Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8que; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.3 Å)
- Summary
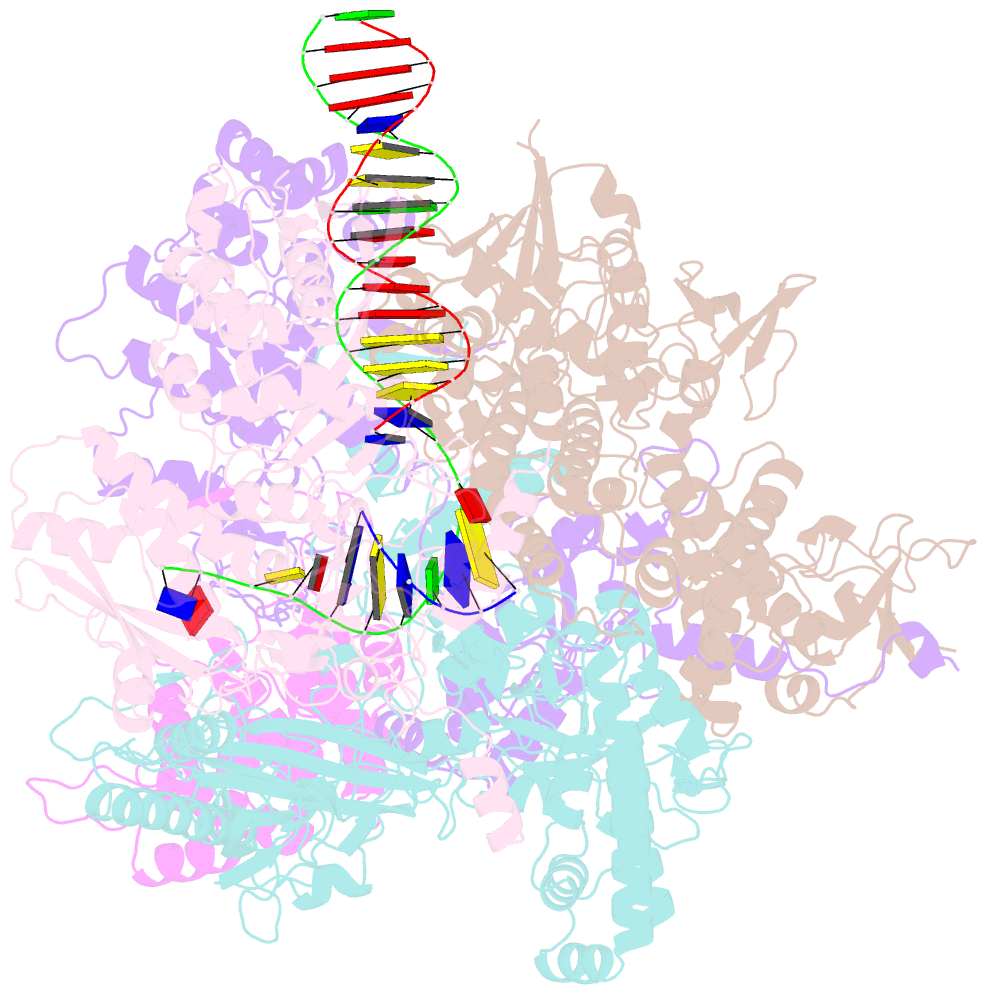
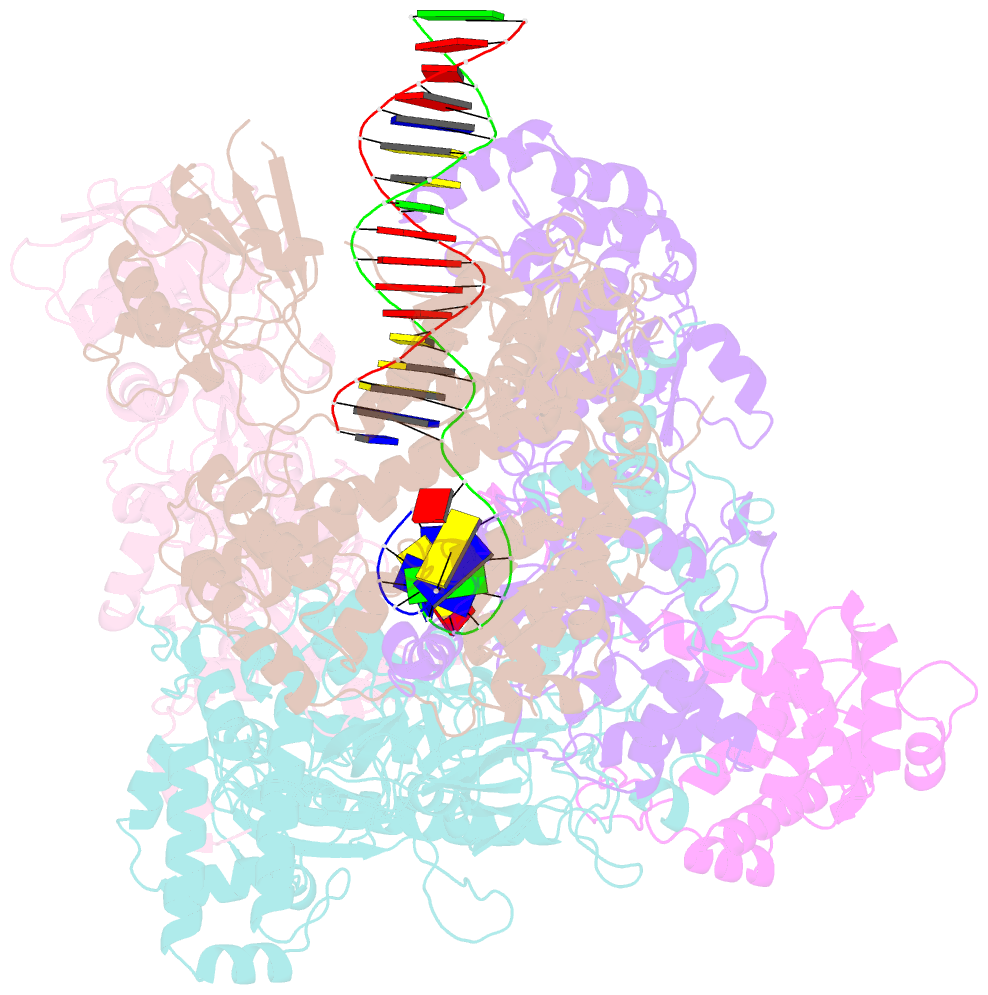
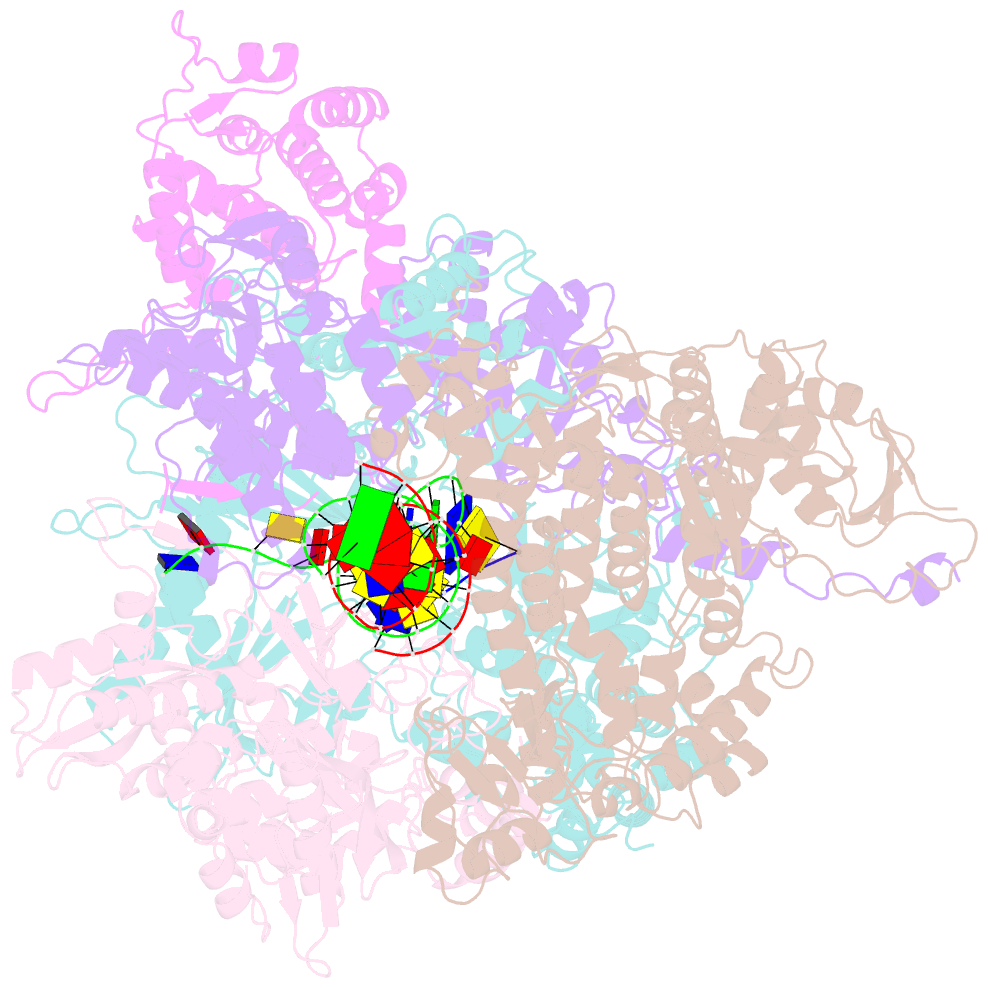
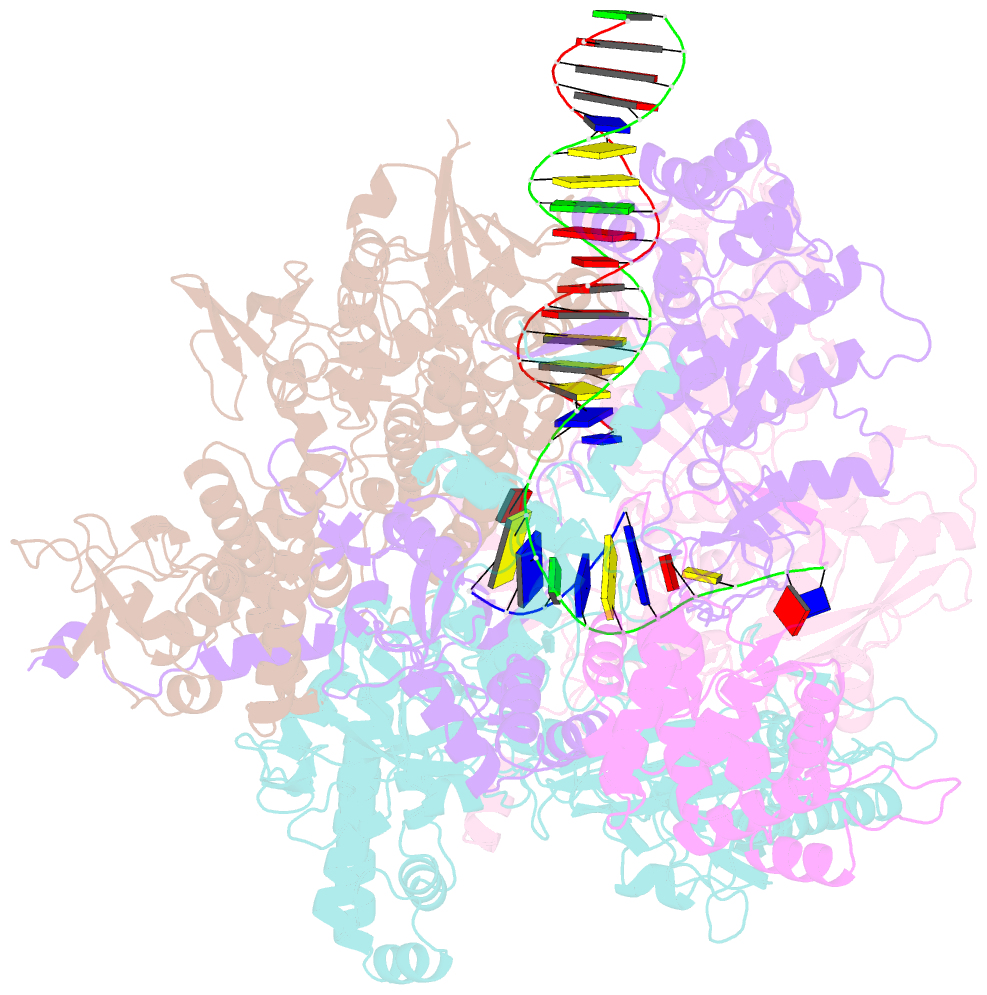
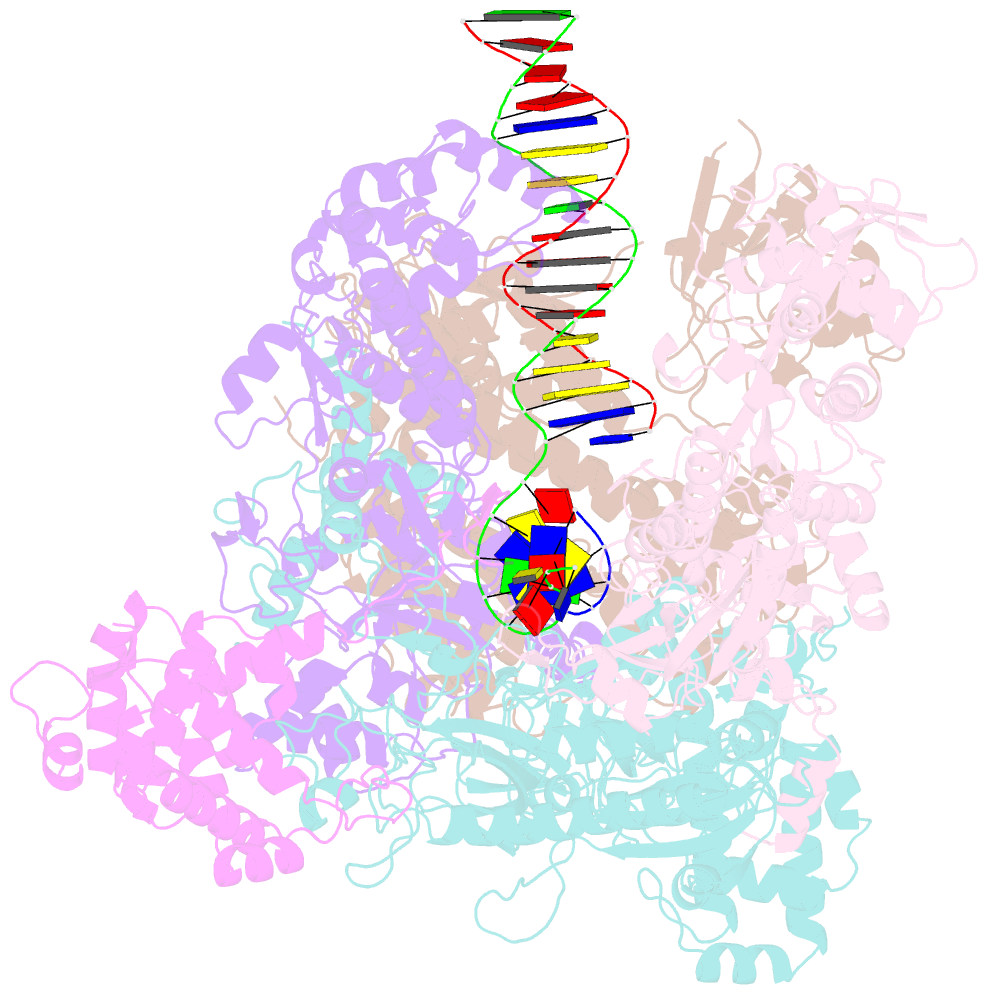
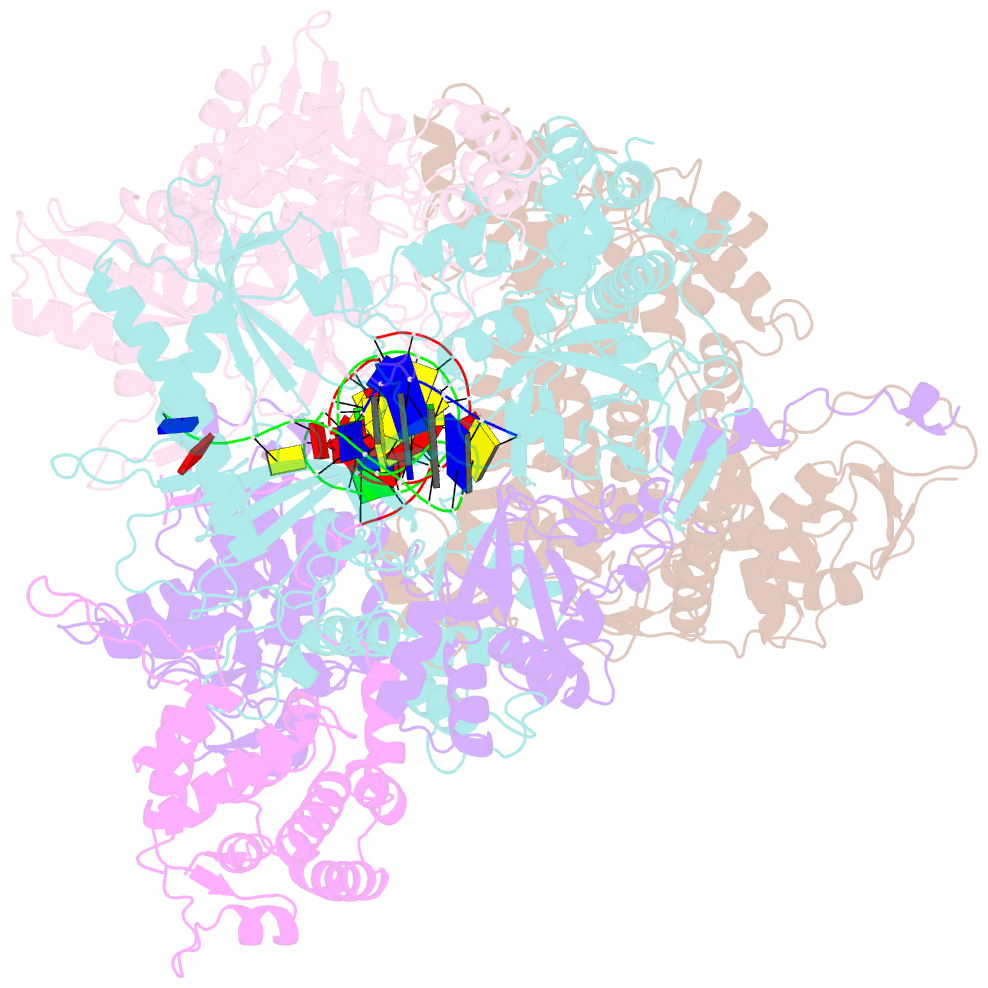
- Structure of the bacteriophage phikz non-virion RNA polymerase bound to DNA and RNA
- Reference
- de Martin Garrido N, Chen CS, Ramlaul K, Aylett CHS, Yakunina M (2024): "Structure of the Bacteriophage PhiKZ Non-virion RNA Polymerase Transcribing from its Promoter p119L." J.Mol.Biol., 436, 168713. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168713.
- Abstract
- Bacteriophage ΦKZ (phiKZ) is the founding member of a family of giant bacterial viruses. It has potential as a therapeutic as its host, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, kills tens of thousands of people worldwide each year. ΦKZ infection is independent of the host transcriptional apparatus; the virus forms a "nucleus", producing a proteinaceous barrier around the ΦKZ genome that excludes the host immune systems. It expresses its own non-canonical multi-subunit non-virion RNA polymerase (nvRNAP), which is imported into its "nucleus" to transcribe viral genes. The ΦKZ nvRNAP is formed by four polypeptides representing homologues of the eubacterial β/β' subunits, and a fifth that is likely to have evolved from an ancestral homologue to σ-factor. We have resolved the structure of the ΦKZ nvRNAP initiating transcription from its cognate promoter, p119L, including previously disordered domains and regions. Our results shed light on the similarities and differences between ΦKZ nvRNAP mechanisms of transcription and those of canonical eubacterial RNAPs and the related non-canonical nvRNAP of bacteriophage AR9.