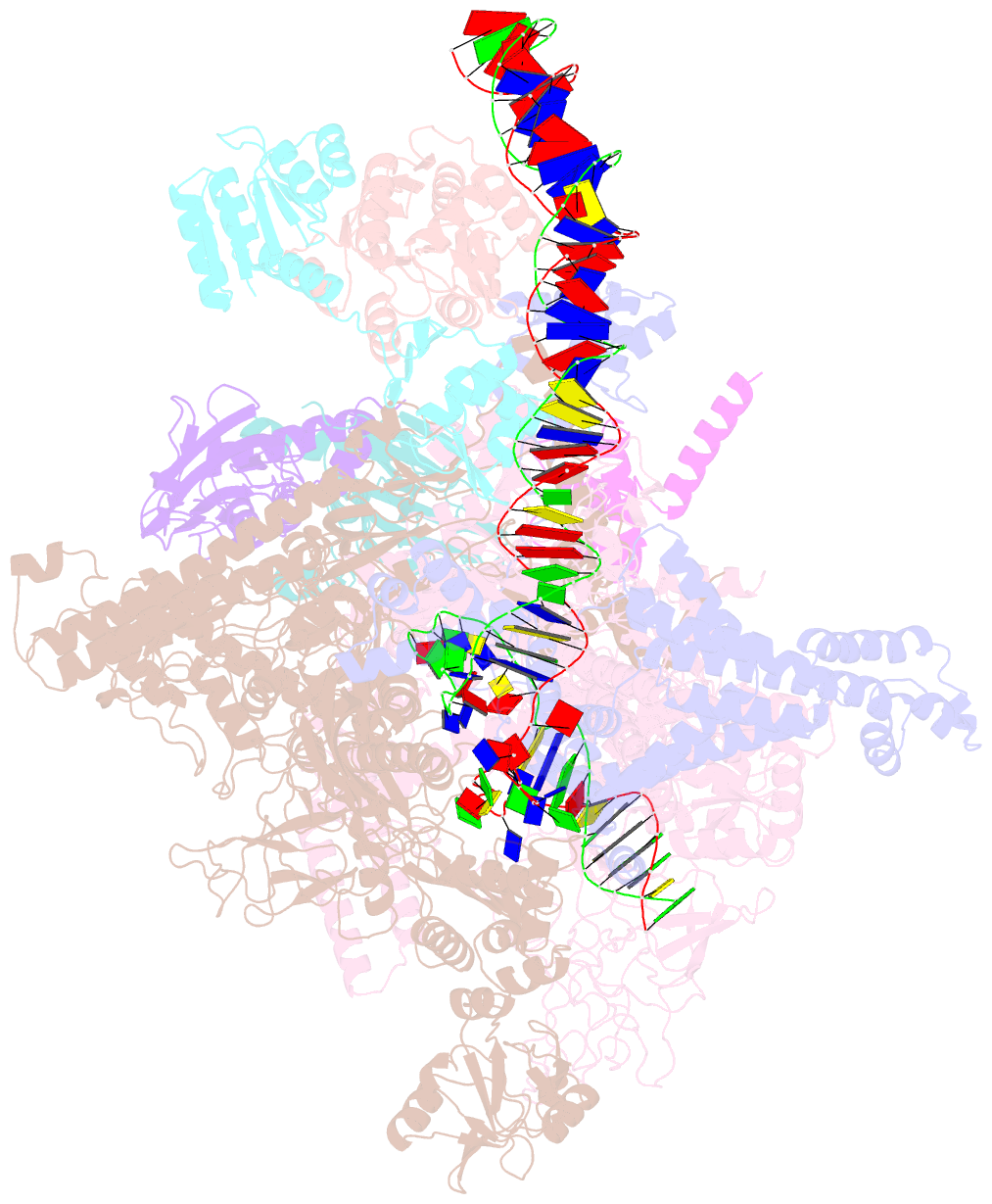
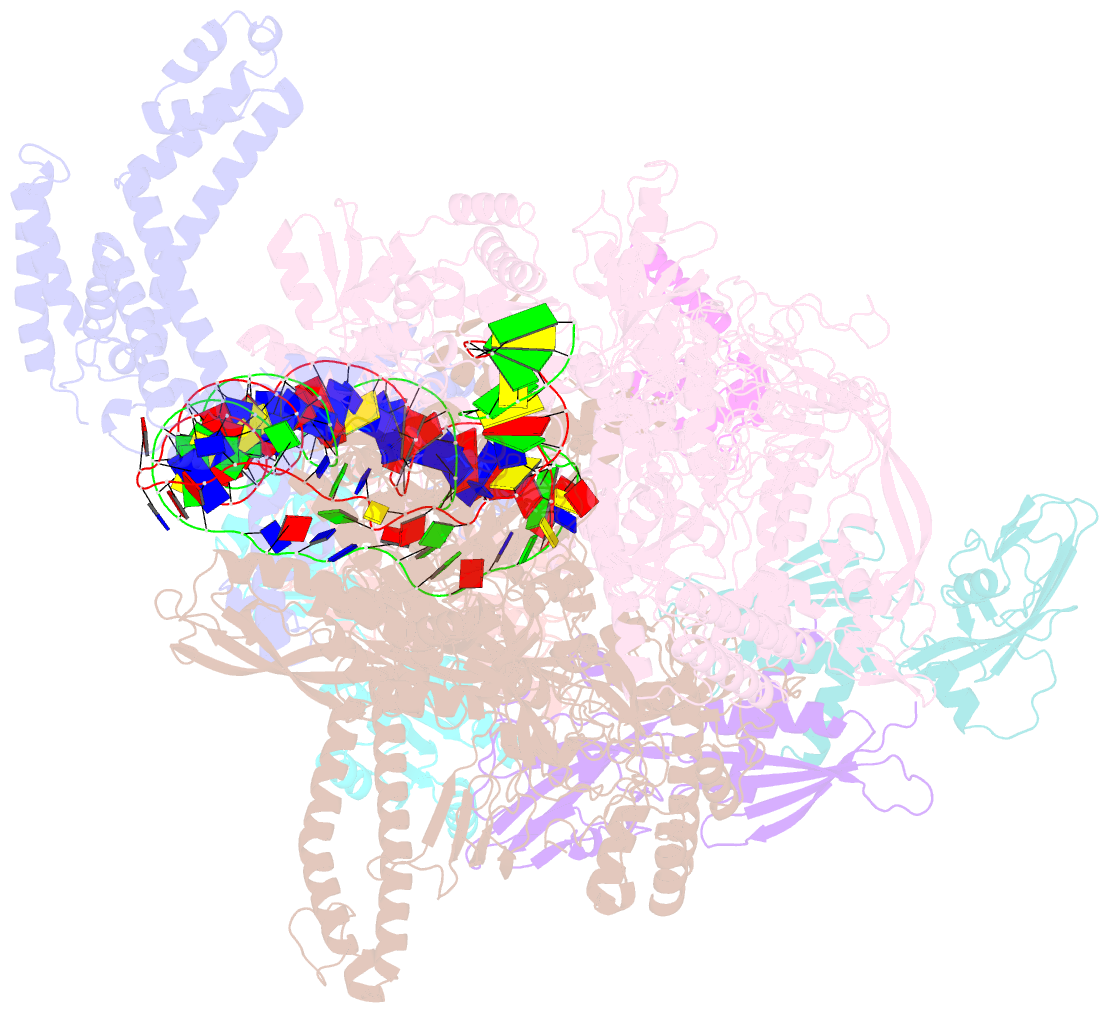
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8jo2; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.74 Å)
- Summary
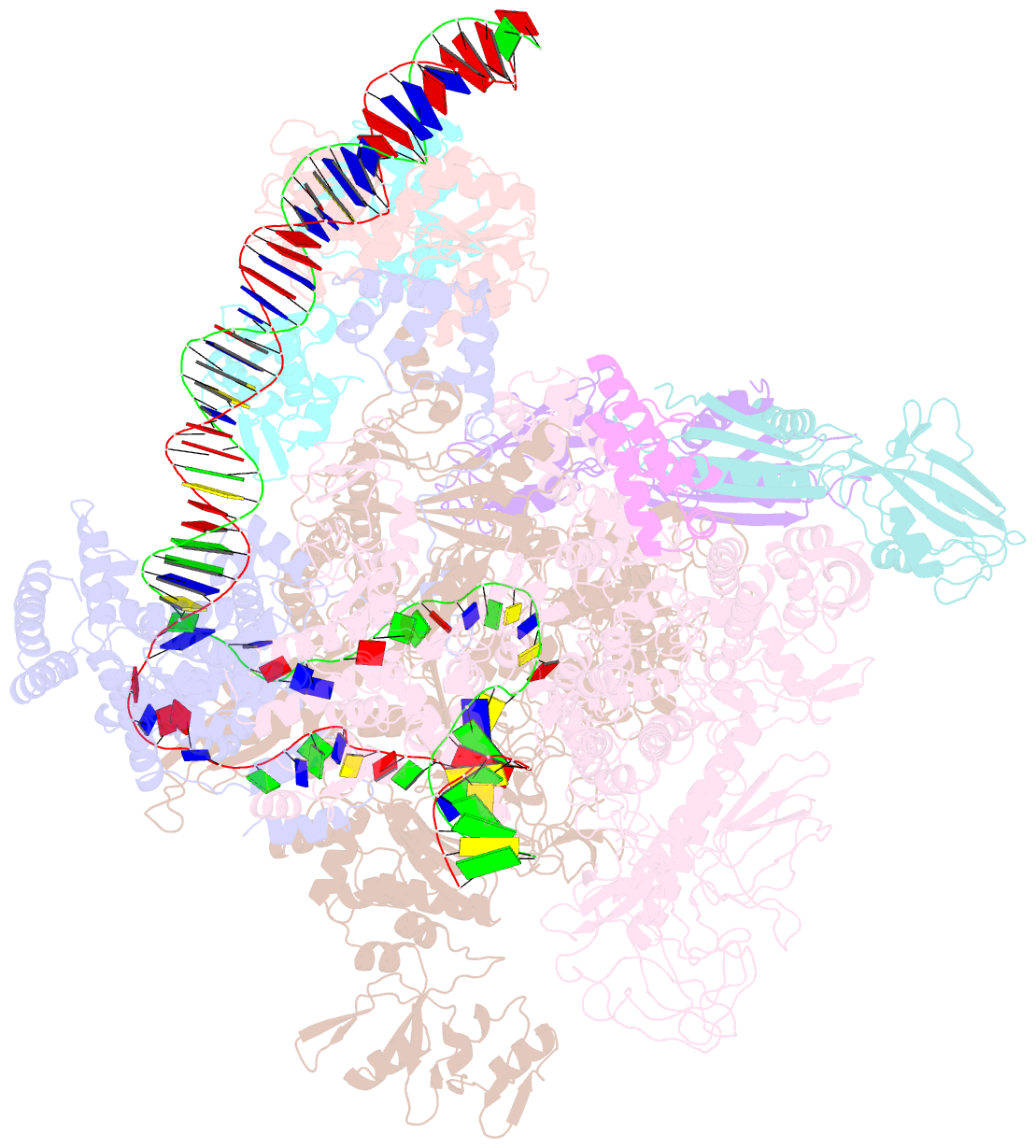
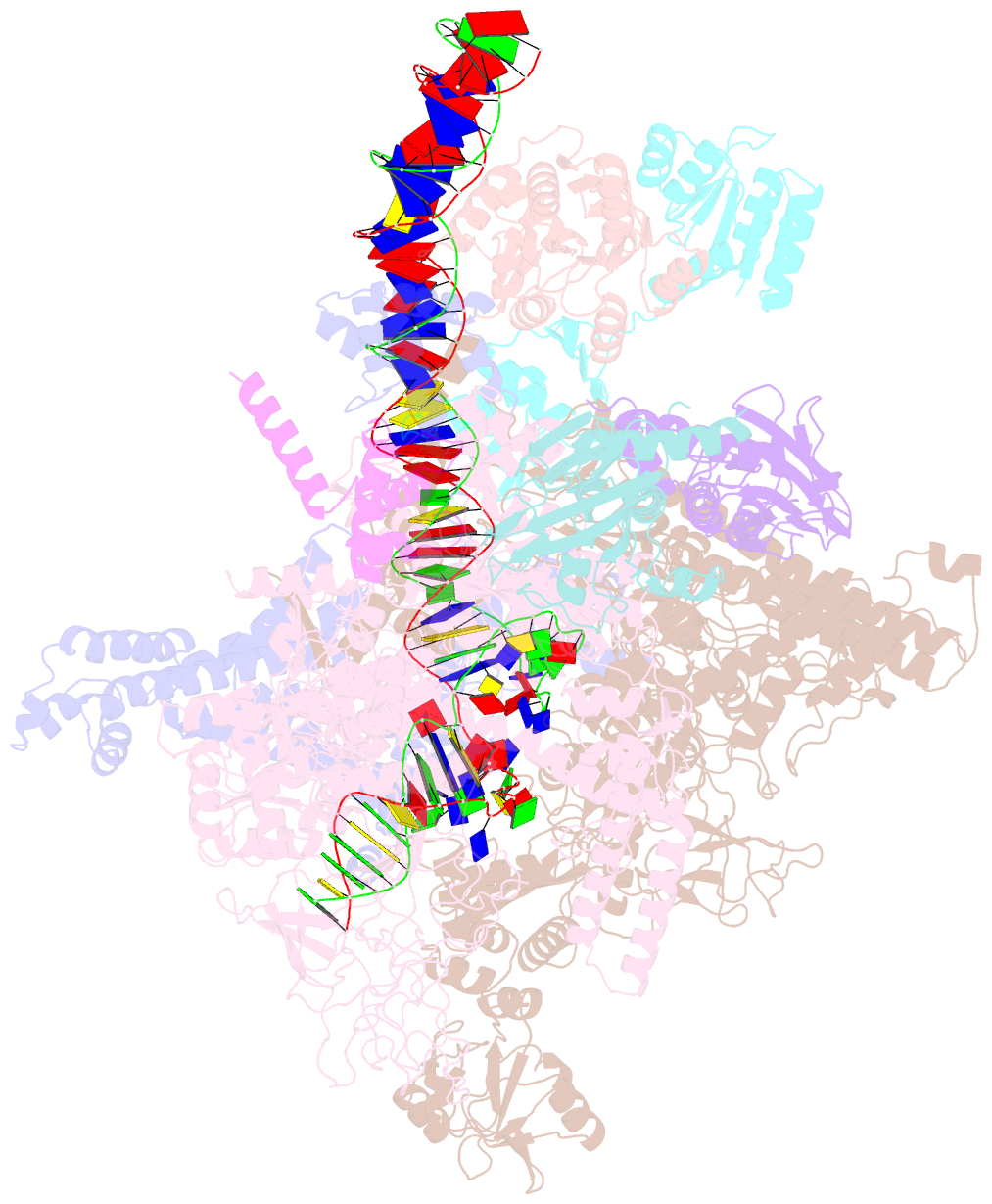
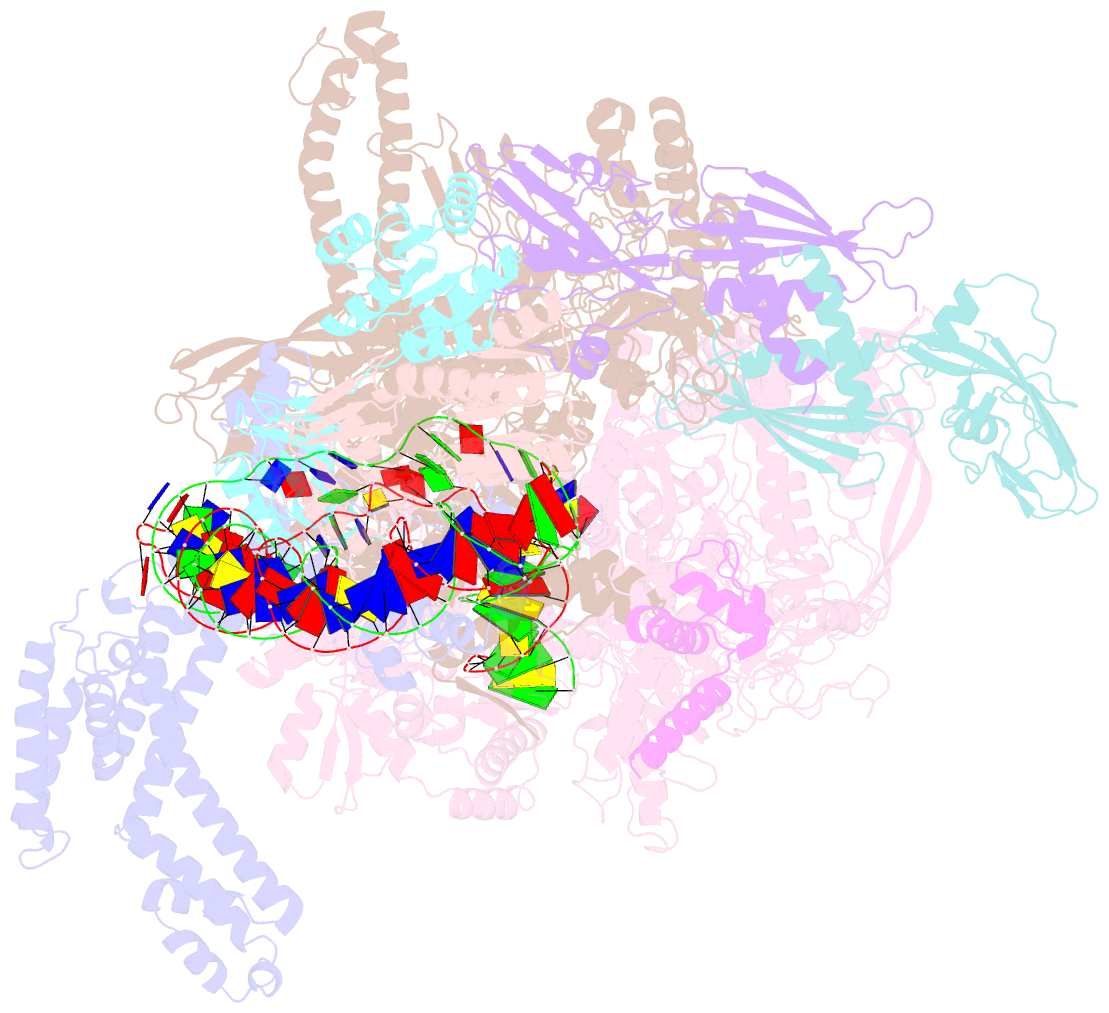
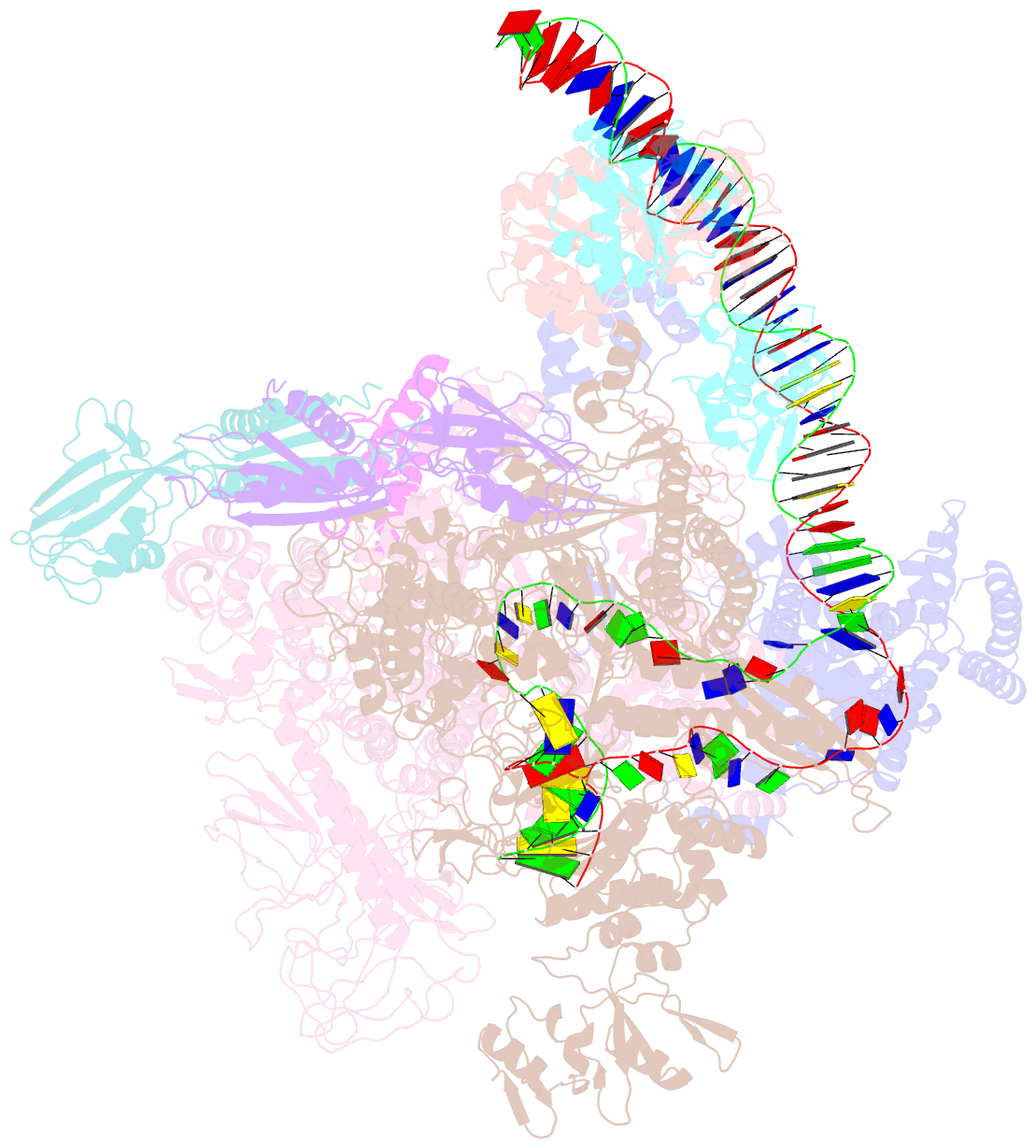
- Structural basis of transcriptional activation by the ompr-phob-family response regulator pmra
- Reference
- Lou YC, Huang HY, Yeh HH, Chiang WH, Chen C, Wu KP (2023): "Structural basis of transcriptional activation by the OmpR/PhoB-family response regulator PmrA." Nucleic Acids Res., 51, 10049-10058. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad724.
- Abstract
- PmrA, an OmpR/PhoB-family response regulator, triggers gene transcription responsible for polymyxin resistance in bacteria by recognizing promoters where the canonical-35 element is replaced by the pmra-box, representing the PmrA recognition sequence. Here, we report a cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of a bacterial PmrA-dependent transcription activation complex (TAC) containing a PmrA dimer, an RNA polymerase σ70 holoenzyme (RNAPH) and the pbgP promoter DNA. Our structure reveals that the RNAPH mainly contacts the PmrA C-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD) via electrostatic interactions and reorients the DBD three base pairs upstream of the pmra-box, resulting in a dynamic TAC conformation. In vivo assays show that the substitution of the DNA-recognition residue eliminated its transcriptional activity, while variants with altered RNAPH-interacting residues resulted in enhanced transcriptional activity. Our findings suggest that both PmrA recognition-induced DNA distortion and PmrA promoter escape play crucial roles in its transcriptional activation.