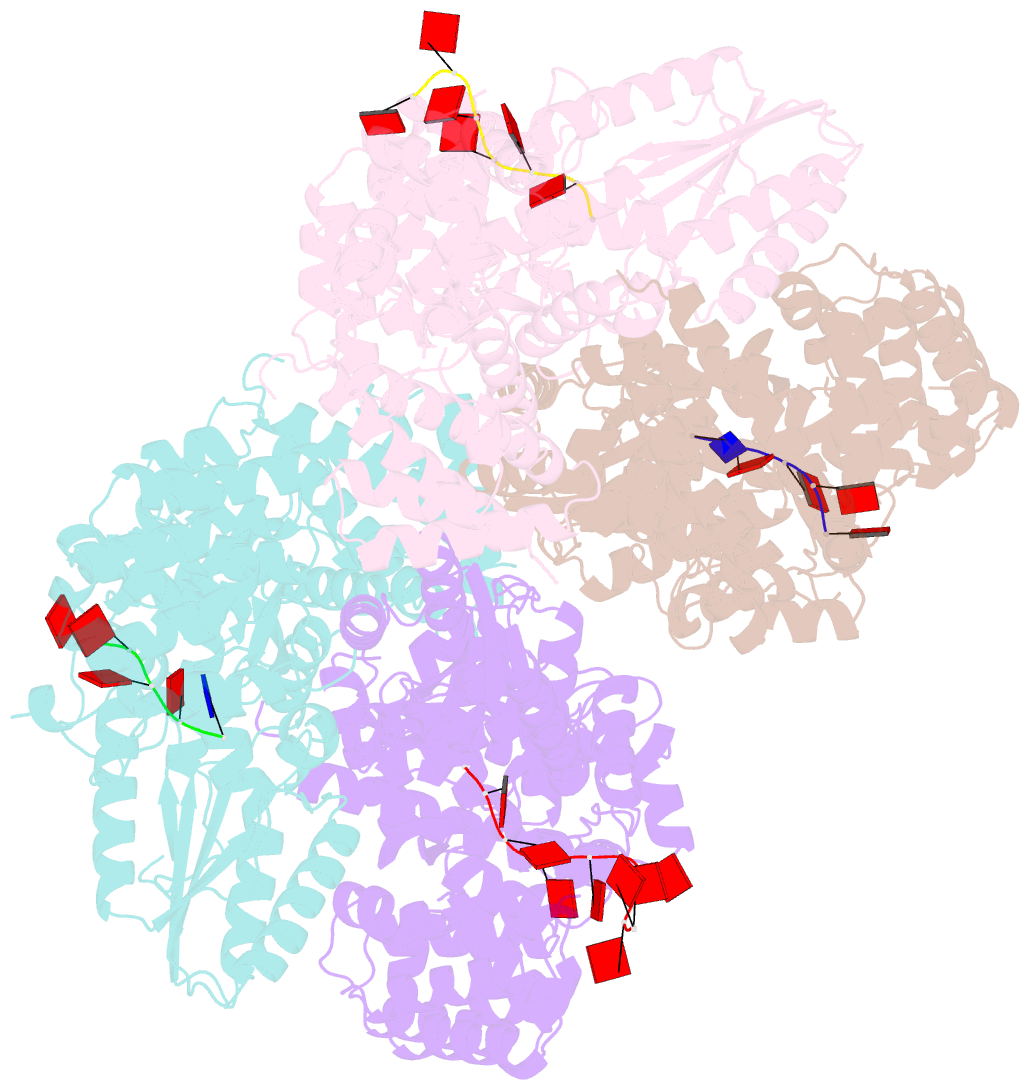
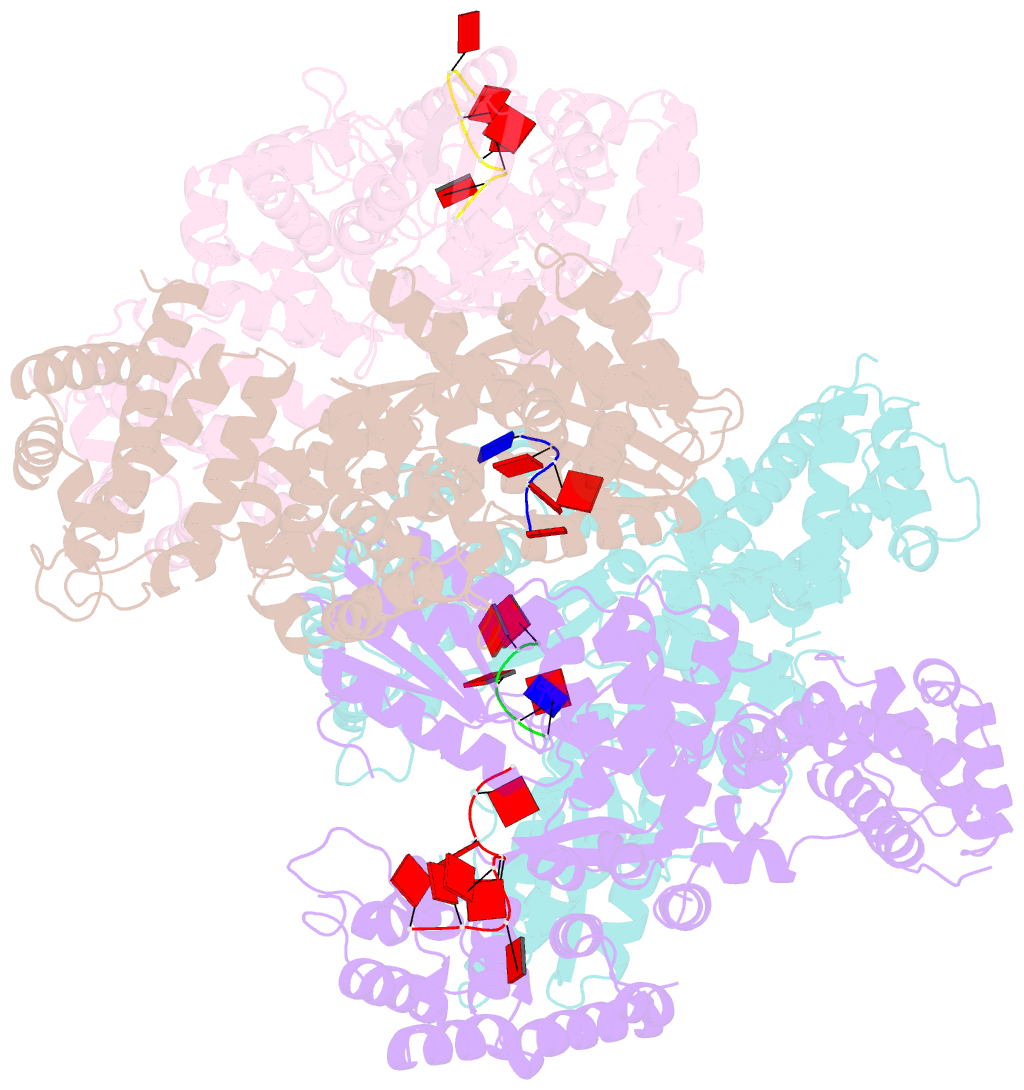
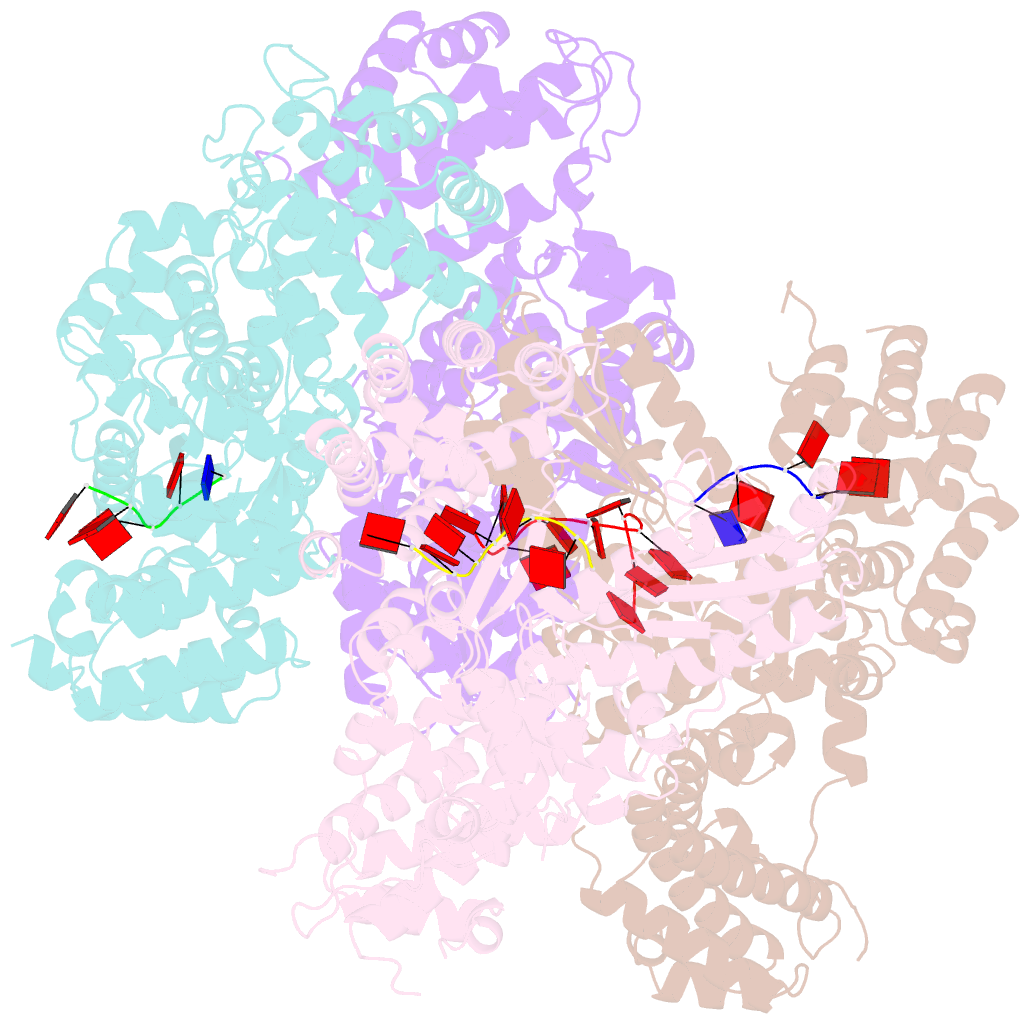
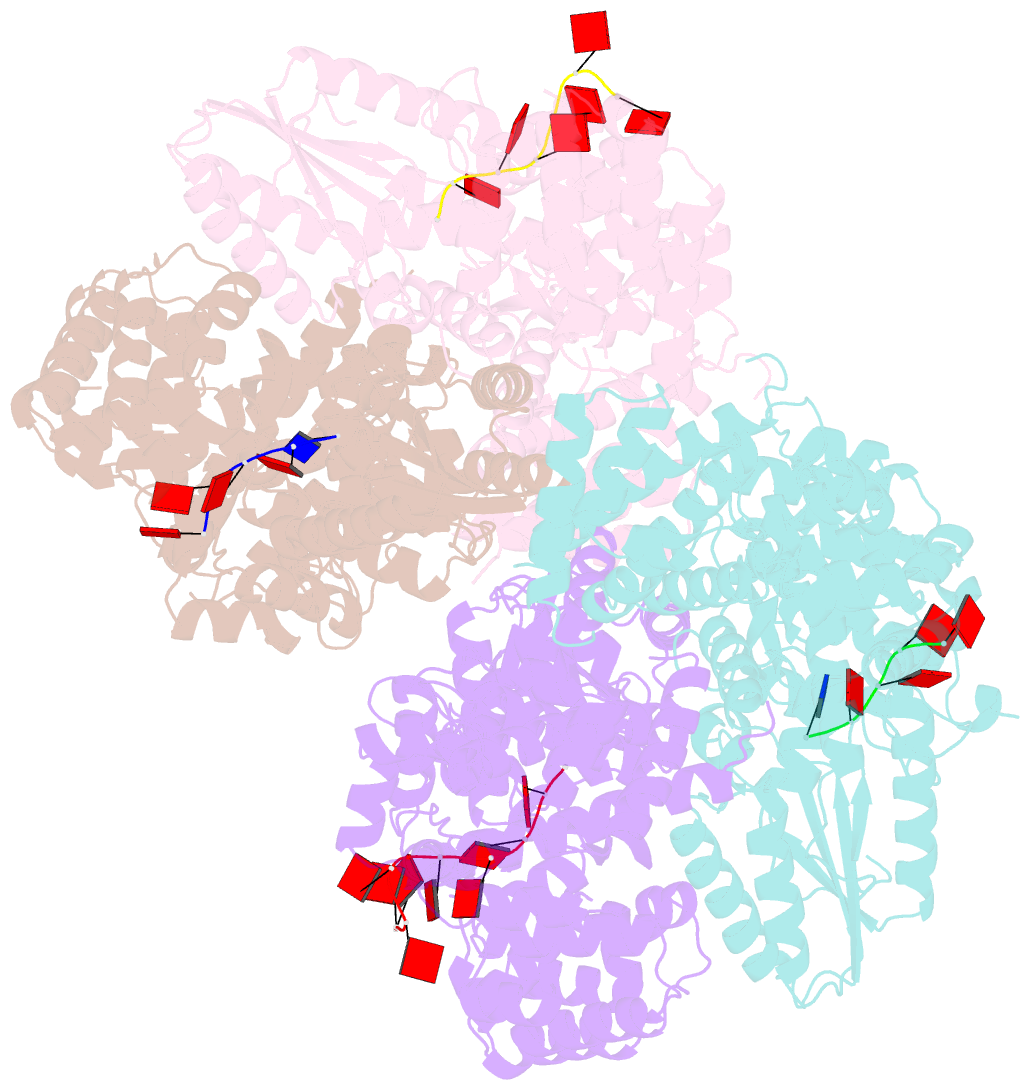
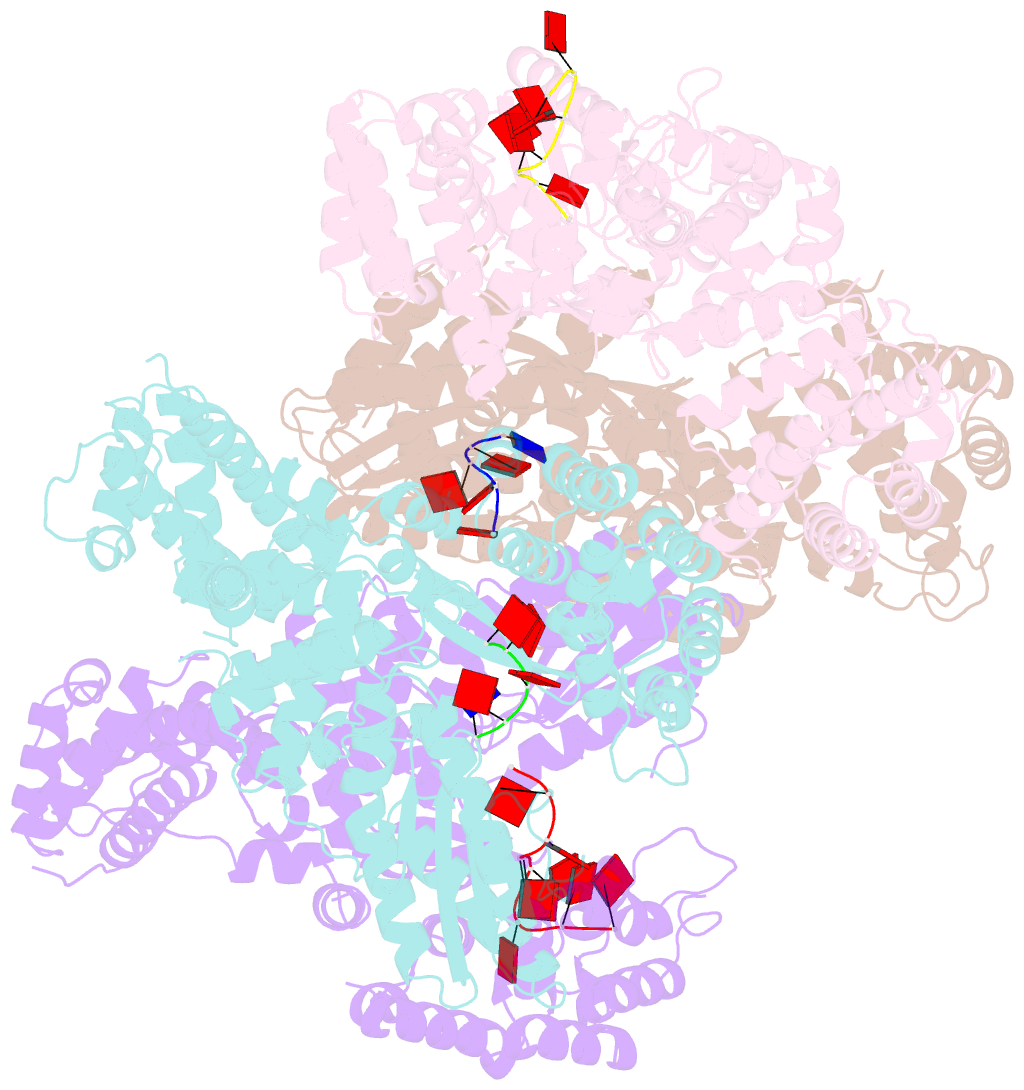
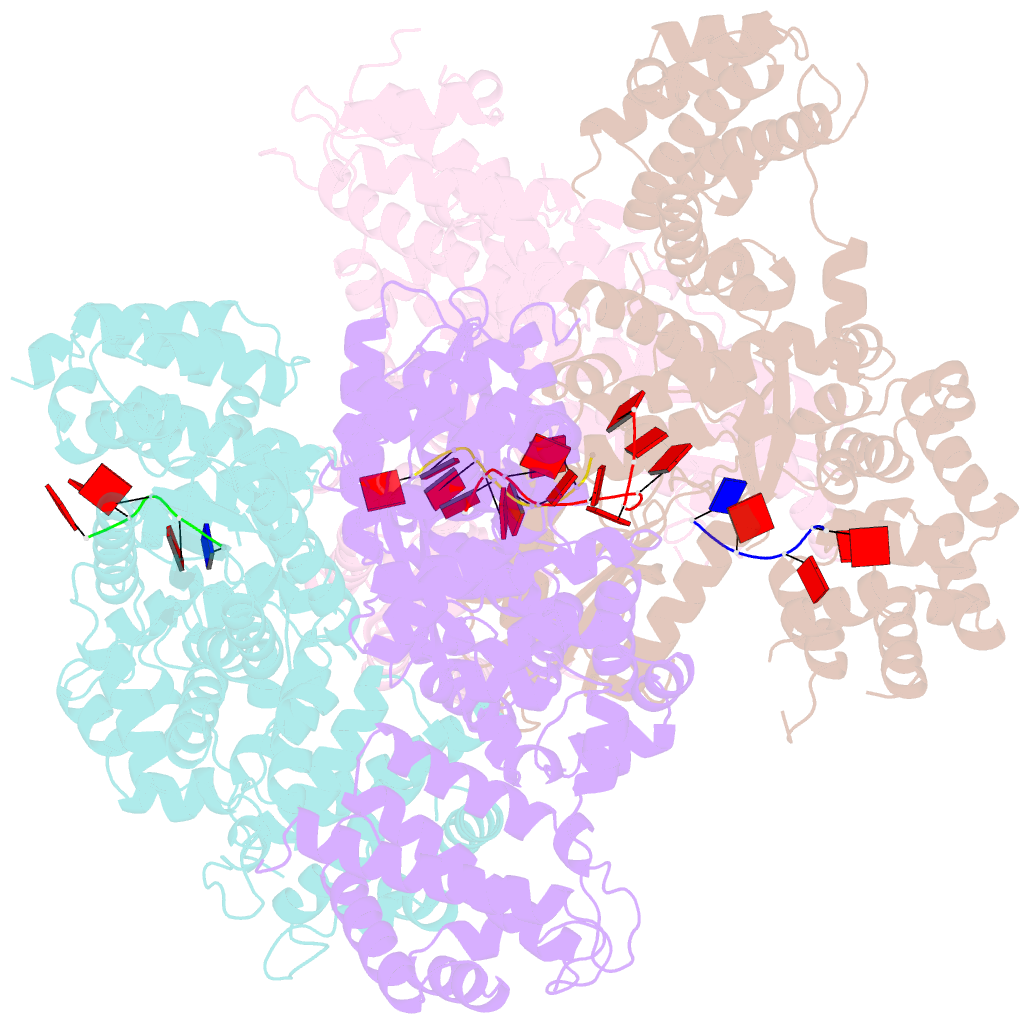
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8oz7; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- antiviral protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.75 Å)
- Summary
- Abortive infection DNA polymerase abia from lactococcus lactis
- Reference
- Gapinska M, Zajko W, Skowronek K, Figiel M, Krawczyk PS, Egorov AA, Dziembowski A, Johansson MJO, Nowotny M (2024): "Structure-functional characterization of Lactococcus AbiA phage defense system." Nucleic Acids Res., 52, 4723-4738. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae230.
- Abstract
- Bacterial reverse transcriptases (RTs) are a large and diverse enzyme family. AbiA, AbiK and Abi-P2 are abortive infection system (Abi) RTs that mediate defense against bacteriophages. What sets Abi RTs apart from other RT enzymes is their ability to synthesize long DNA products of random sequences in a template- and primer-independent manner. Structures of AbiK and Abi-P2 representatives have recently been determined, but there are no structural data available for AbiA. Here, we report the crystal structure of Lactococcus AbiA polymerase in complex with a single-stranded polymerization product. AbiA comprises three domains: an RT-like domain, a helical domain that is typical for Abi polymerases, and a higher eukaryotes and prokaryotes nucleotide-binding (HEPN) domain that is common for many antiviral proteins. AbiA forms a dimer that distinguishes it from AbiK and Abi-P2, which form trimers/hexamers. We show the DNA polymerase activity of AbiA in an in vitro assay and demonstrate that it requires the presence of the HEPN domain which is enzymatically inactive. We validate our biochemical and structural results in vivo through bacteriophage infection assays. Finally, our in vivo results suggest that AbiA-mediated phage defense may not rely on AbiA-mediated cell death.