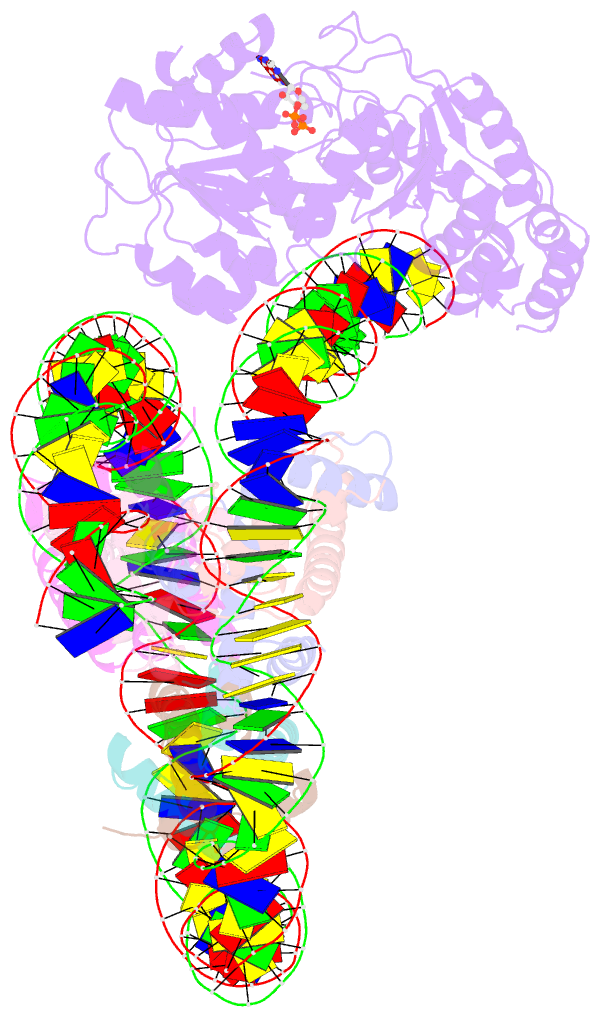
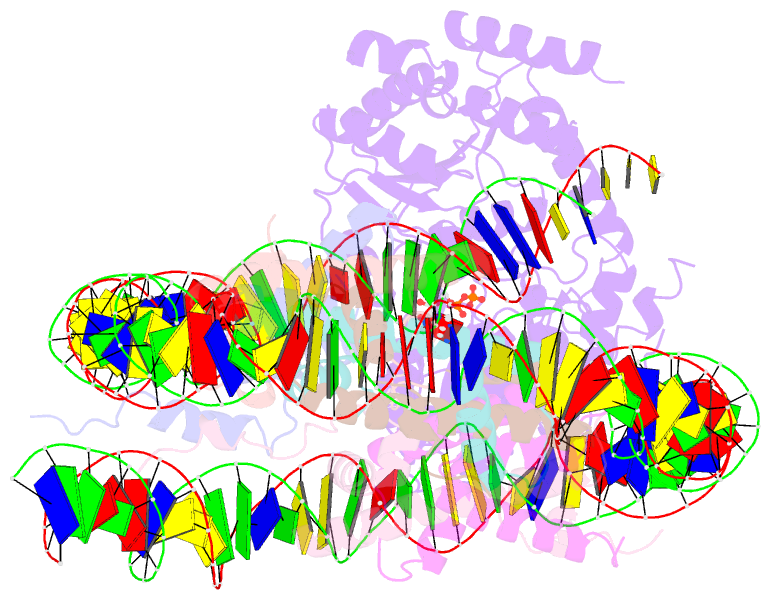
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8oos; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.29 Å)
- Summary
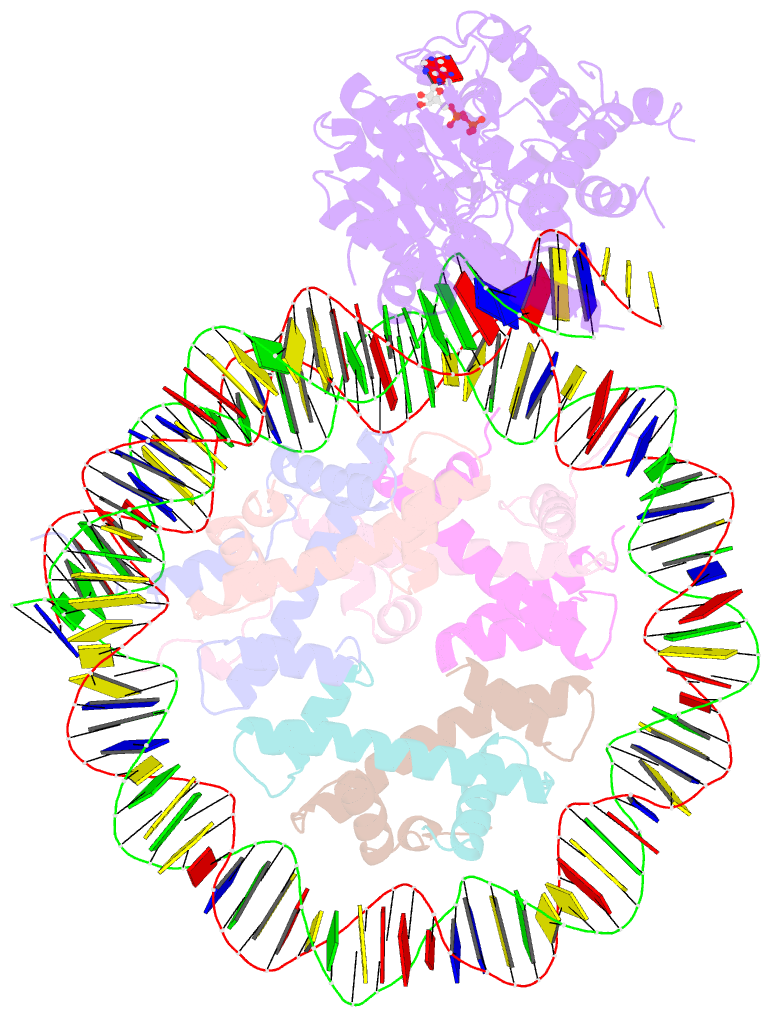
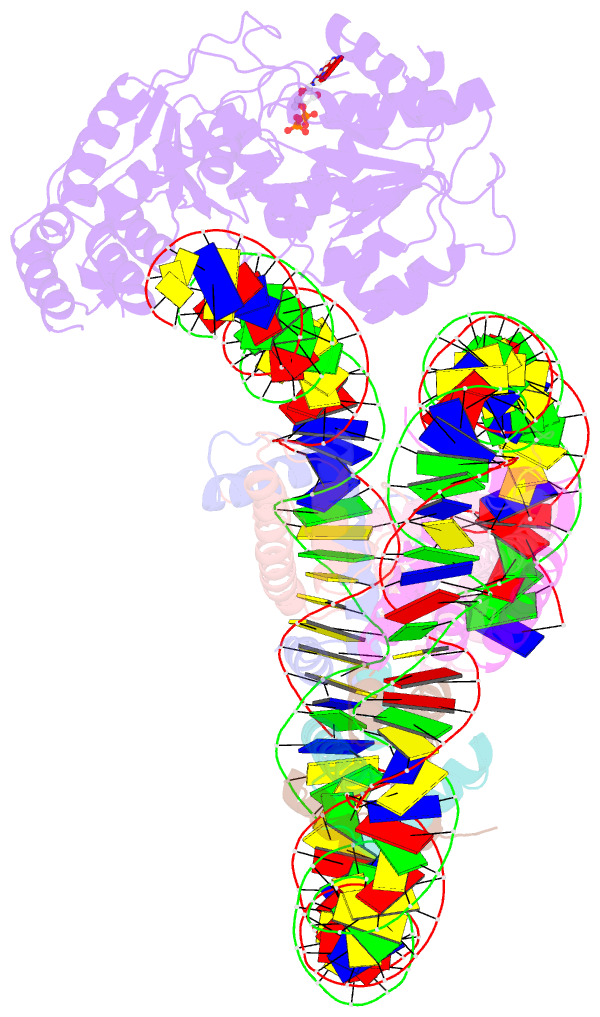
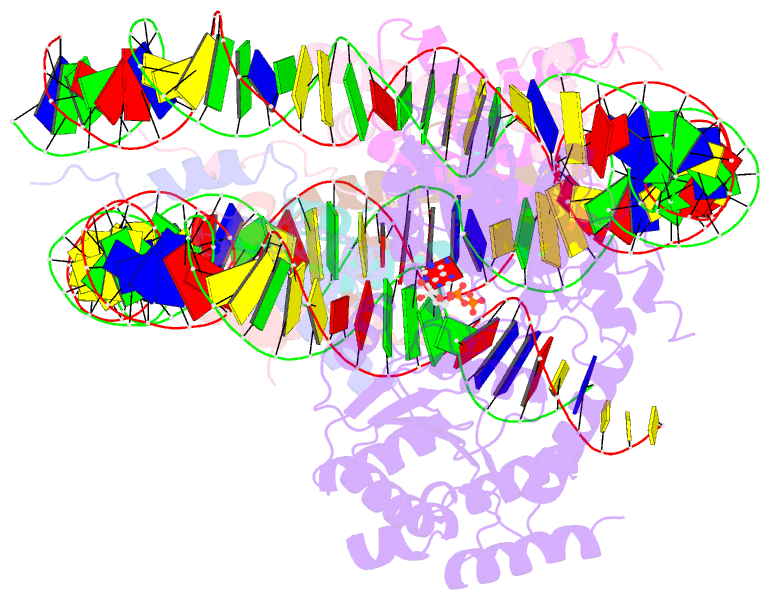
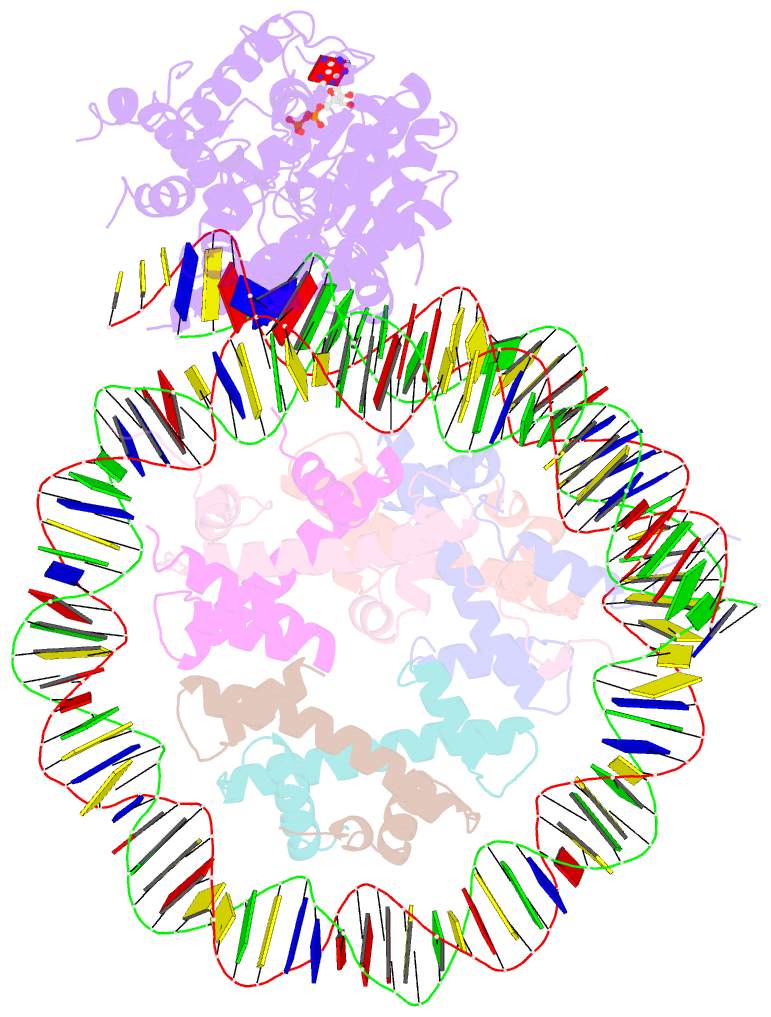
- Cryoem structure ino80core hexasome complex atpase-hexasome refinement state 2
- Reference
- Zhang M, Jungblut A, Kunert F, Hauptmann L, Hoffmann T, Kolesnikova O, Metzner F, Moldt M, Weis F, DiMaio F, Hopfner KP, Eustermann S (2023): "Hexasome-INO80 complex reveals structural basis of noncanonical nucleosome remodeling." Science, 381, 313-319. doi: 10.1126/science.adf6287.
- Abstract
- Loss of H2A-H2B histone dimers is a hallmark of actively transcribed genes, but how the cellular machinery functions in the context of non-canonical nucleosomal particles remains largely elusive. Here, we report the structural mechanism for ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling of hexasomes by the INO80 complex. We show how INO80 recognizes non-canonical DNA and histone features of hexasomes emerging from the loss of H2A-H2B. A large structural re-arrangement switches the catalytic core of INO80 into a distinct, spin-rotated mode of remodeling, while its nuclear actin module remains tethered to long stretches of unwrapped linker DNA. Direct sensing of an exposed H3-H4 histone interface activates INO80, independently of the H2A-H2B acidic patch. Our findings reveal how the loss of H2A-H2B grants remodelers access to a different, yet unexplored, layer of energy-driven chromatin regulation.