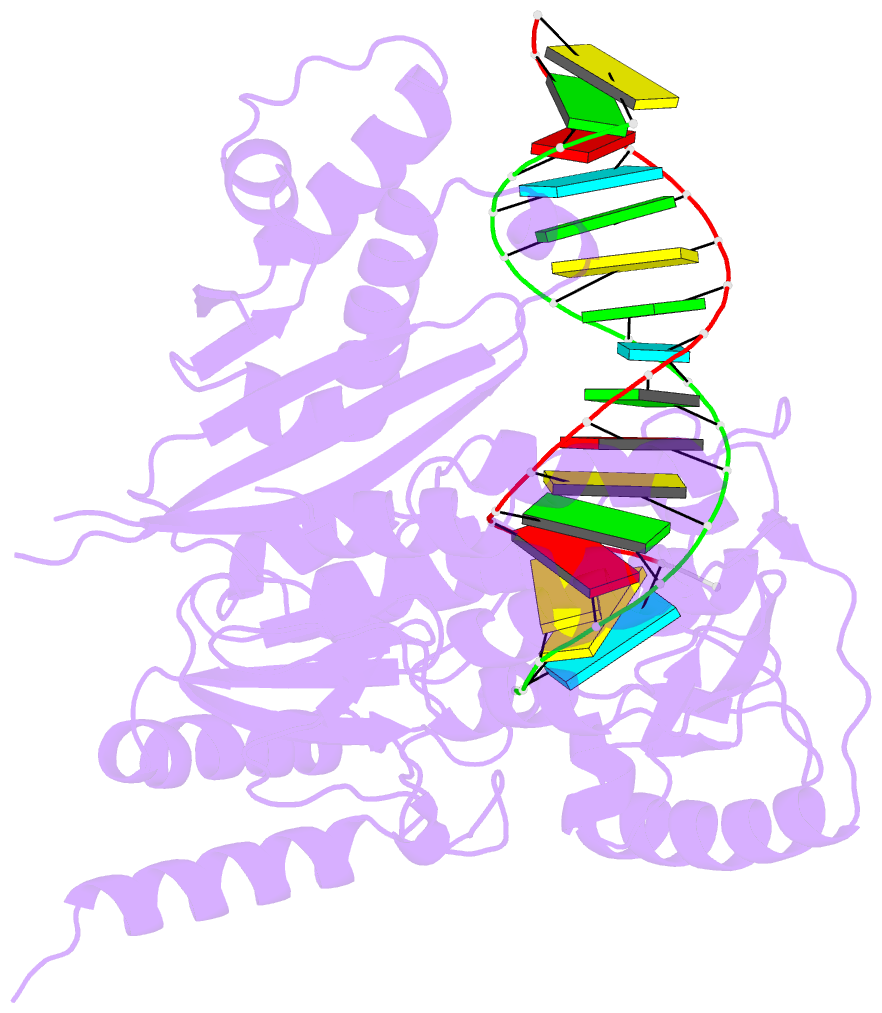
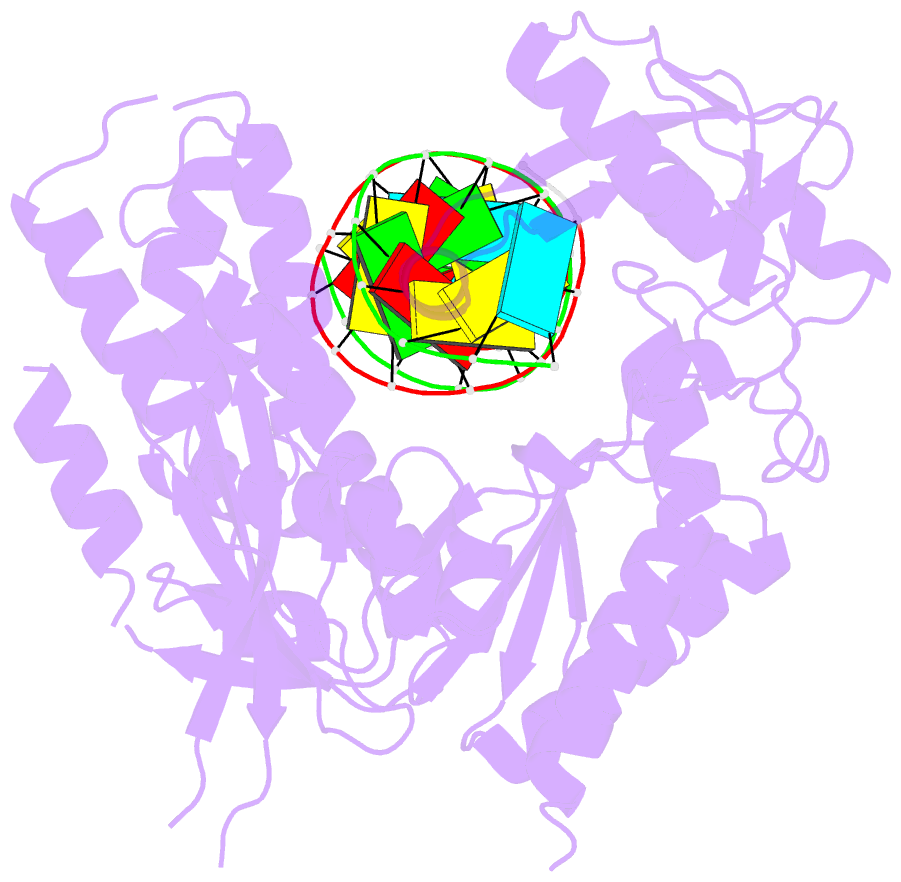
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8r0s; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- viral protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.35 Å)
- Summary
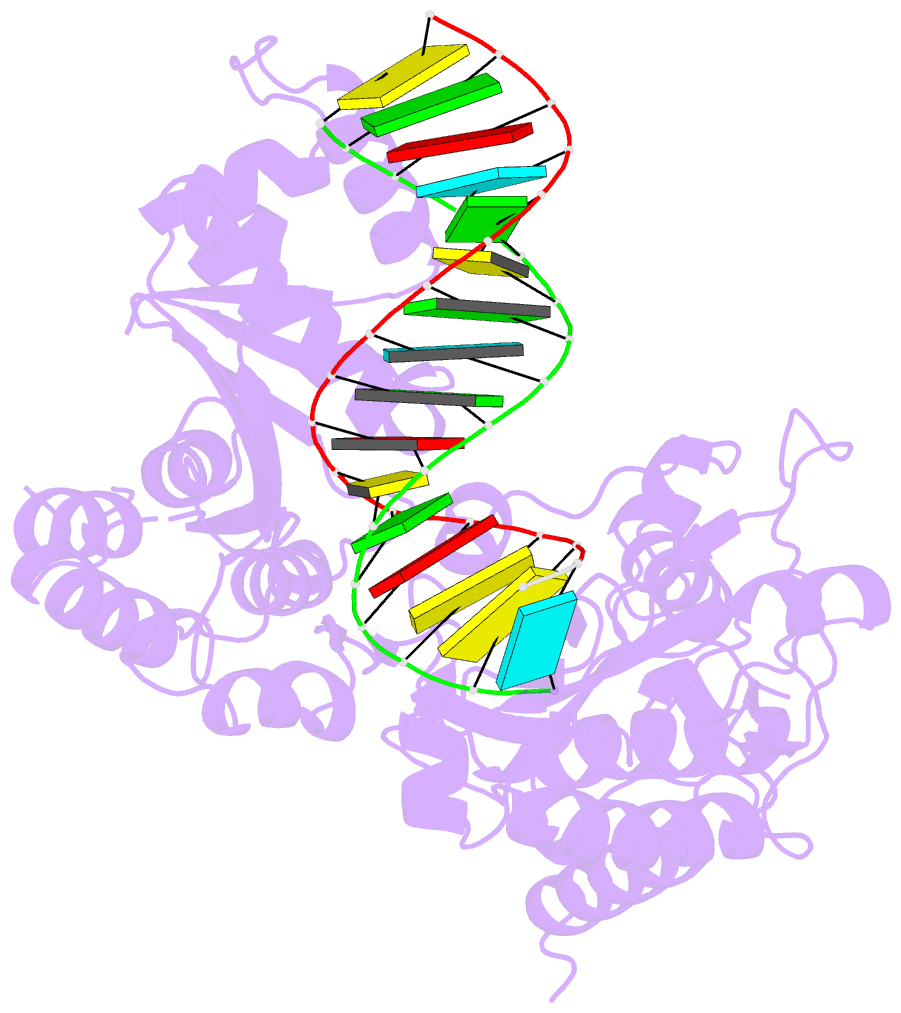
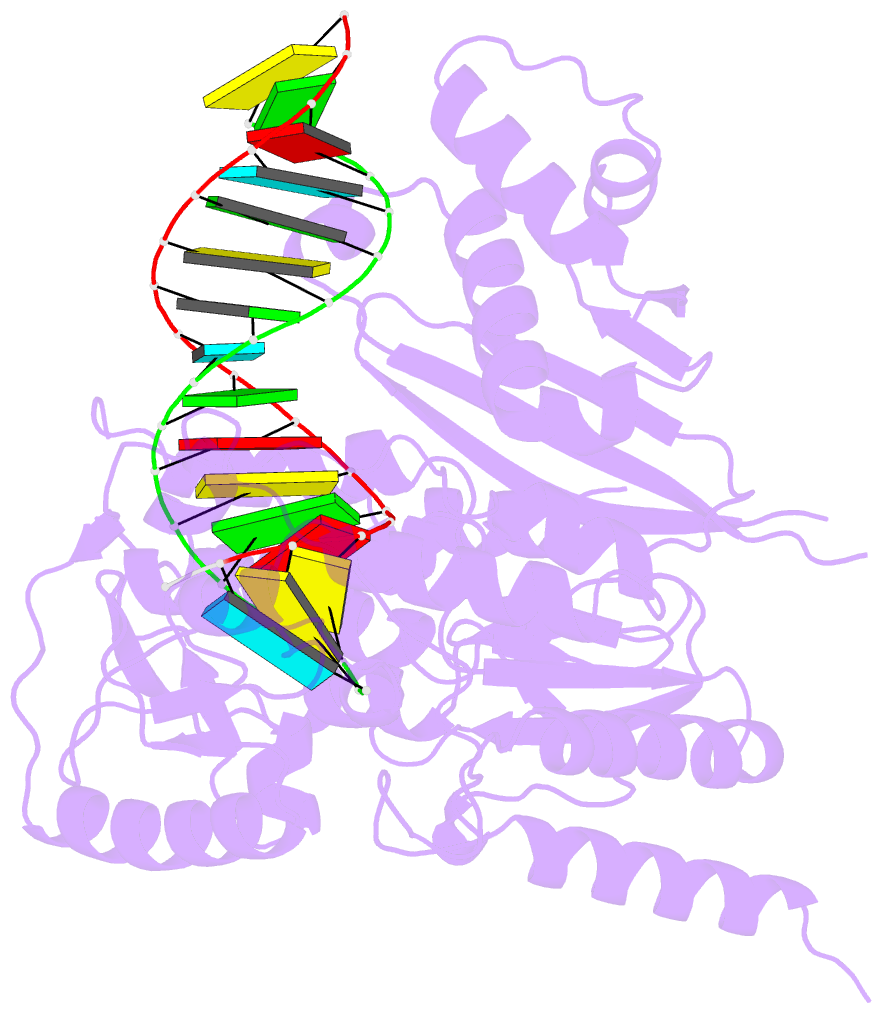
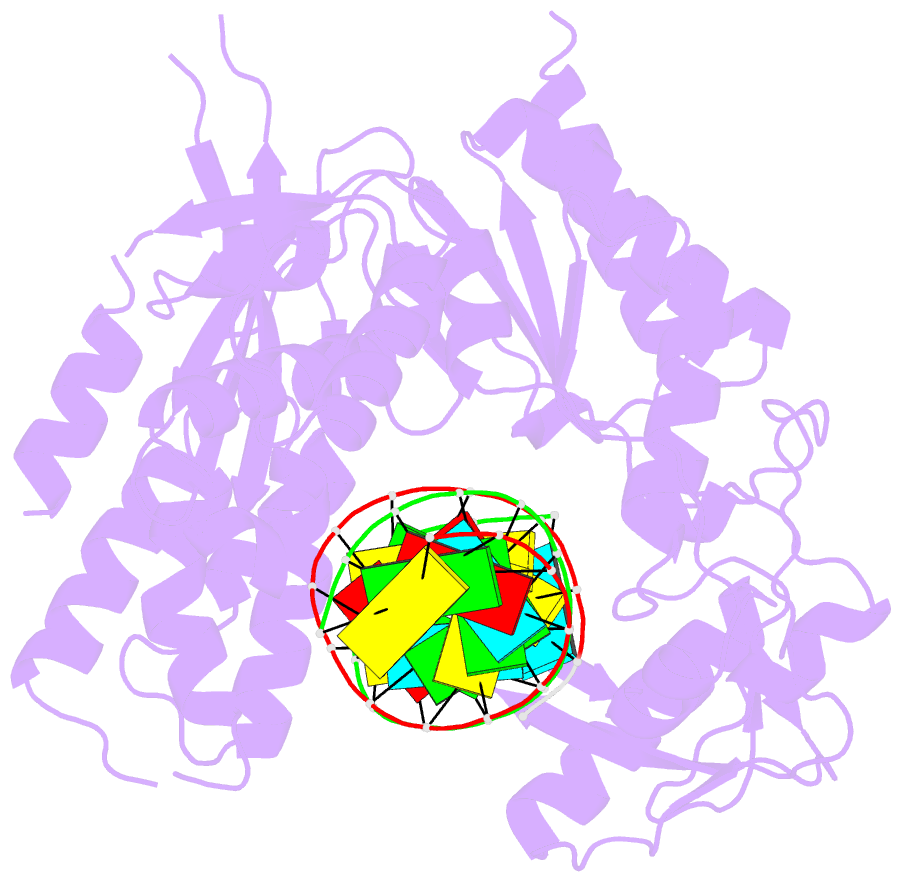
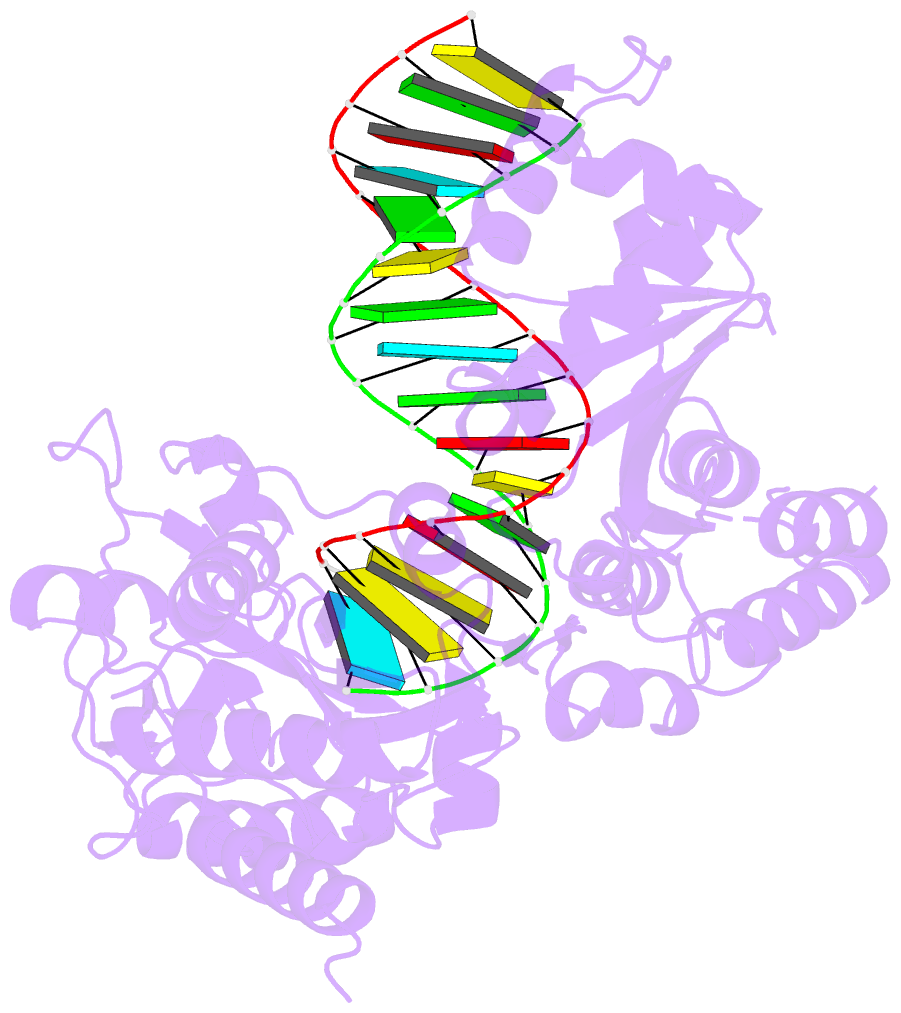
- Structure of reverse transcriptase from cauliflower mosaic virus in complex with RNA-DNA hybrid
- Reference
- Prabaharan C, Figiel M, Szczepanowski RH, Skowronek K, Zajko W, Thangaraj V, Chamera S, Nowak E, Nowotny M (2024): "Structural and biochemical characterization of cauliflower mosaic virus reverse transcriptase." J.Biol.Chem., 300, 107555. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107555.
- Abstract
- Reverse transcriptases (RTs) are enzymes with DNA polymerase and RNase H activities. They convert single-stranded RNA into double-stranded DNA and are key enzymes for the replication of retroviruses and retroelements. Caulimoviridae is a major family of plant-infecting viruses. Caulimoviruses have a circular dsDNA genome that is replicated by reverse transcription, but in contrast to retroviruses, they lack integrase. Caulimoviruses are related to Ty3 retroelements. Ty3 RT has been extensively studied structurally and biochemically, but corresponding information for caulimoviral RTs is unavailable. In the present study, we report the first crystal structure of cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) RT in complex with a duplex made of RNA and DNA strands (RNA/DNA hybrid). CaMV RT forms a monomeric complex with the hybrid, unlike Ty3 RT, which does so as a dimer. Results of the RNA-dependent DNA polymerase and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity assays showed that individual CaMV RT molecules are able to perform full polymerase functions. However, our analyses showed that an additional CaMV RT molecule needs to transiently associate with a polymerase-competent RT molecule to execute RNase H cuts of the RNA strand. Collectively, our results provide details into the structure and function of CaMV RT and describe how the enzyme compares to other related RTs.