-dependent RNA release, and its deletion causes an alternative Rho-RNAP binding mode, which is irrelevant to termination. The Rho binding site overlaps with the binding sites of other macromolecules, such as ribosomes, providing a general basis of gene regulation.