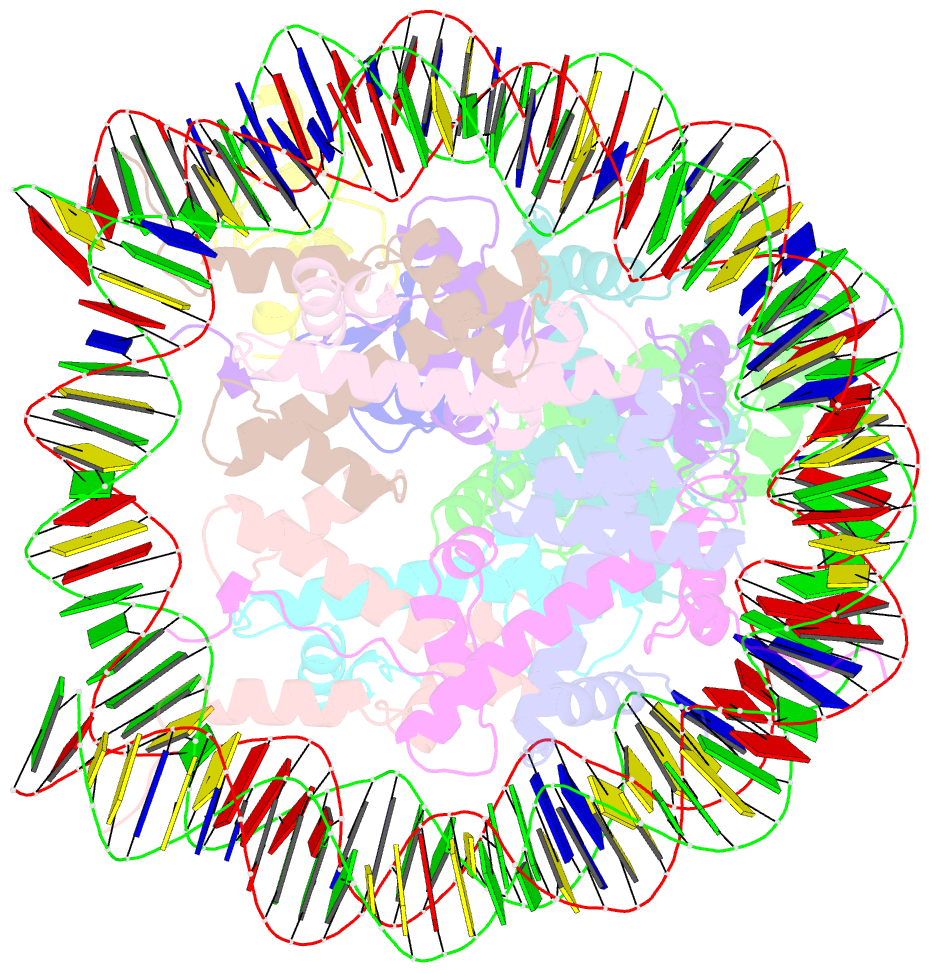
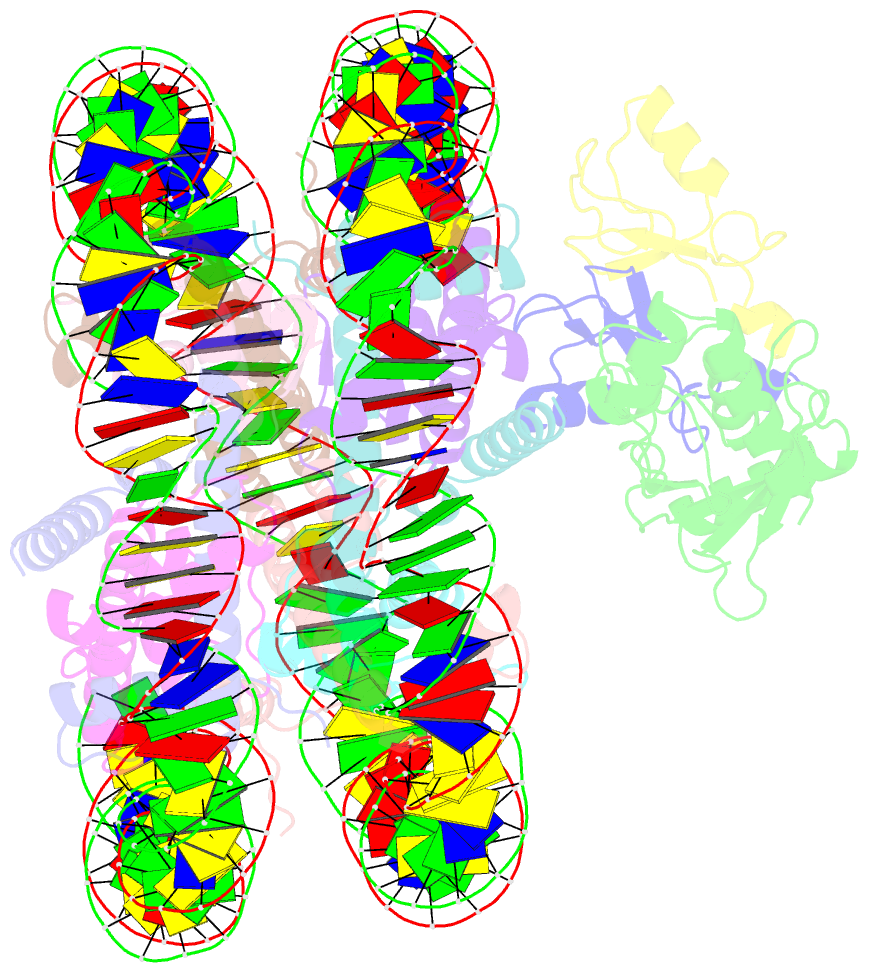
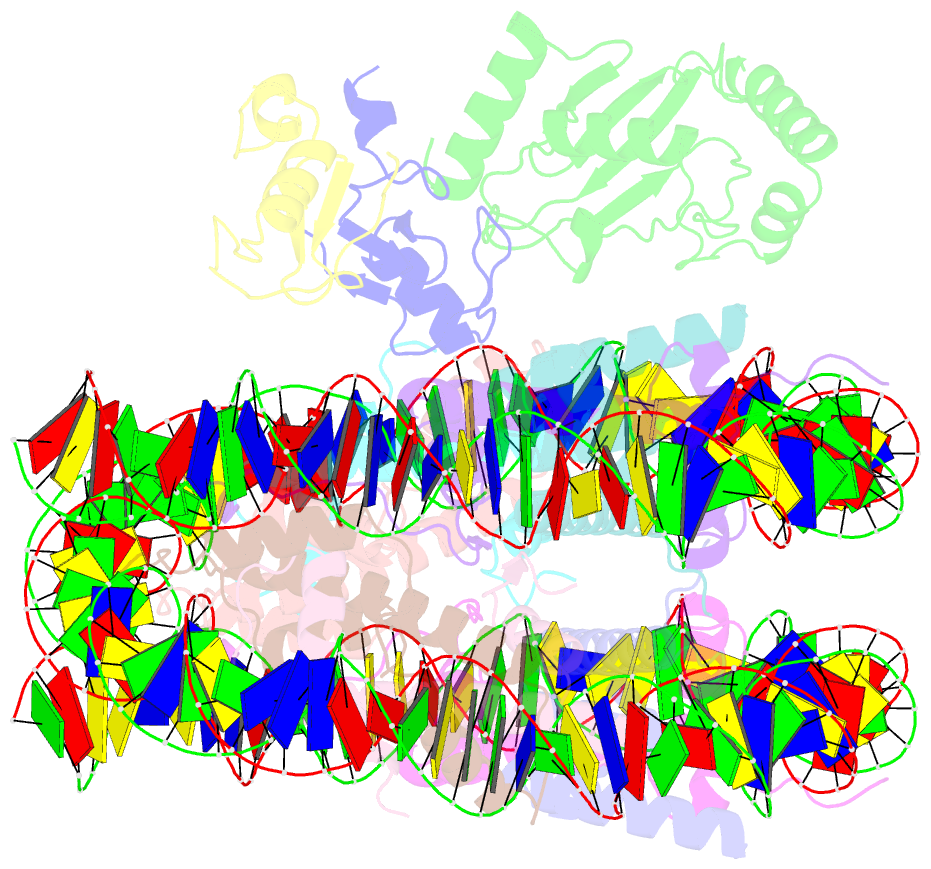
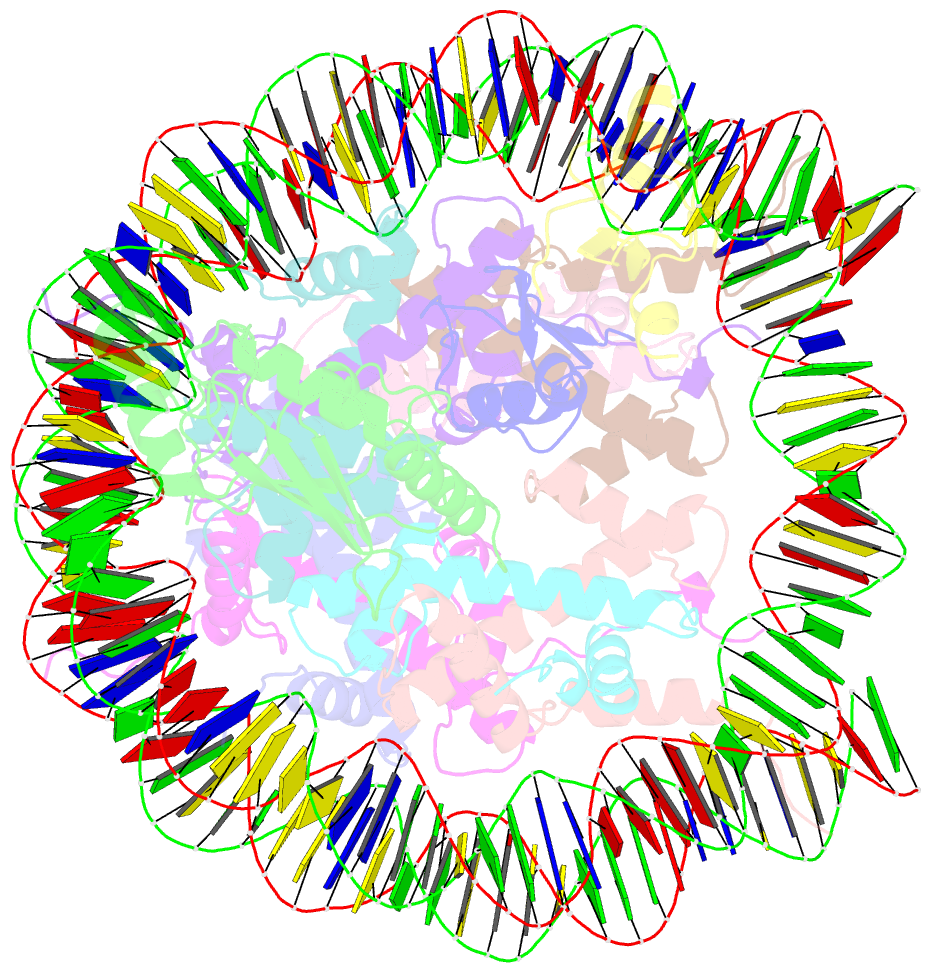
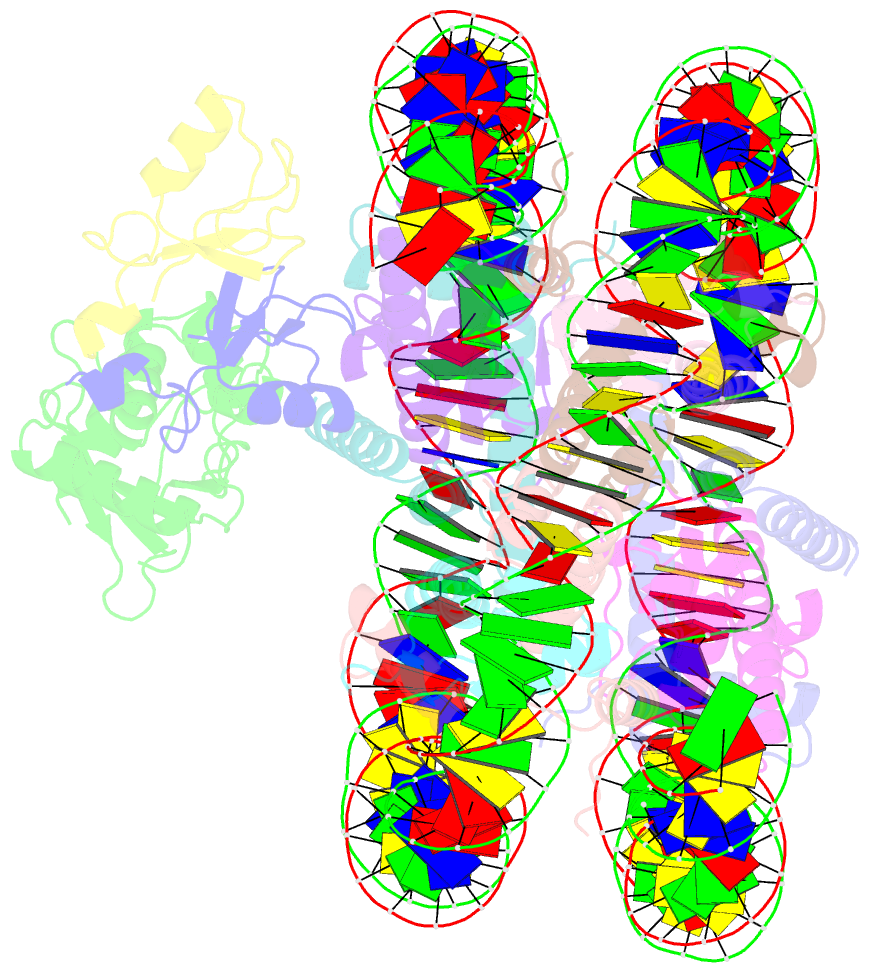
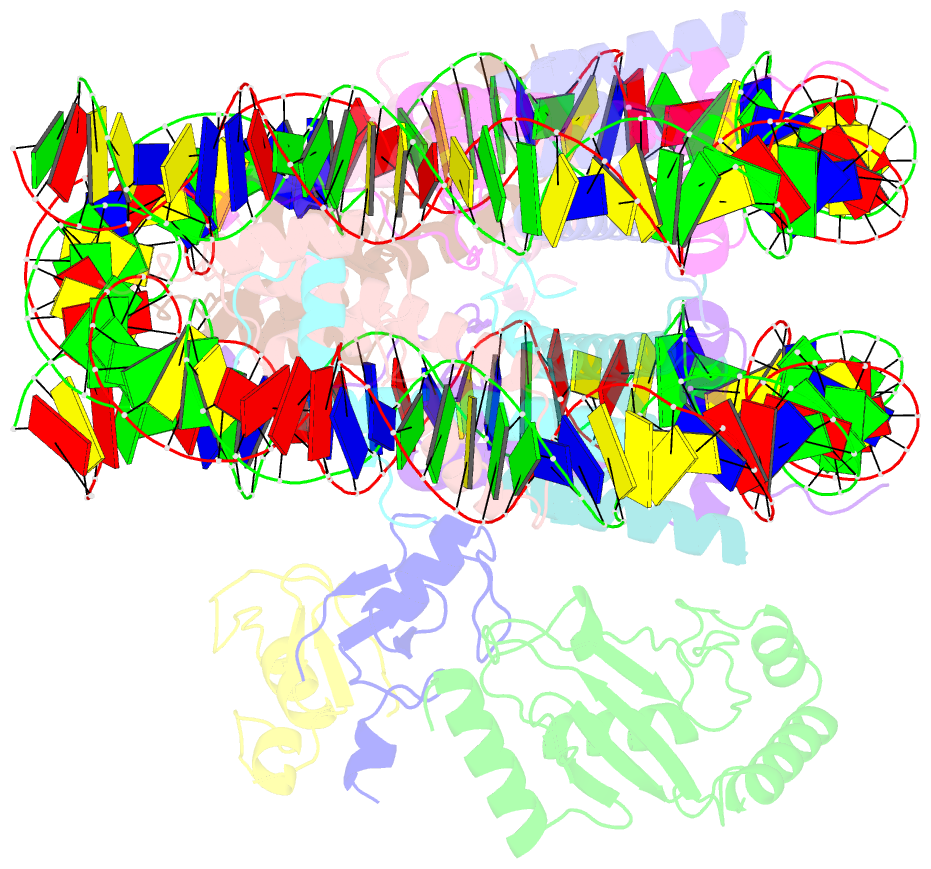
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8iej; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- nuclear protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.12 Å)
- Summary
- Rnf20-rnf40-hrad6a-ub-nucleosome complex
- Reference
- Deng Z, Ai H, Sun M, Tong Z, Du Y, Qu Q, Zhang L, Xu Z, Tao S, Shi Q, Li JB, Pan M, Liu L (2023): "Mechanistic insights into nucleosomal H2B monoubiquitylation mediated by yeast Bre1-Rad6 and its human homolog RNF20/RNF40-hRAD6A." Mol.Cell, 83, 3080-3094.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.08.001.
- Abstract
- Histone H2B monoubiquitylation plays essential roles in chromatin-based transcriptional processes. A RING-type E3 ligase (yeast Bre1 or human RNF20/RNF40) and an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (yeast Rad6 or human hRAD6A), together, precisely deposit ubiquitin on H2B K123 in yeast or K120 in humans. Here, we developed a chemical trapping strategy and successfully captured the transient structures of Bre1- or RNF20/RNF40-mediated ubiquitin transfer from Rad6 or hRAD6A to nucleosomal H2B. Our structures show that Bre1 and RNF40 directly bind nucleosomal DNA, exhibiting a conserved E3/E2/nucleosome interaction pattern from yeast to humans for H2B monoubiquitylation. We also find an uncanonical non-hydrophobic contact in the Bre1 RING-Rad6 interface, which positions Rad6 directly above the target H2B lysine residue. Our study provides mechanistic insights into the site-specific monoubiquitylation of H2B, reveals a critical role of nucleosomal DNA in mediating E3 ligase recognition, and provides a framework for understanding the cancer-driving mutations of RNF20/RNF40.