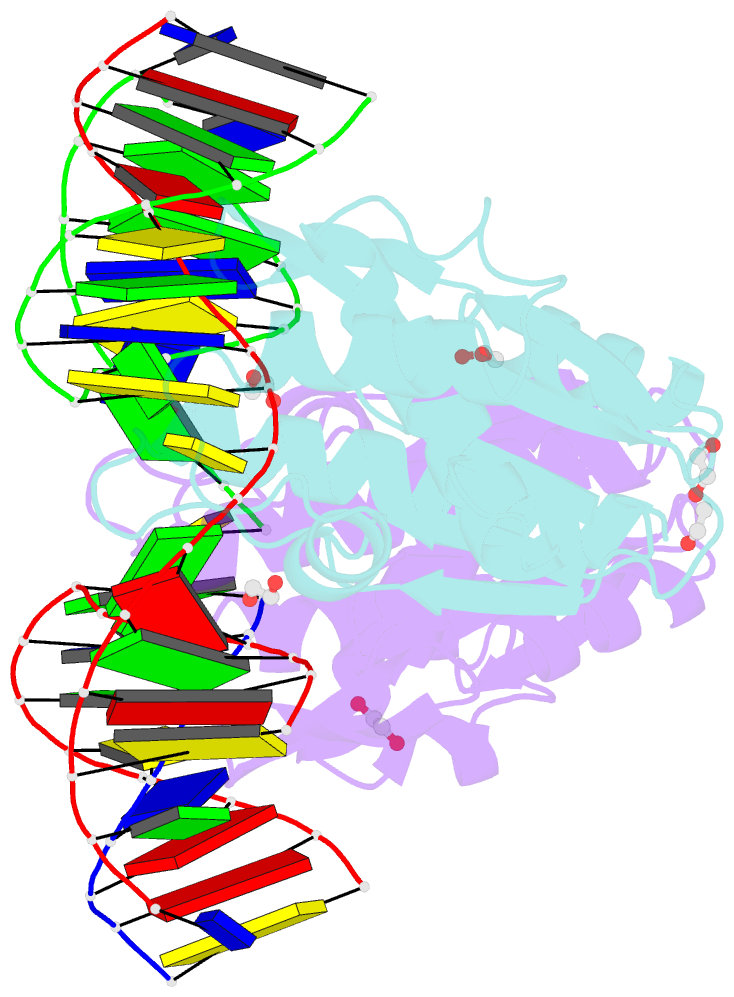
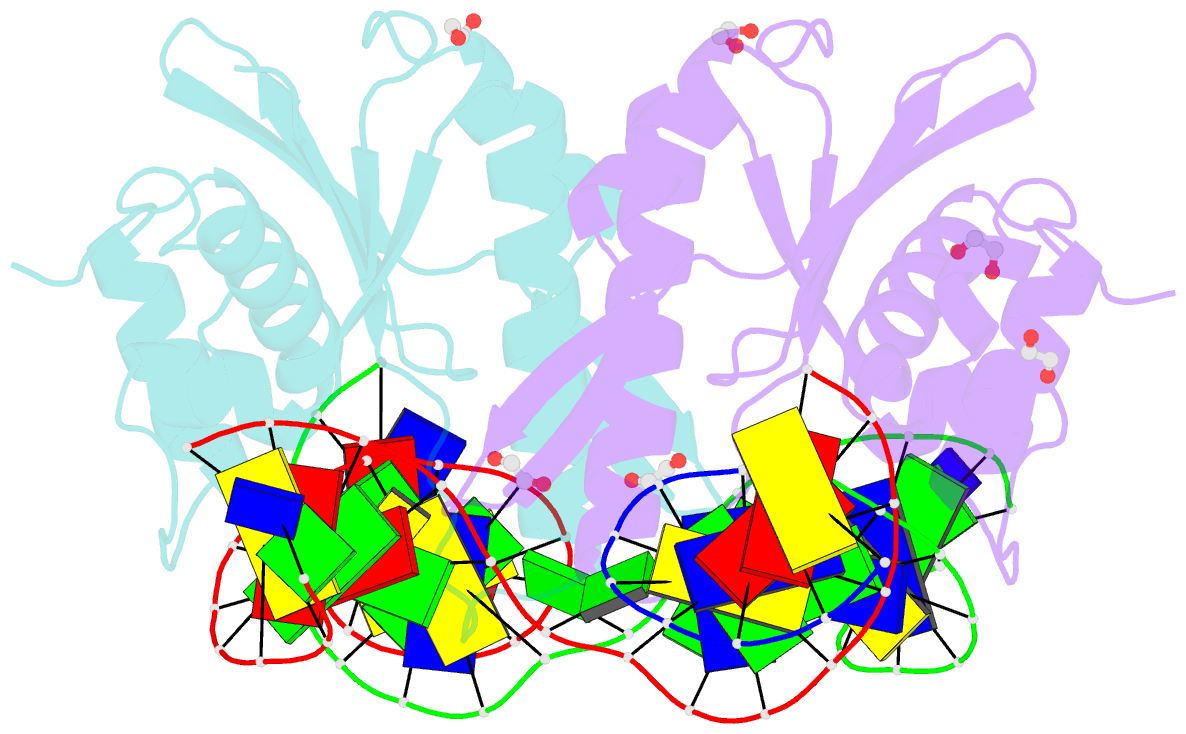
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8kfw; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.3 Å)
- Summary
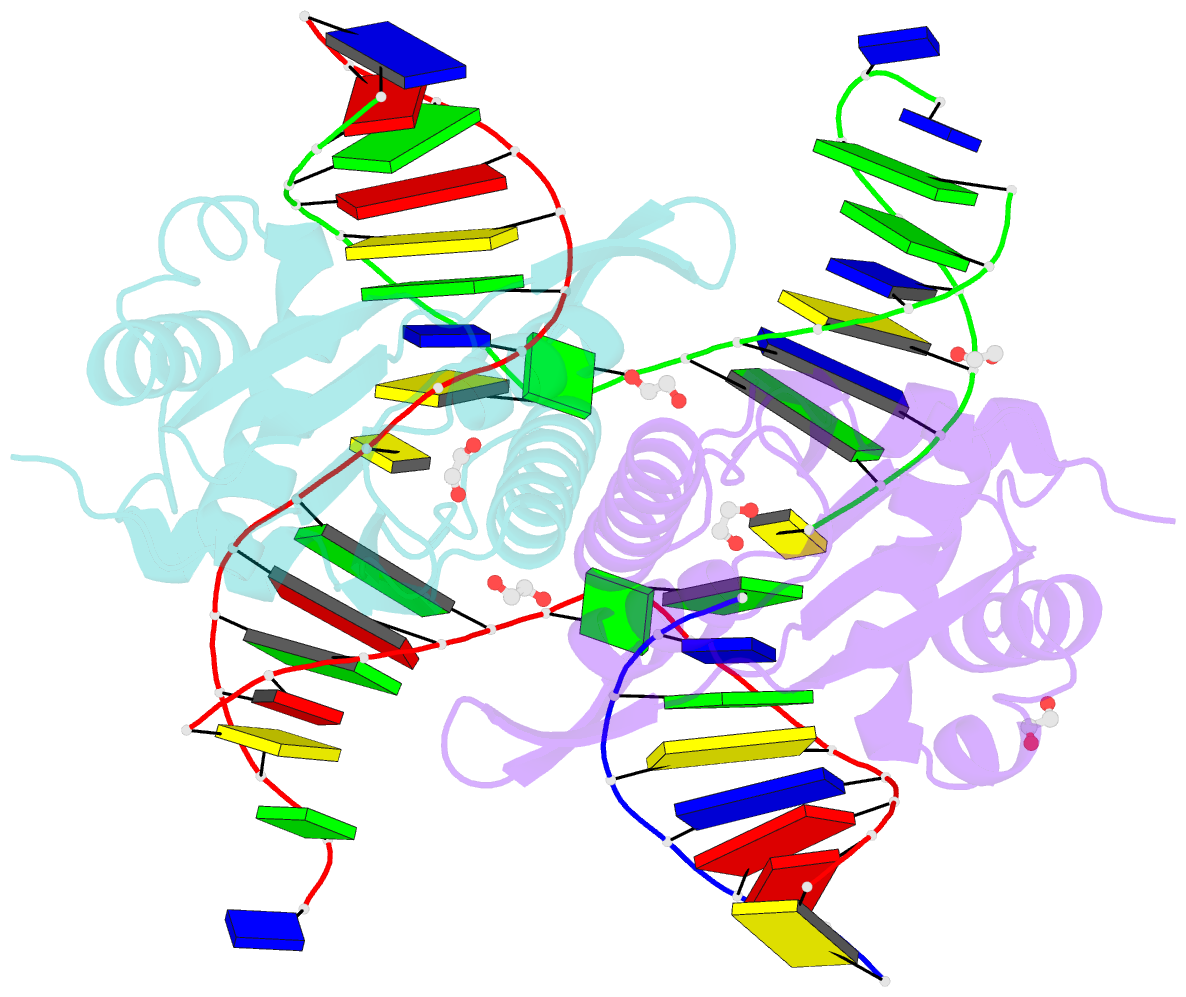
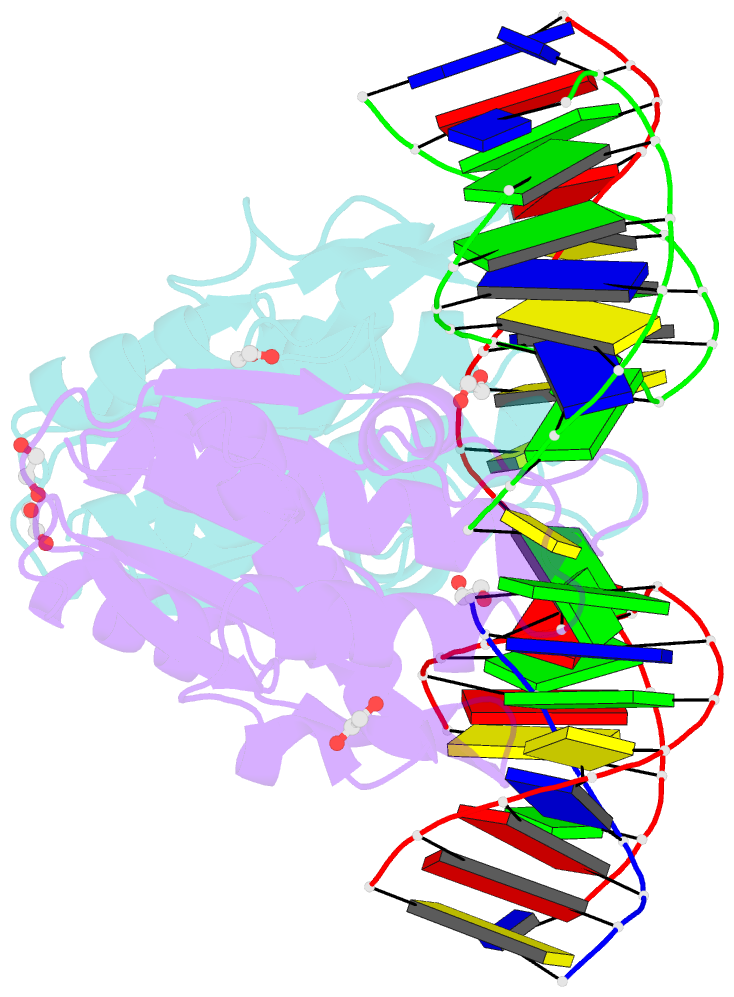
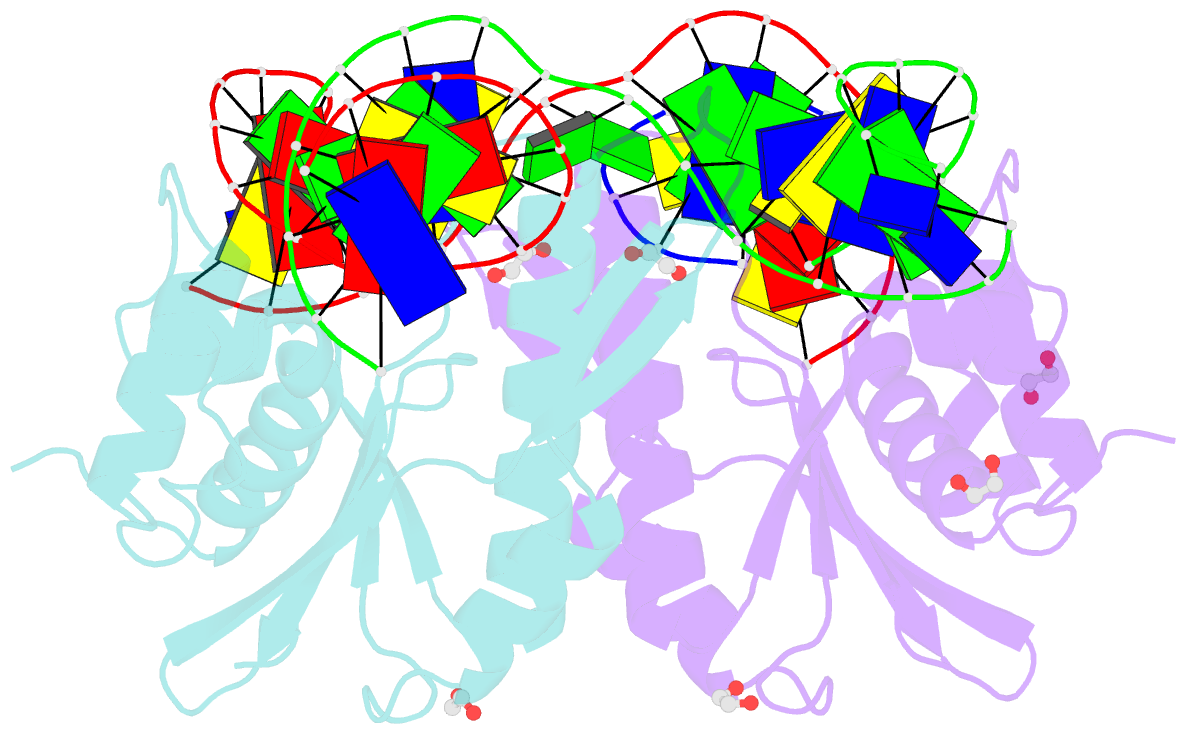
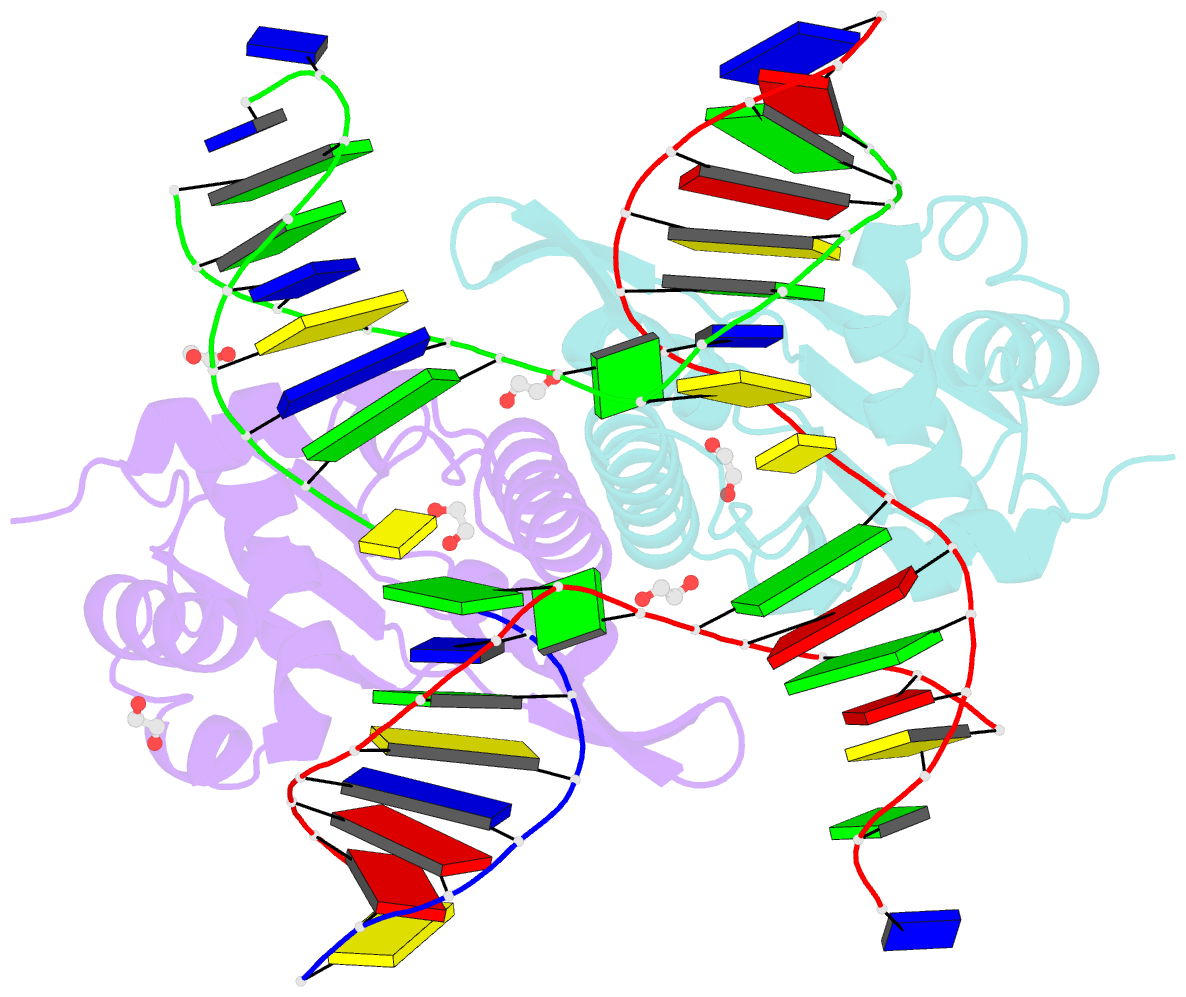
- Crystal structure of zmmoc1 k229a in complex with a nicked holliday junction soaked in mn2+ for 600 seconds
- Reference
- Zhang D, Xu S, Luo Z, Lin Z (2024): "MOC1 cleaves Holliday junctions through a cooperative nick and counter-nick mechanism mediated by metal ions." Nat Commun, 15, 5140. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49490-9.
- Abstract
- Holliday junction resolution is a crucial process in homologous recombination and DNA double-strand break repair. Complete Holliday junction resolution requires two stepwise incisions across the center of the junction, but the precise mechanism of metal ion-catalyzed Holliday junction cleavage remains elusive. Here, we perform a metal ion-triggered catalysis in crystals to investigate the mechanism of Holliday junction cleavage by MOC1. We capture the structures of MOC1 in complex with a nicked Holliday junction at various catalytic states, including the ground state, the one-metal ion binding state, and the two-metal ion binding state. Moreover, we also identify a third metal ion that may aid in the nucleophilic attack on the scissile phosphate. Further structural and biochemical analyses reveal a metal ion-mediated allosteric regulation between the two active sites, contributing to the enhancement of the second strand cleavage following the first strand cleavage, as well as the precise symmetric cleavage across the Holliday junction. Our work provides insights into the mechanism of metal ion-catalyzed Holliday junction resolution by MOC1, with implications for understanding how cells preserve genome integrity during the Holliday junction resolution phase.