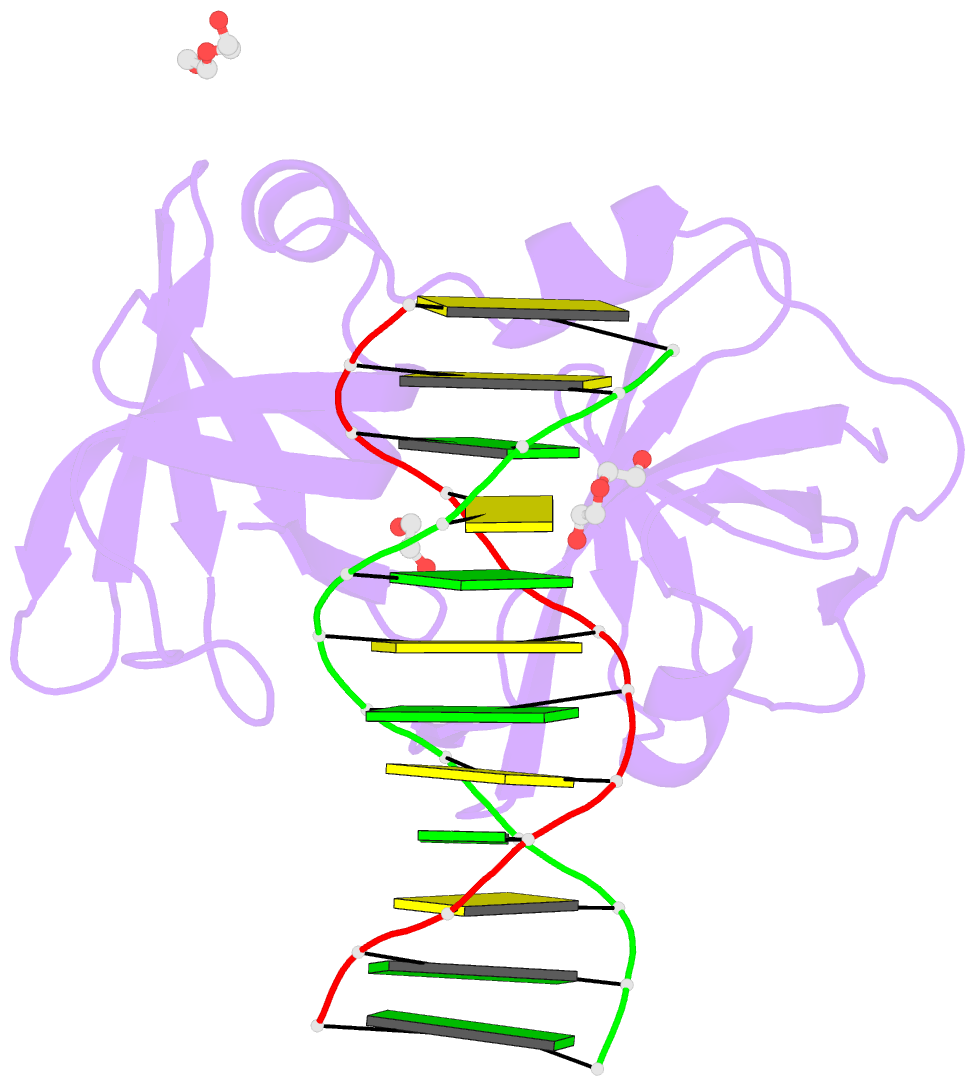
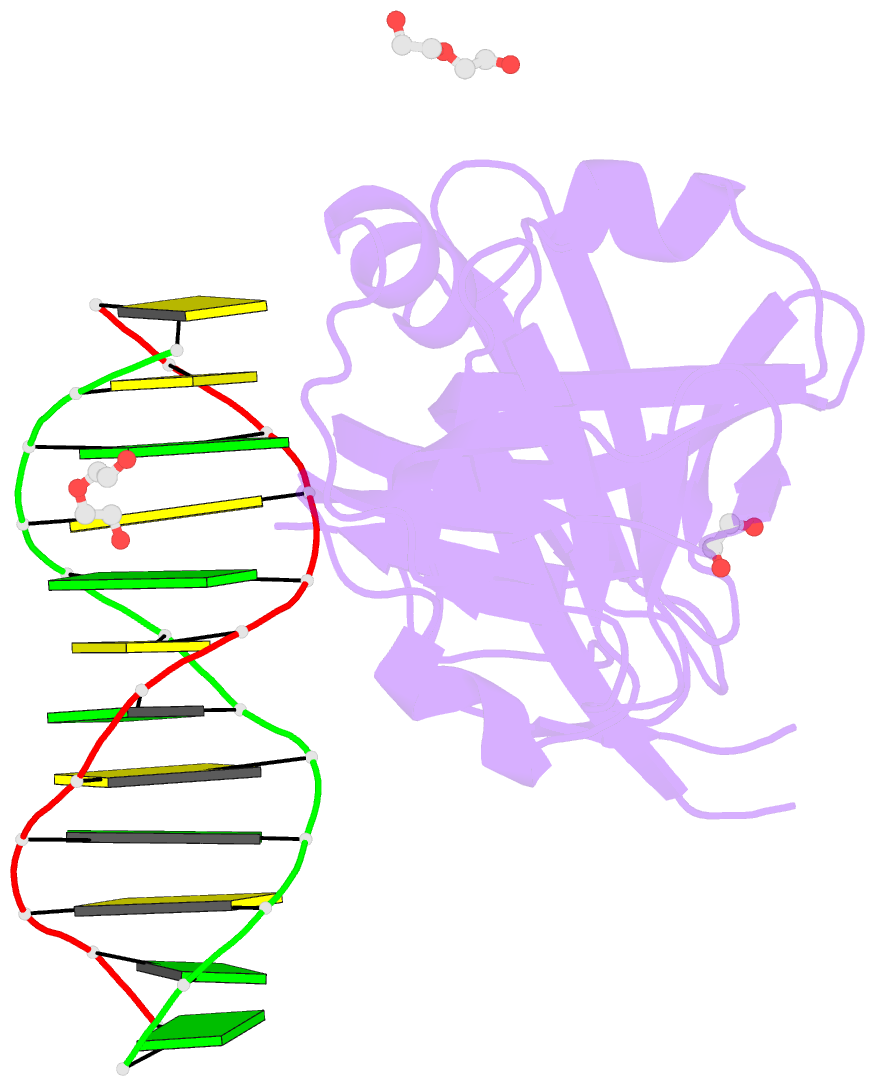
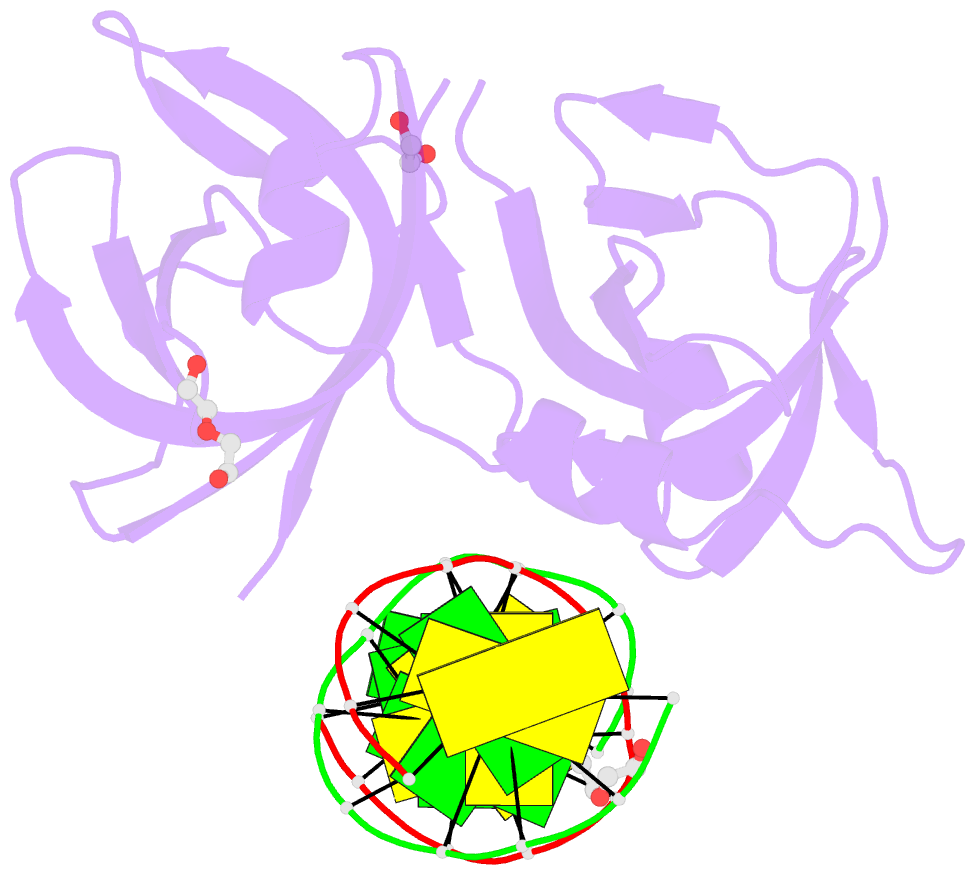
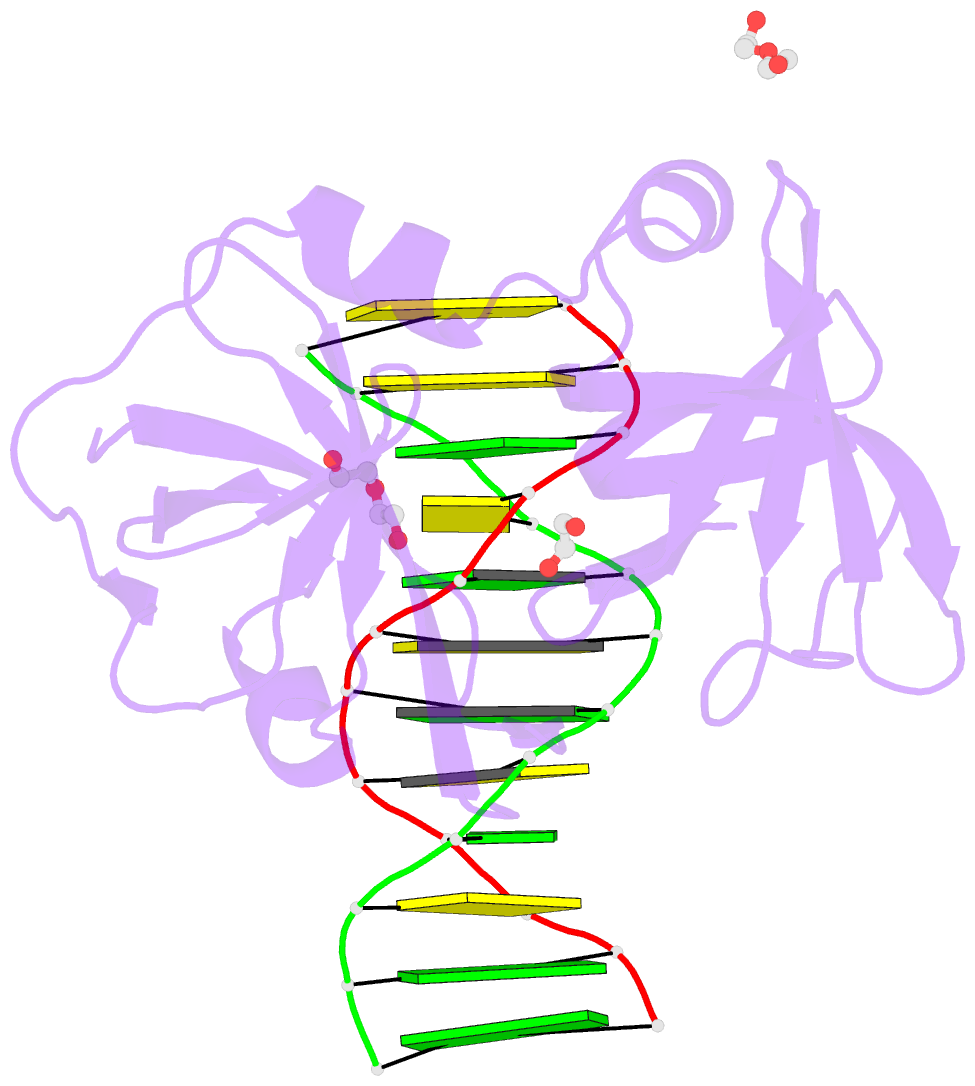
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8i6k; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.4 Å)
- Summary
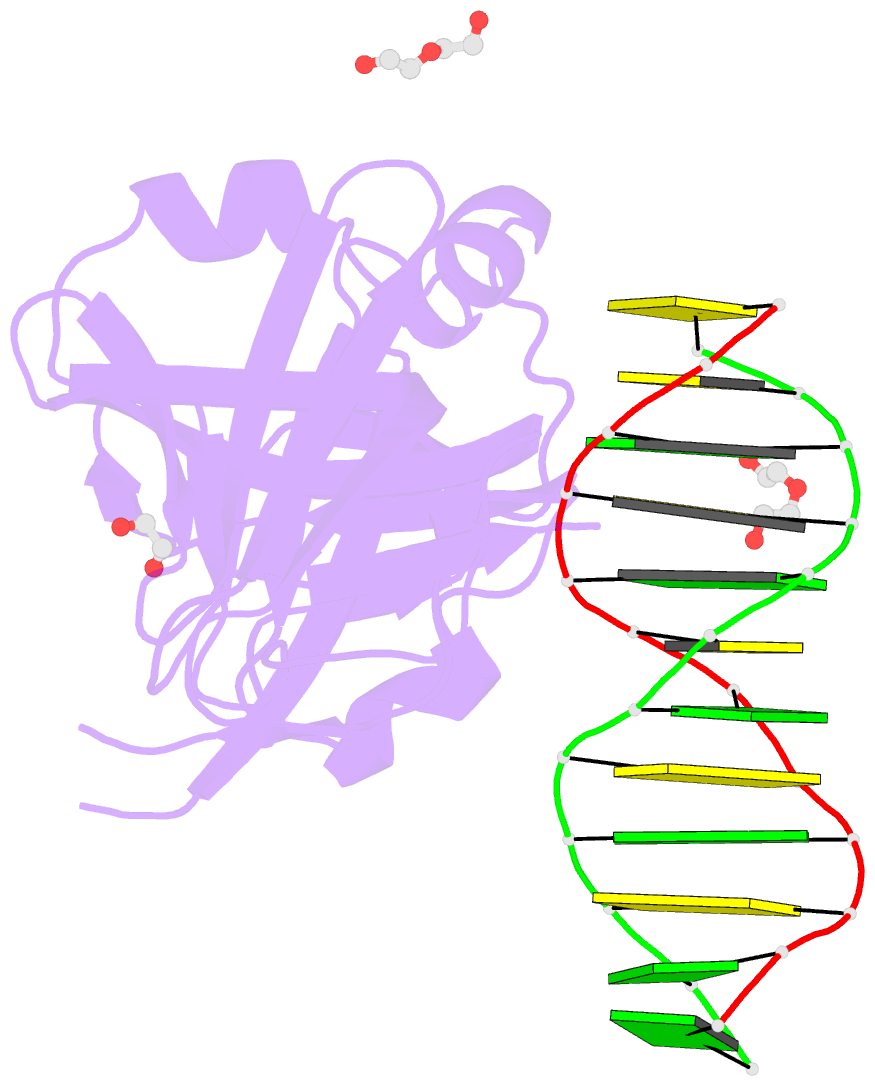
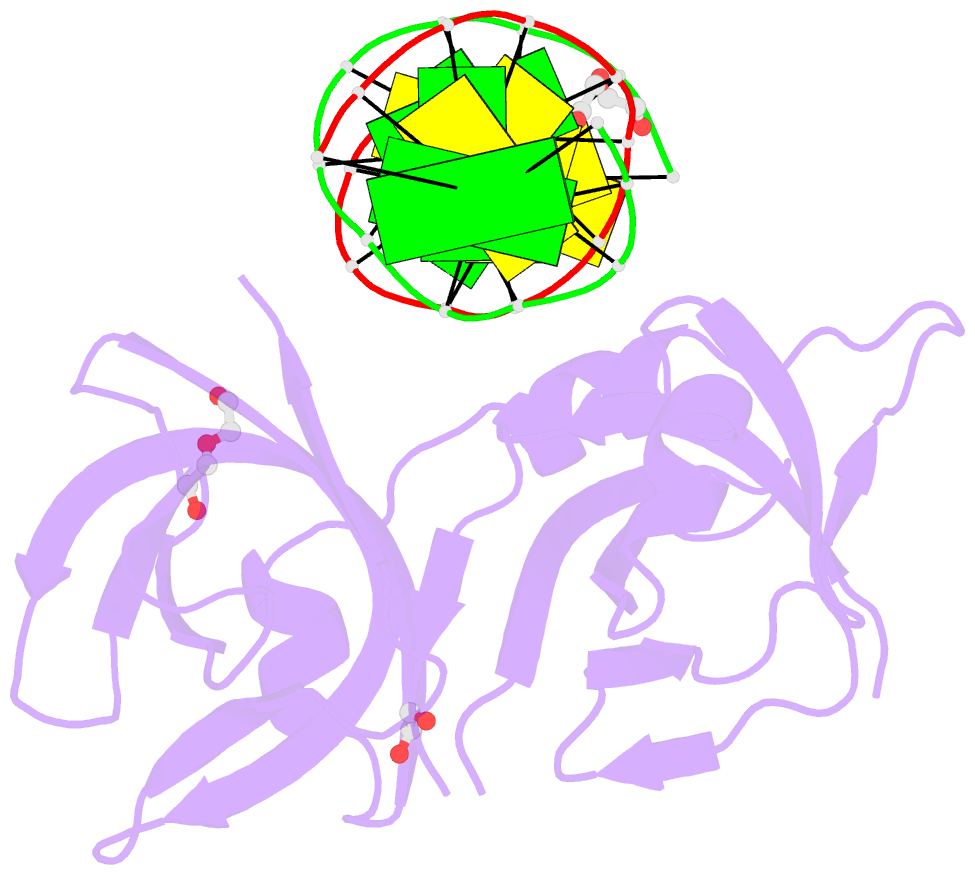
- Structure of hmnda hin with dsDNA
- Reference
- Li Y, Zhang C, Samad A, Zheng P, Li Y, Chen F, Jin T (2023): "Structural mechanism of dsDNA recognition by the hMNDA HIN domain: New insights into the DNA-binding model of a PYHIN protein." Int.J.Biol.Macromol., 245, 125461. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125461.
- Abstract
- The hematopoietic interferon-inducible nuclear (HIN) domain of the PYHIN family of proteins recognizes double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) through different dsDNA-binding modes. These modes apparently confer different roles upon these proteins in the regulation of innate immune responses, gene transcription, and apoptosis. Myeloid cell nuclear differentiation antigen (MNDA), a member of the human PYHIN family, binds DNA and regulates gene transcription in monocytes. However, the mechanism of DNA recognition and DNA-binding modes of human MNDA (hMNDA) remain unclear. Here, we determined the crystal structure of the hMNDA-HIN domain in complex with dsDNA at 2.4 Å resolution, and reveal that hMNDA-HIN binds to dsDNA in a sequence-independent manner. Structure and mutation studies indicated that hMNDA-HIN binds to dsDNA through a unique mode, involving two dsDNA-binding interfaces. Interface I exhibits an AIM2-like dsDNA-binding mode, and interface II has a previously unreported mode of dsDNA-binding. These results provide new insights into the DNA-binding modes of this PYHIN protein.