Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8k87; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA-RNA-cell invasion
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.9 Å)
- Summary
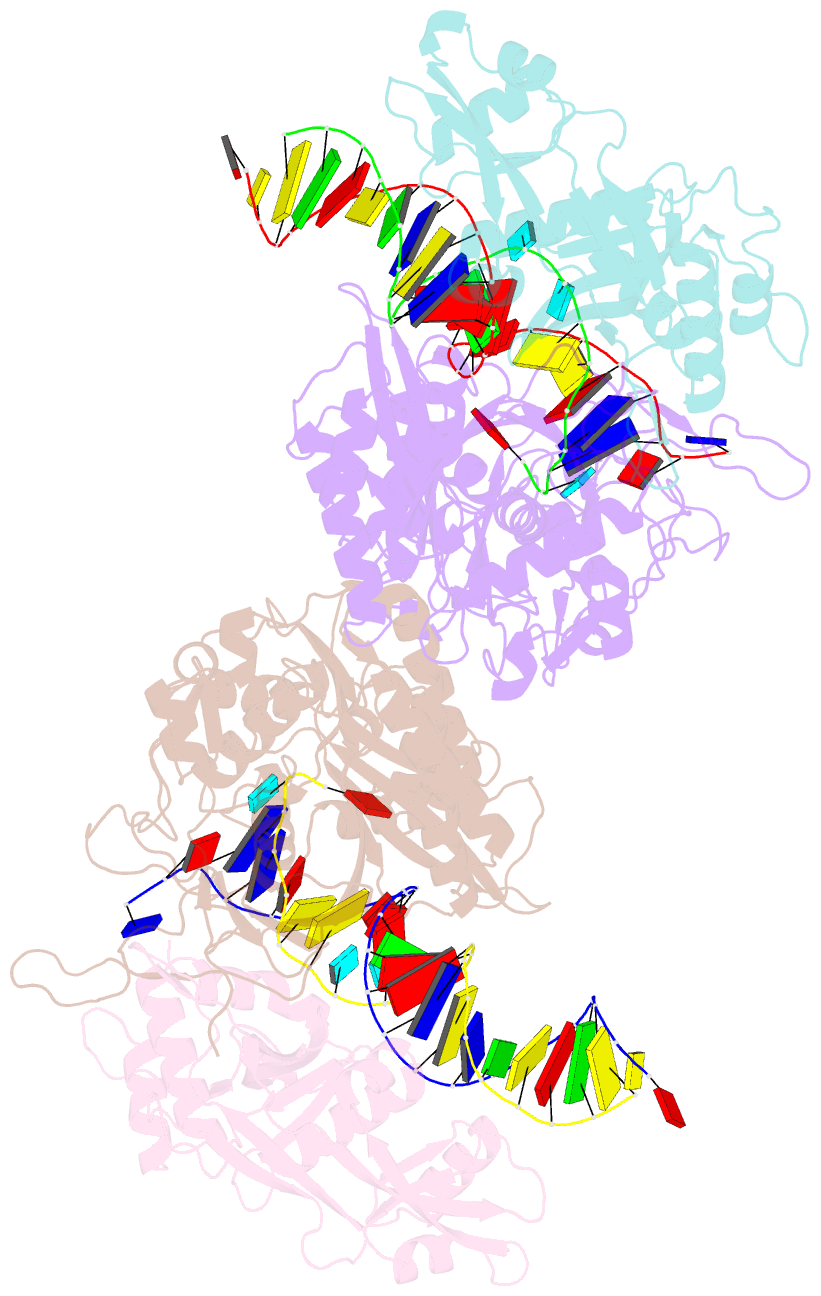
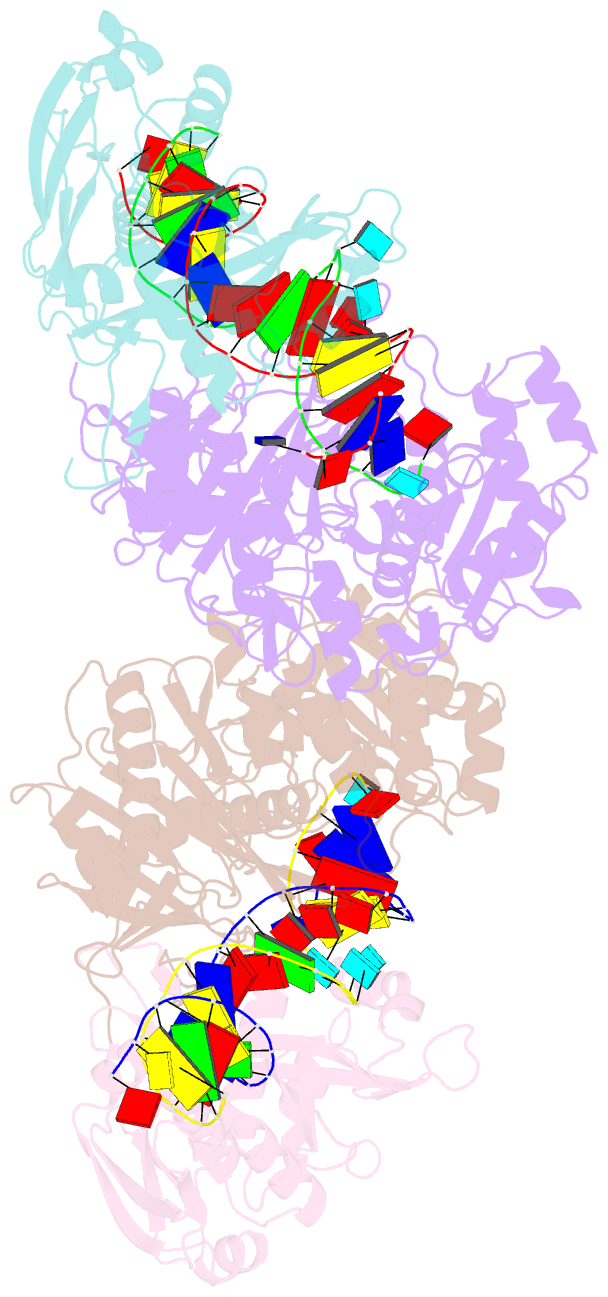
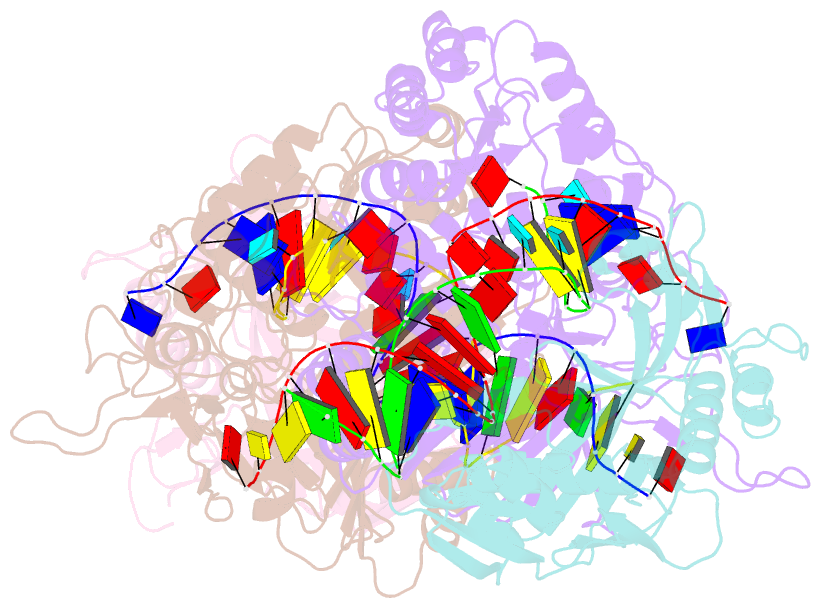
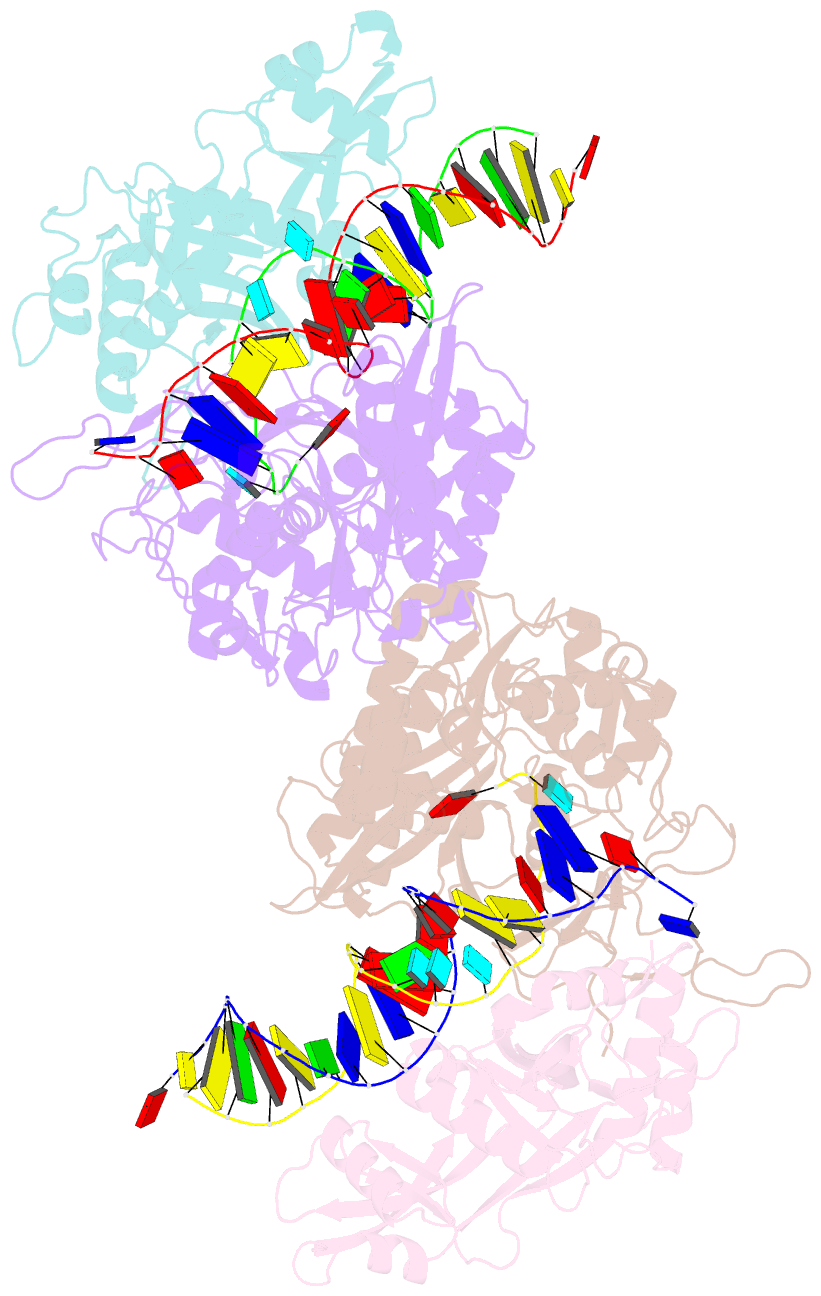
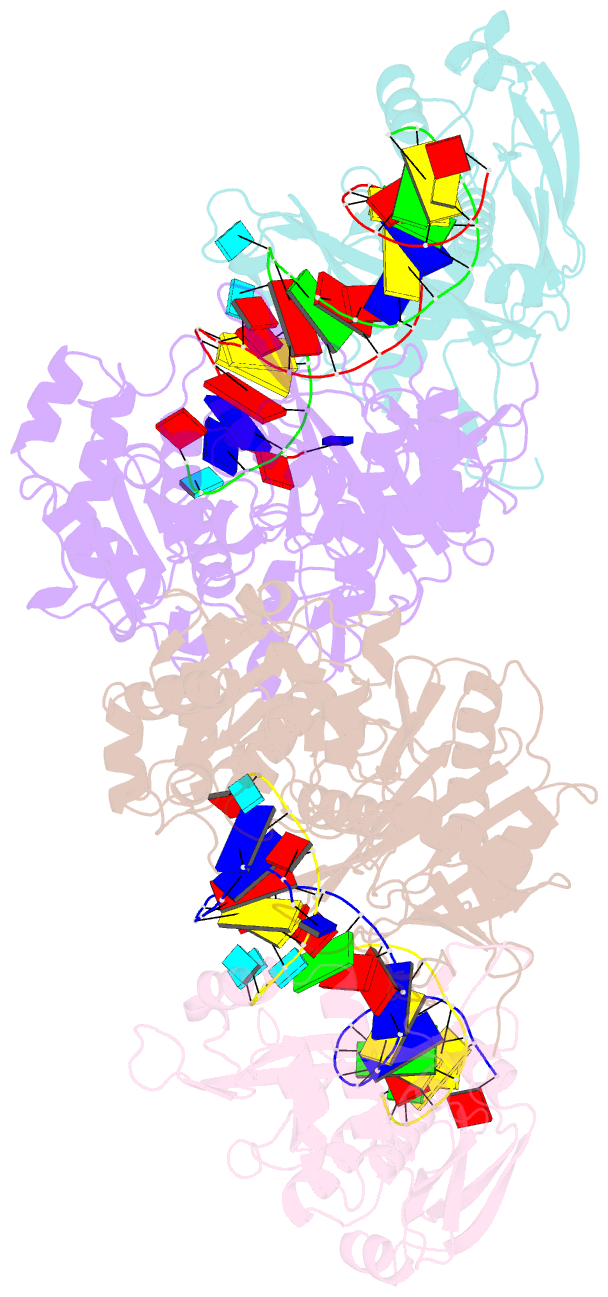
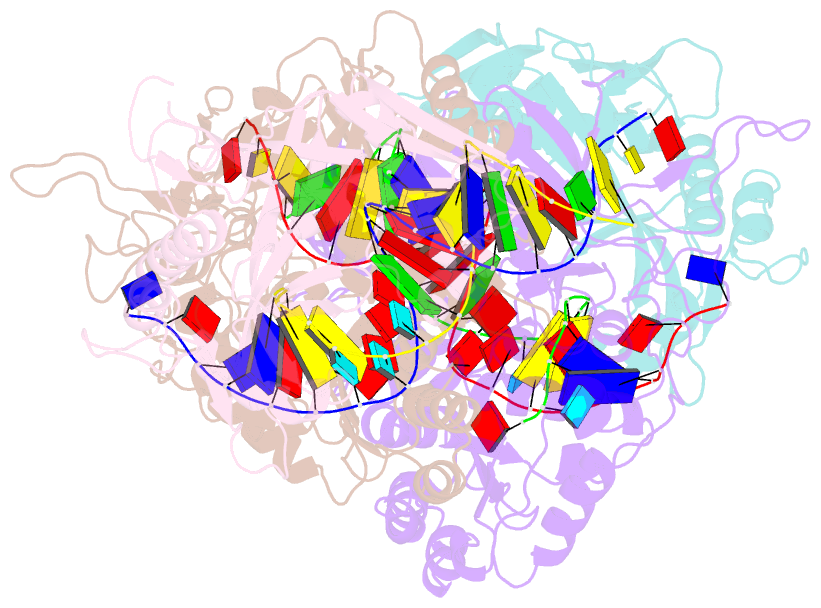
- Dimer structure of procaryotic ago
- Reference
- Sun D, Zhu K, Wang L, Mu Z, Wu K, Hua L, Qin B, Gao X, Wang Y, Cui S (2024): "Nucleic acid-induced NADase activation of a short Sir2-associated prokaryotic Argonaute system." Cell Rep, 43, 114391. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114391.
- Abstract
- Inhibition of nucleic acid targets is mediated by Argonaute (Ago) proteins guided by RNA or DNA. Although the mechanisms underpinning the functions of eukaryotic and "long" prokaryotic Ago proteins (pAgos) are well understood, those for short pAgos remain enigmatic. Here, we determine two cryoelectron microscopy structures of short pAgos in association with the NADase-domain-containing protein Sir2-APAZ from Geobacter sulfurreducens (GsSir2/Ago): the guide RNA-target DNA-loaded GsSir2/Ago quaternary complex (2.58 Å) and the dimer of the quaternary complex (2.93Å). These structures show that the nucleic acid binding causes profound conformational changes that result in disorder or partial dissociation of the Sir2 domain, suggesting that it adopts a NADase-active conformation. Subsequently, two RNA-/DNA-loaded GsSir2/Ago complexes form a dimer through their MID domains, further enhancing NADase activity through synergistic effects. The findings provide a structural basis for short-pAgo-mediated defense against invading nucleic acids.