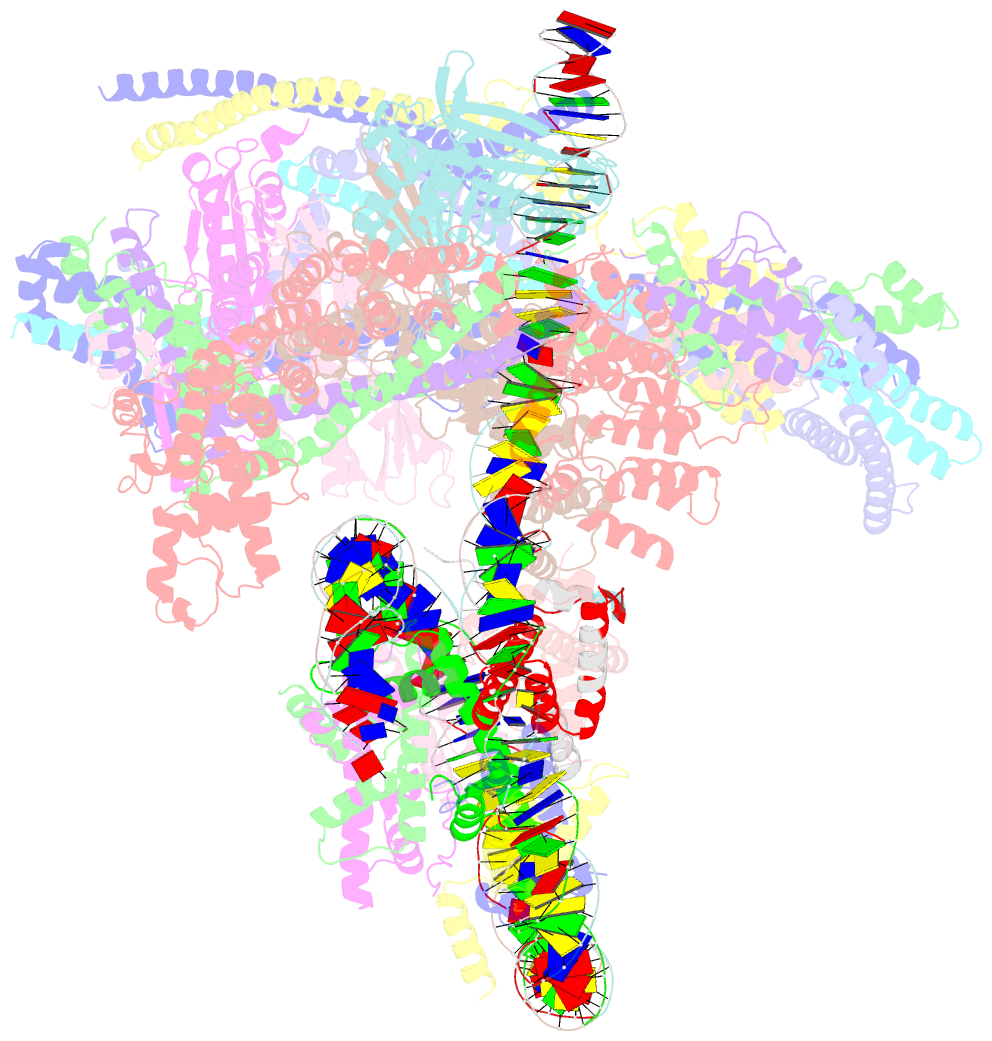
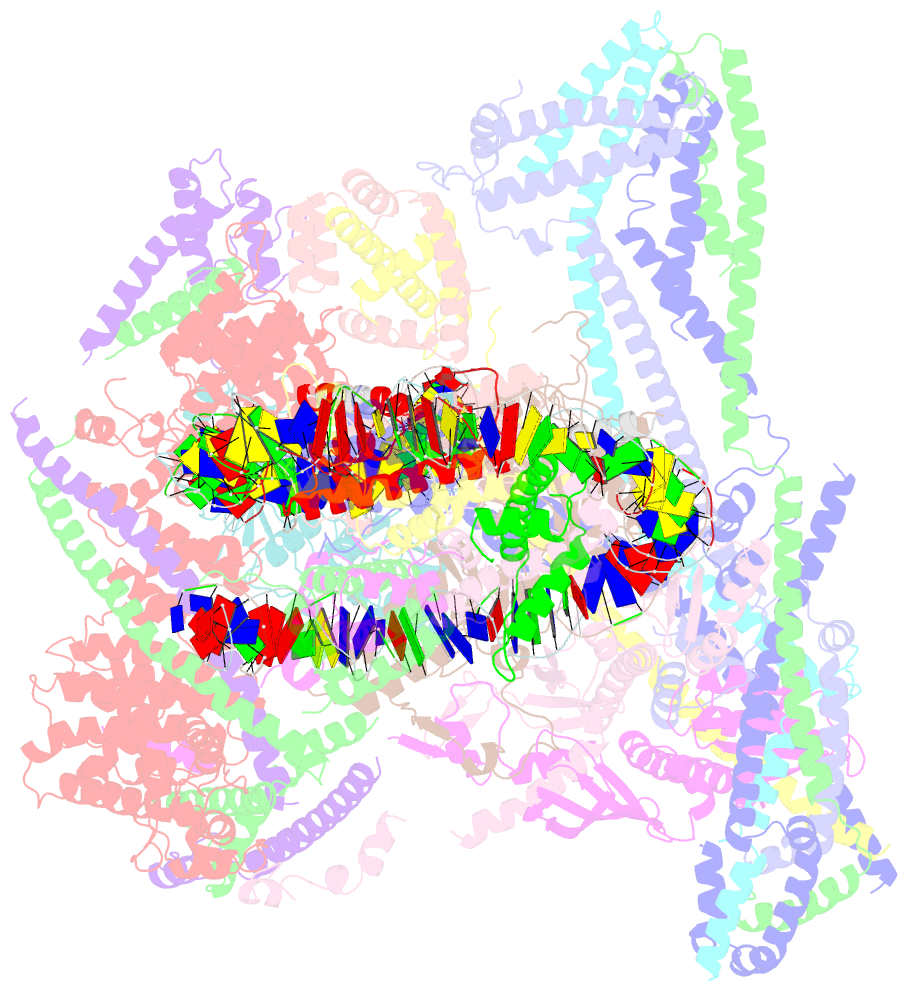
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8ow0; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- cell cycle
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.4 Å)
- Summary
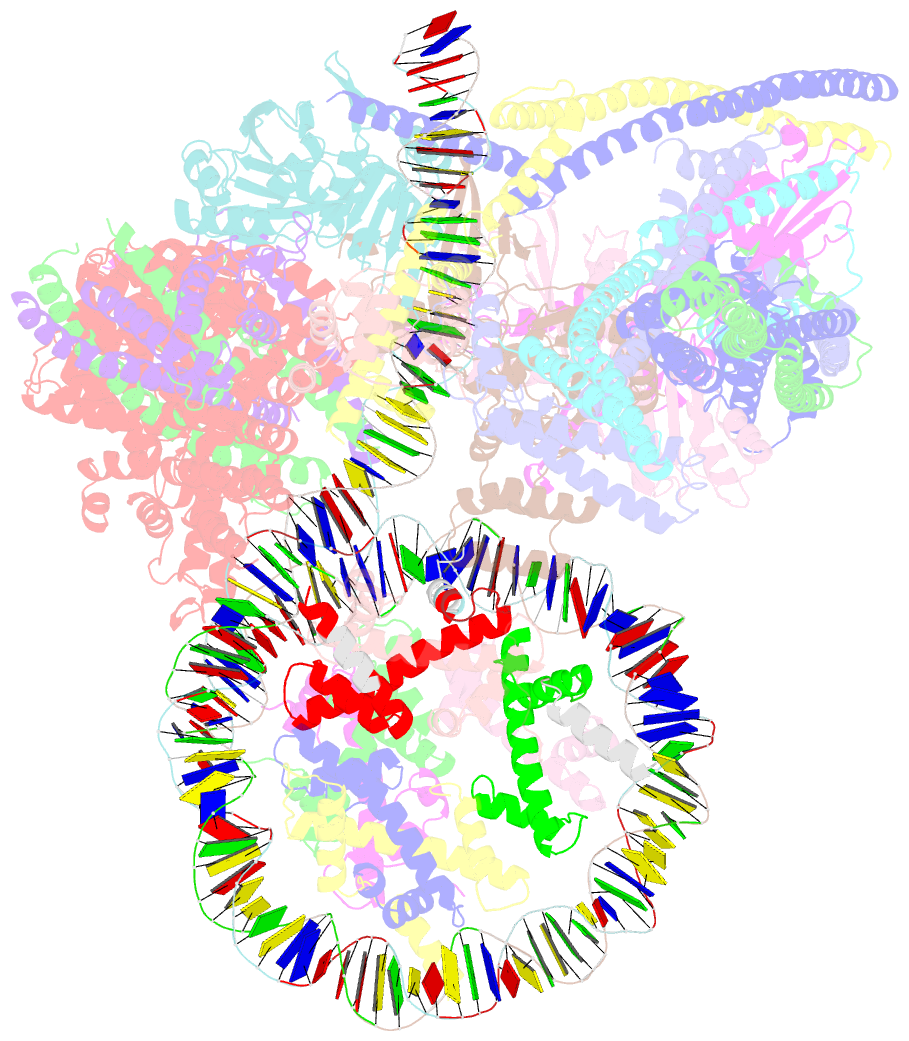
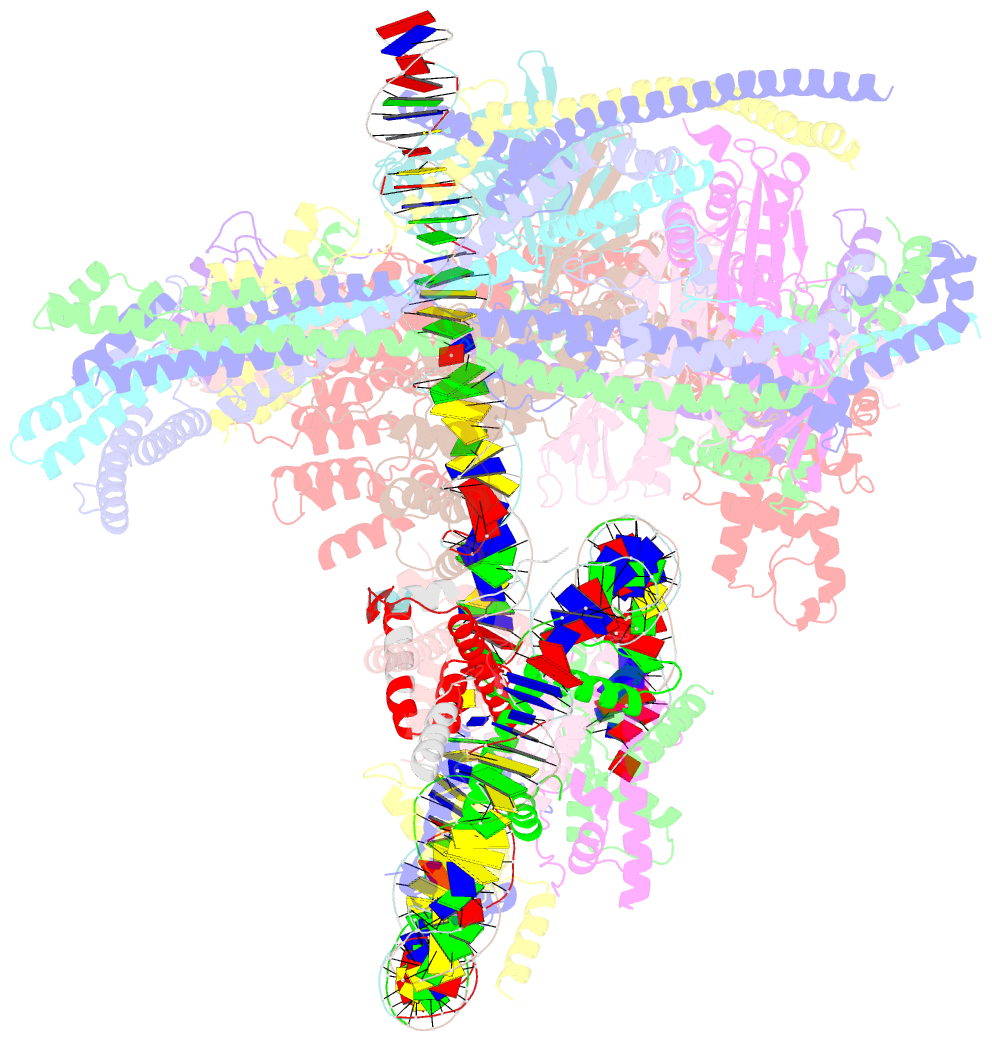
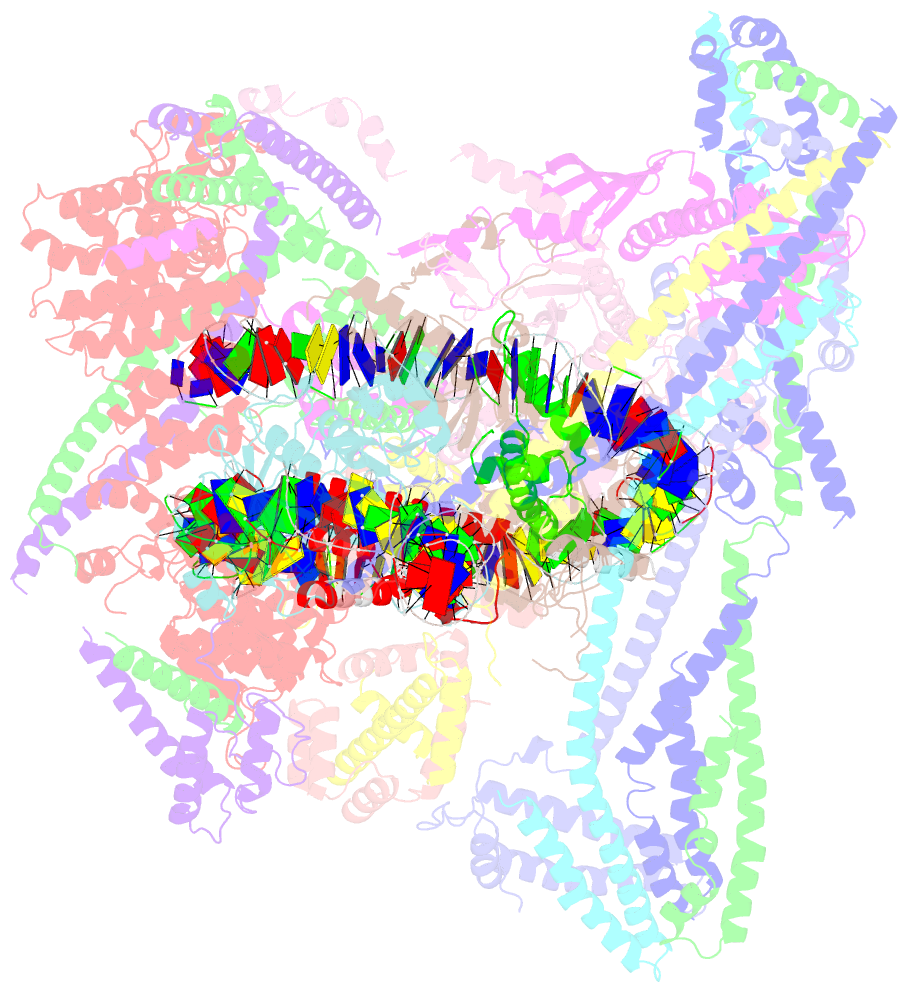
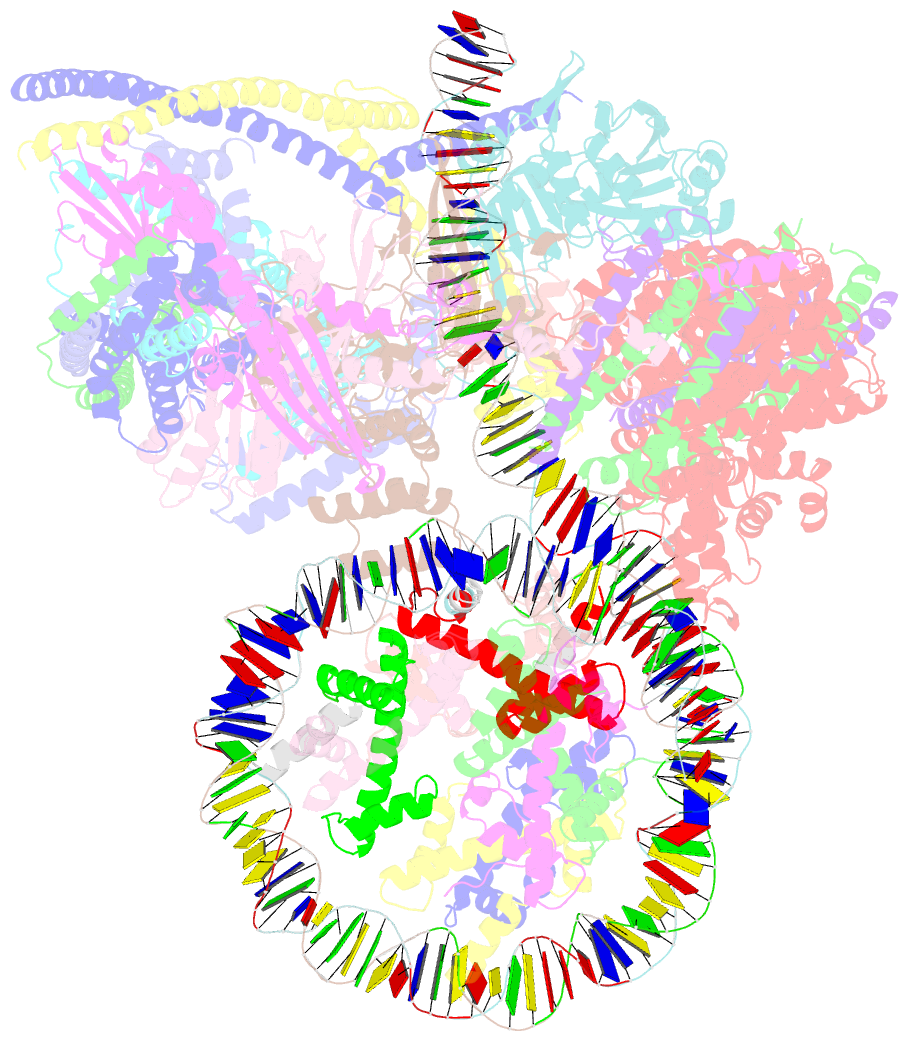
- cryo-EM structure of cbf1-ccan bound topologically to a centromeric cenp-a nucleosome
- Reference
- Dendooven T, Zhang Z, Yang J, McLaughlin SH, Schwab J, Scheres SHW, Yatskevich S, Barford D (2023): "Cryo-EM structure of the complete inner kinetochore of the budding yeast point centromere." Sci Adv, 9, eadg7480. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg7480.
- Abstract
- The point centromere of budding yeast specifies assembly of the large kinetochore complex to mediate chromatid segregation. Kinetochores comprise the centromere-associated inner kinetochore (CCAN) complex and the microtubule-binding outer kinetochore KNL1-MIS12-NDC80 (KMN) network. The budding yeast inner kinetochore also contains the DNA binding centromere-binding factor 1 (CBF1) and CBF3 complexes. We determined the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the yeast inner kinetochore assembled onto the centromere-specific centromere protein A nucleosomes (CENP-ANuc). This revealed a central CENP-ANuc with extensively unwrapped DNA ends. These free DNA duplexes bind two CCAN protomers, one of which entraps DNA topologically, positioned on the centromere DNA element I (CDEI) motif by CBF1. The two CCAN protomers are linked through CBF3 forming an arch-like configuration. With a structural mechanism for how CENP-ANuc can also be linked to KMN involving only CENP-QU, we present a model for inner kinetochore assembly onto a point centromere and how it organizes the outer kinetochore for chromosome attachment to the mitotic spindle.