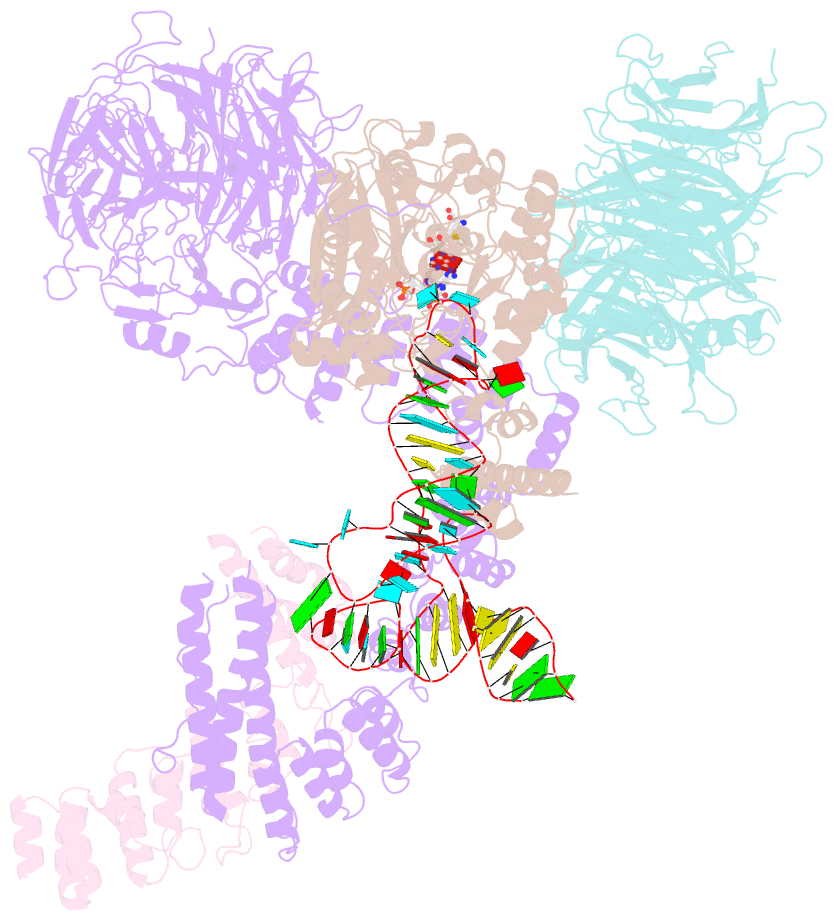
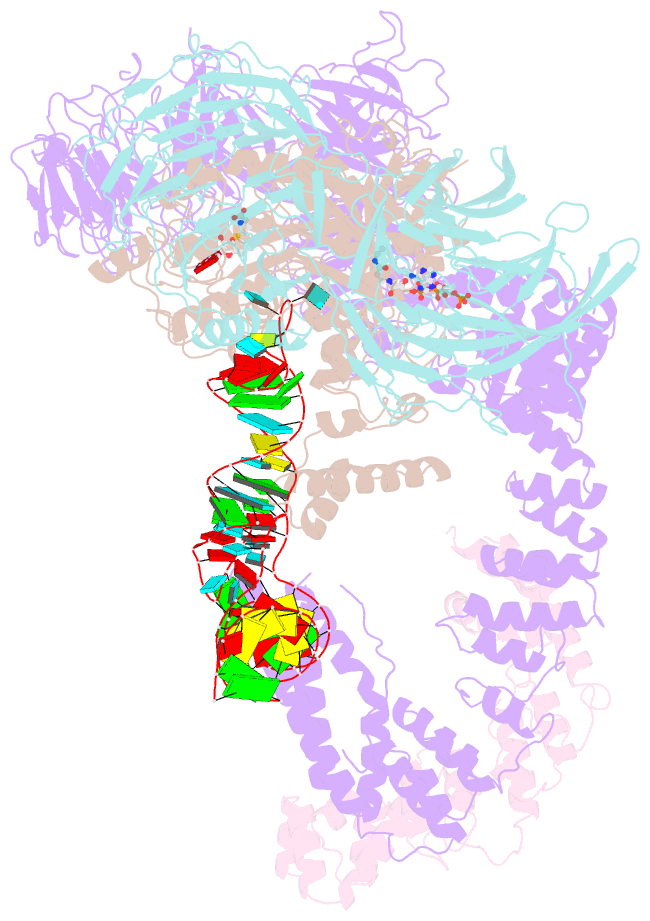
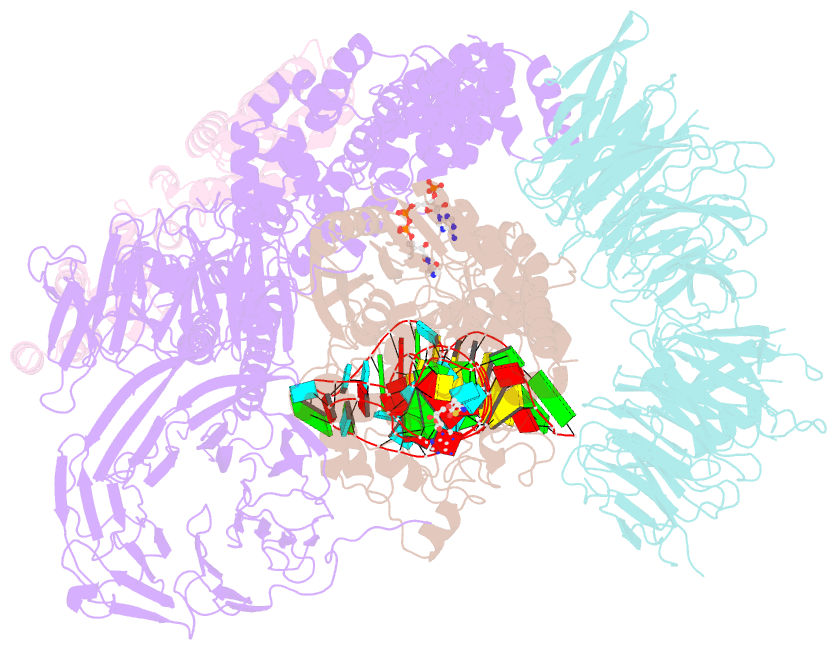
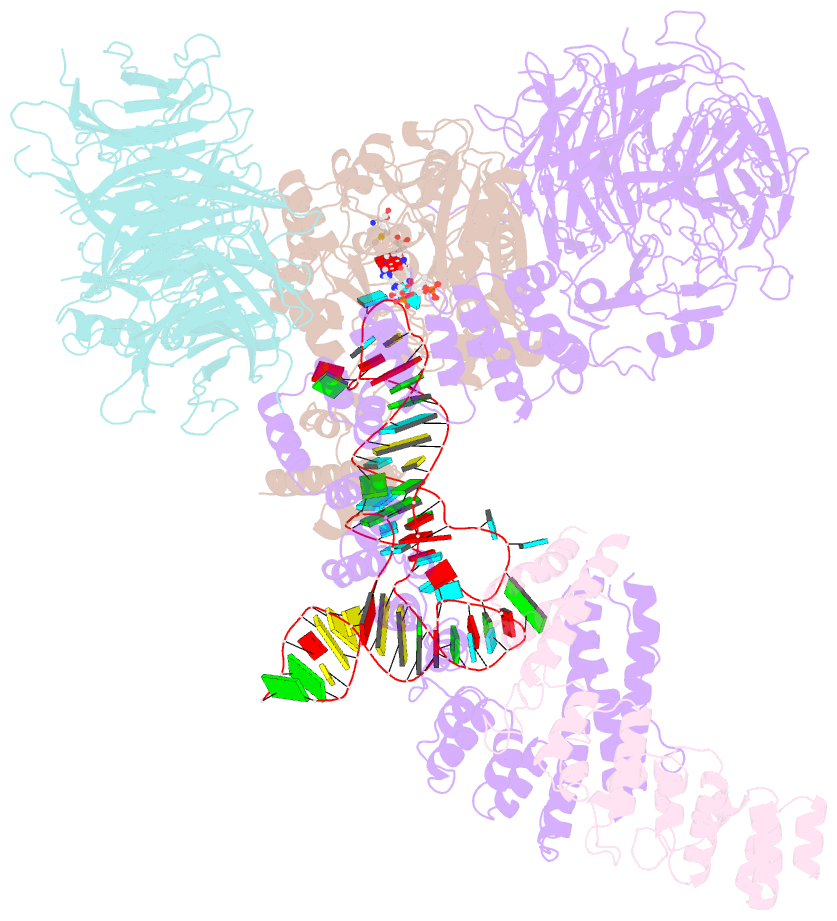
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8pu0; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- translation
- Method
- cryo-EM (4.25 Å)
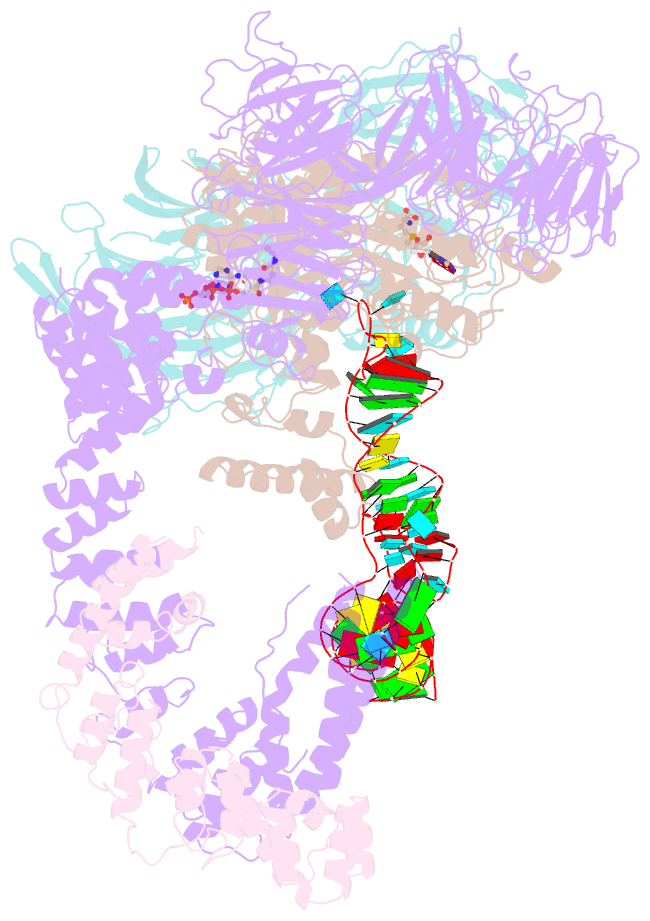
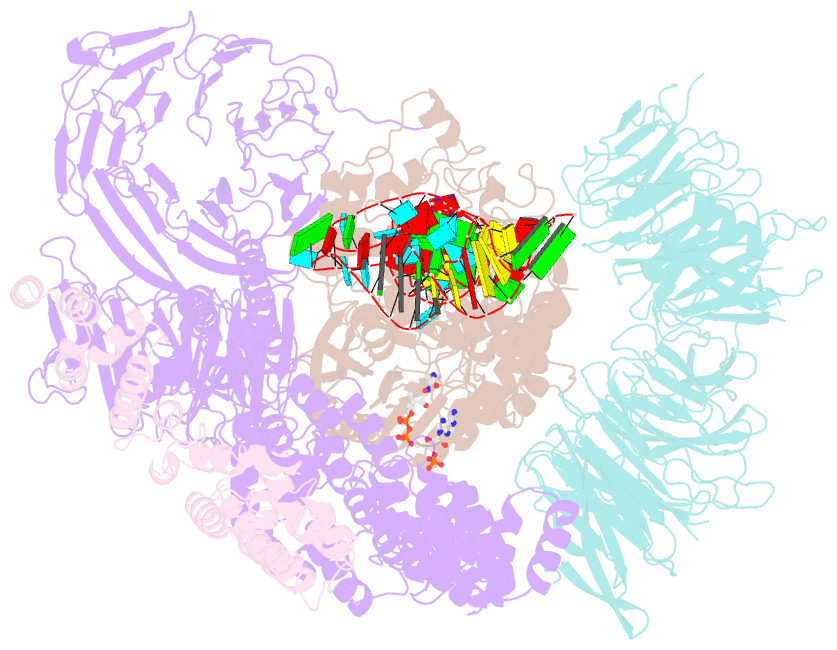
- Summary
- cryo-EM structure of human elp123 in complex with trna, desulpho-coa, 5'-deoxyadenosine and methionine
- Reference
- Abbassi NE, Jaciuk M, Scherf D, Bohnert P, Rau A, Hammermeister A, Rawski M, Indyka P, Wazny G, Chramiec-Glabik A, Dobosz D, Skupien-Rabian B, Jankowska U, Rappsilber J, Schaffrath R, Lin TY, Glatt S (2024): "Cryo-EM structures of the human Elongator complex at work." Nat Commun, 15, 4094. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48251-y.
- Abstract
- tRNA modifications affect ribosomal elongation speed and co-translational folding dynamics. The Elongator complex is responsible for introducing 5-carboxymethyl at wobble uridine bases (cm5U34) in eukaryotic tRNAs. However, the structure and function of human Elongator remain poorly understood. In this study, we present a series of cryo-EM structures of human ELP123 in complex with tRNA and cofactors at four different stages of the reaction. The structures at resolutions of up to 2.9 Å together with complementary functional analyses reveal the molecular mechanism of the modification reaction. Our results show that tRNA binding exposes a universally conserved uridine at position 33 (U33), which triggers acetyl-CoA hydrolysis. We identify a series of conserved residues that are crucial for the radical-based acetylation of U34 and profile the molecular effects of patient-derived mutations. Together, we provide the high-resolution view of human Elongator and reveal its detailed mechanism of action.