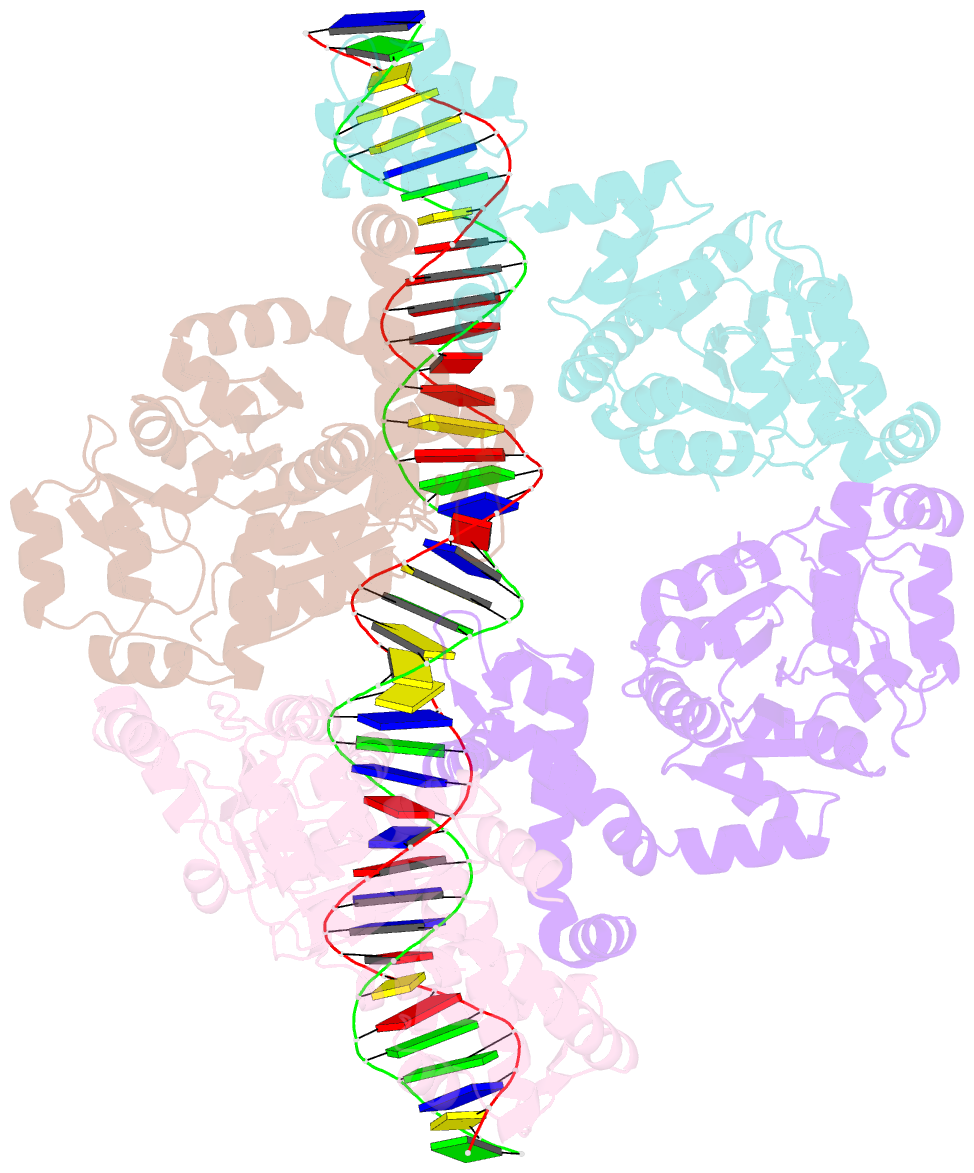
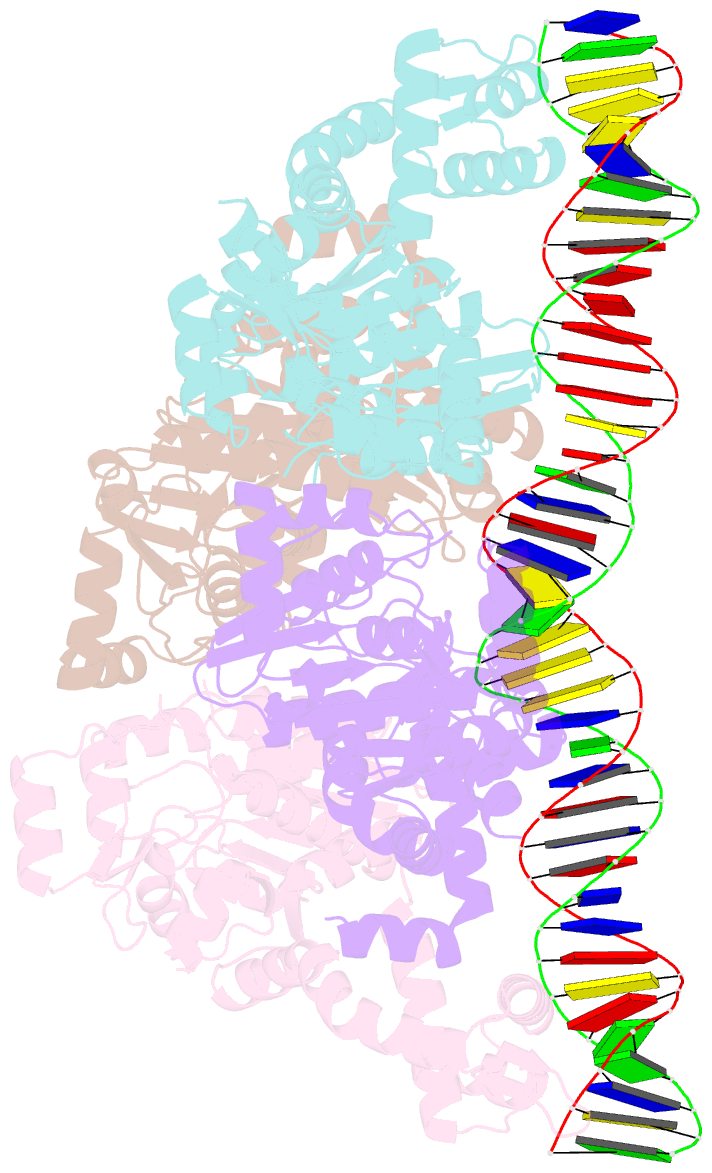
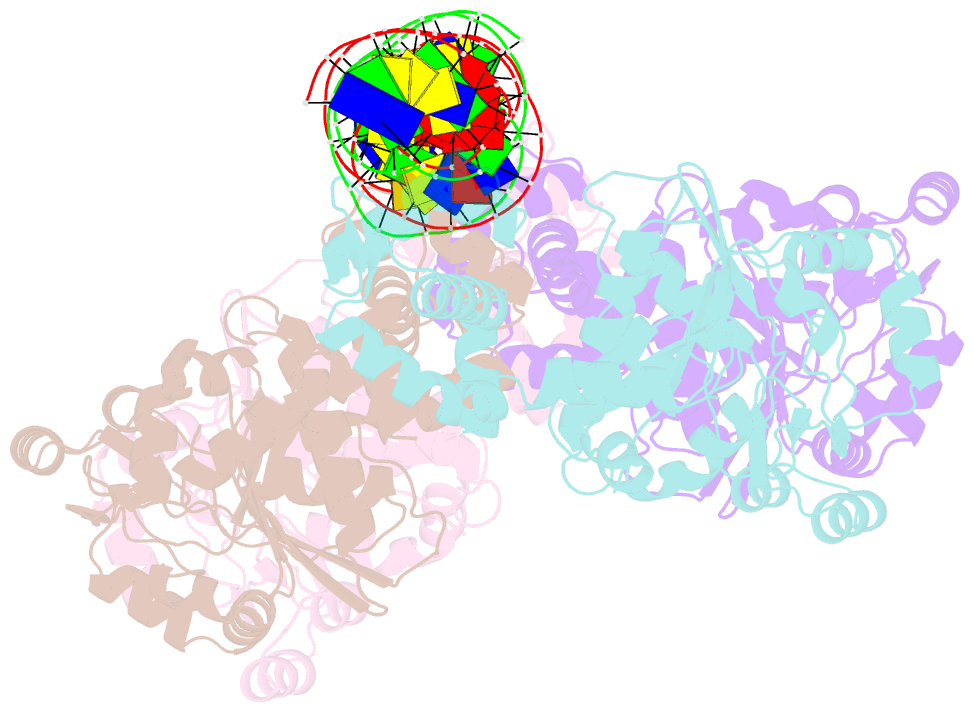
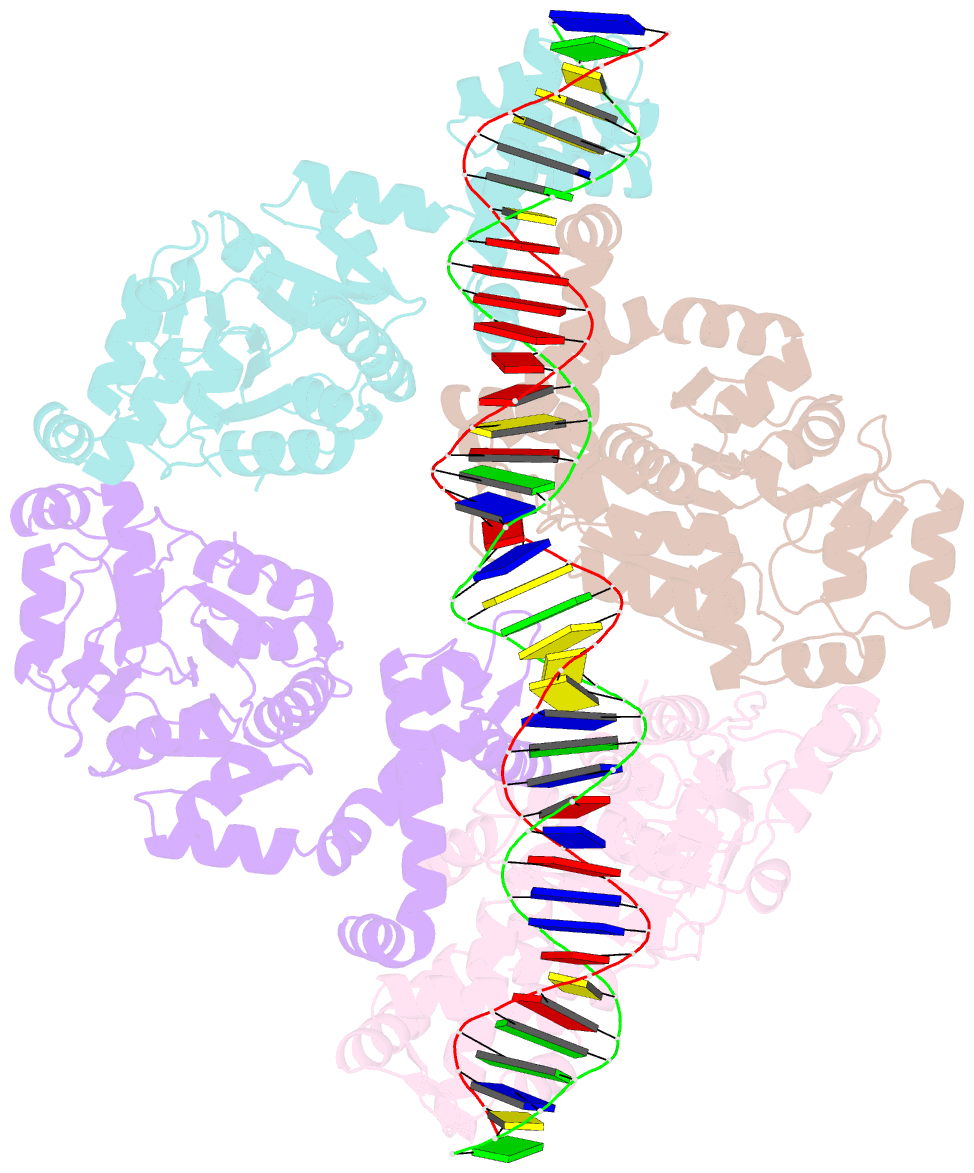
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8r3g; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (4.4 Å)
- Summary
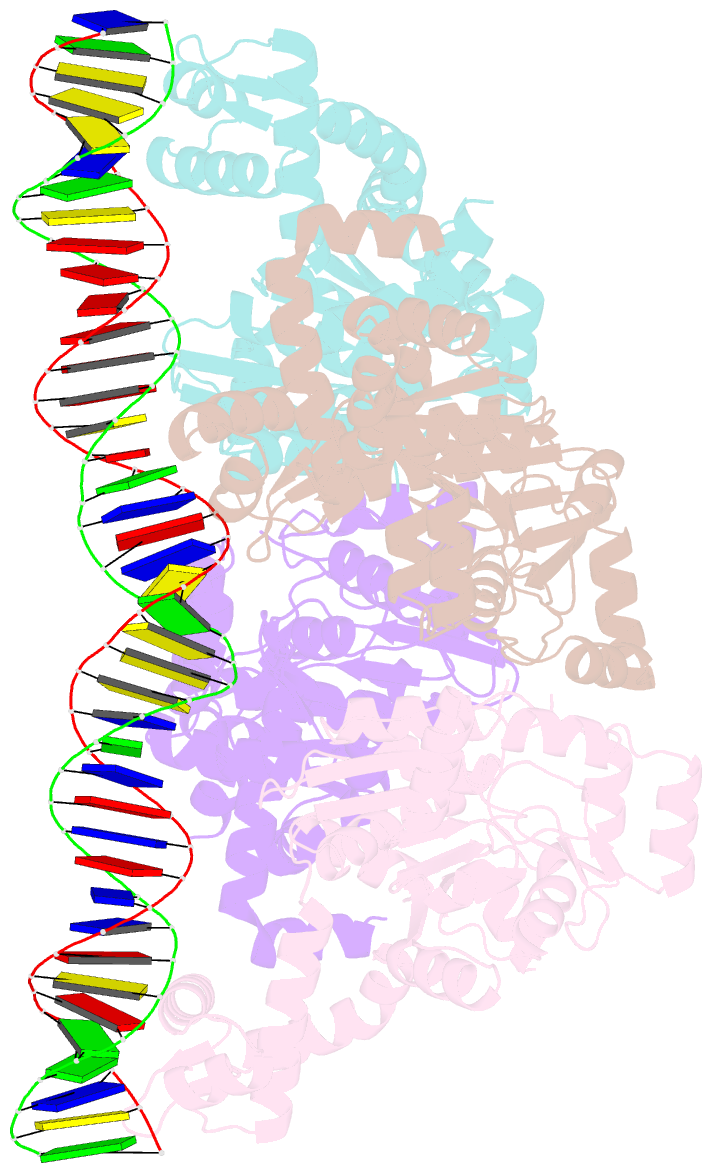
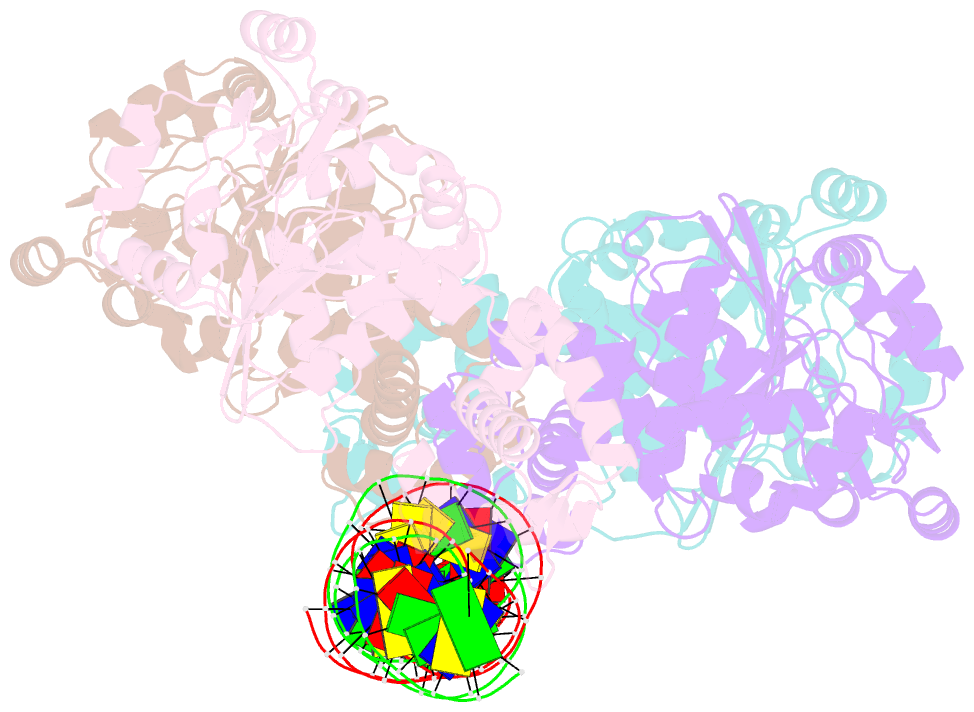
- Central glycolytic genes regulator (cggr) bound to DNA operator
- Reference
- Soltysova M, Skerlova J, Pachl P, Skubnik K, Fabry M, Sieglova I, Farolfi M, Grishkovskaya I, Babiak M, Novacek J, Krasny L, Rezacova P (2024): "Structural characterization of two prototypical repressors of SorC family reveals tetrameric assemblies on DNA and mechanism of function." Nucleic Acids Res., 52, 7305-7320. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae434.
- Abstract
- The SorC family of transcriptional regulators plays a crucial role in controlling the carbohydrate metabolism and quorum sensing. We employed an integrative approach combining X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy to investigate architecture and functional mechanism of two prototypical representatives of two sub-classes of the SorC family: DeoR and CggR from Bacillus subtilis. Despite possessing distinct DNA-binding domains, both proteins form similar tetrameric assemblies when bound to their respective DNA operators. Structural analysis elucidates the process by which the CggR-regulated gapA operon is derepressed through the action of two effectors: fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and newly confirmed dihydroxyacetone phosphate. Our findings provide the first comprehensive understanding of the DNA binding mechanism of the SorC-family proteins, shedding new light on their functional characteristics.