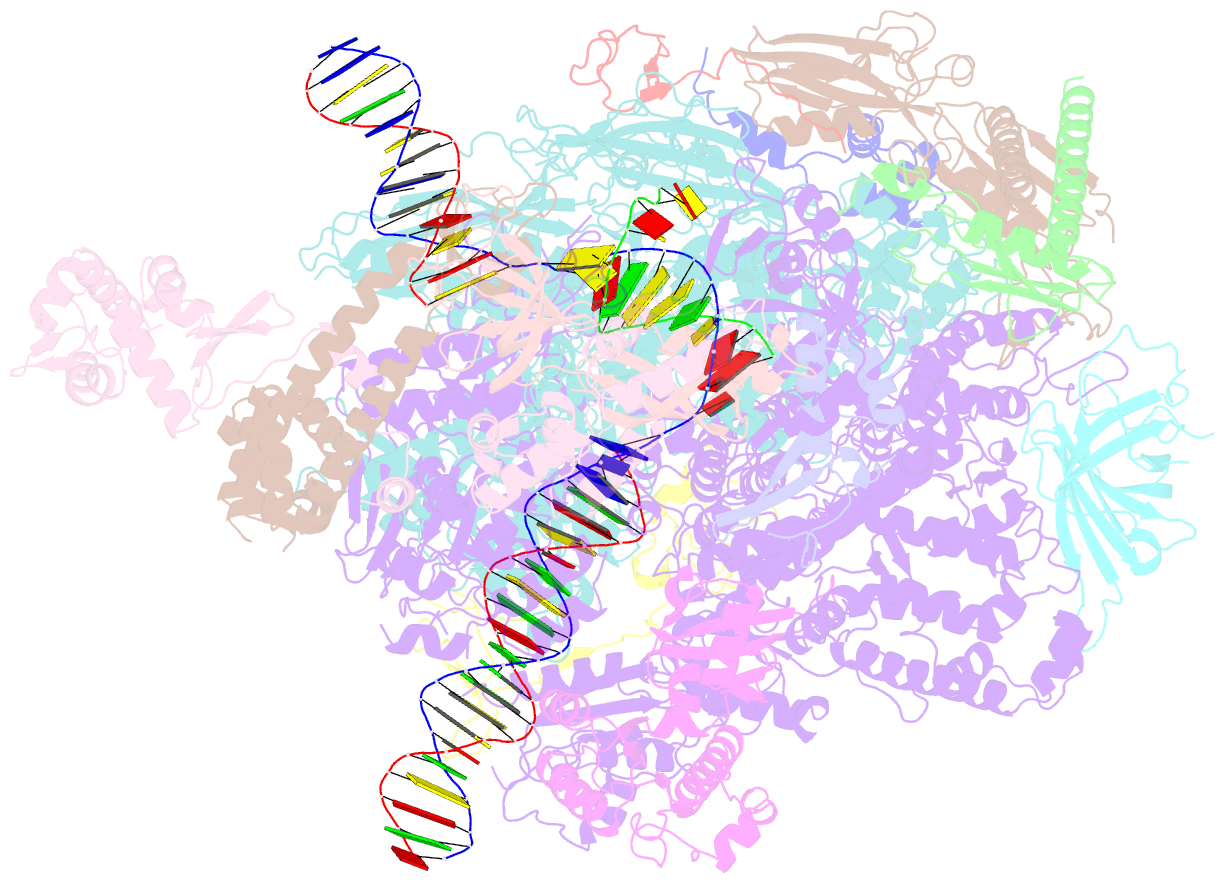
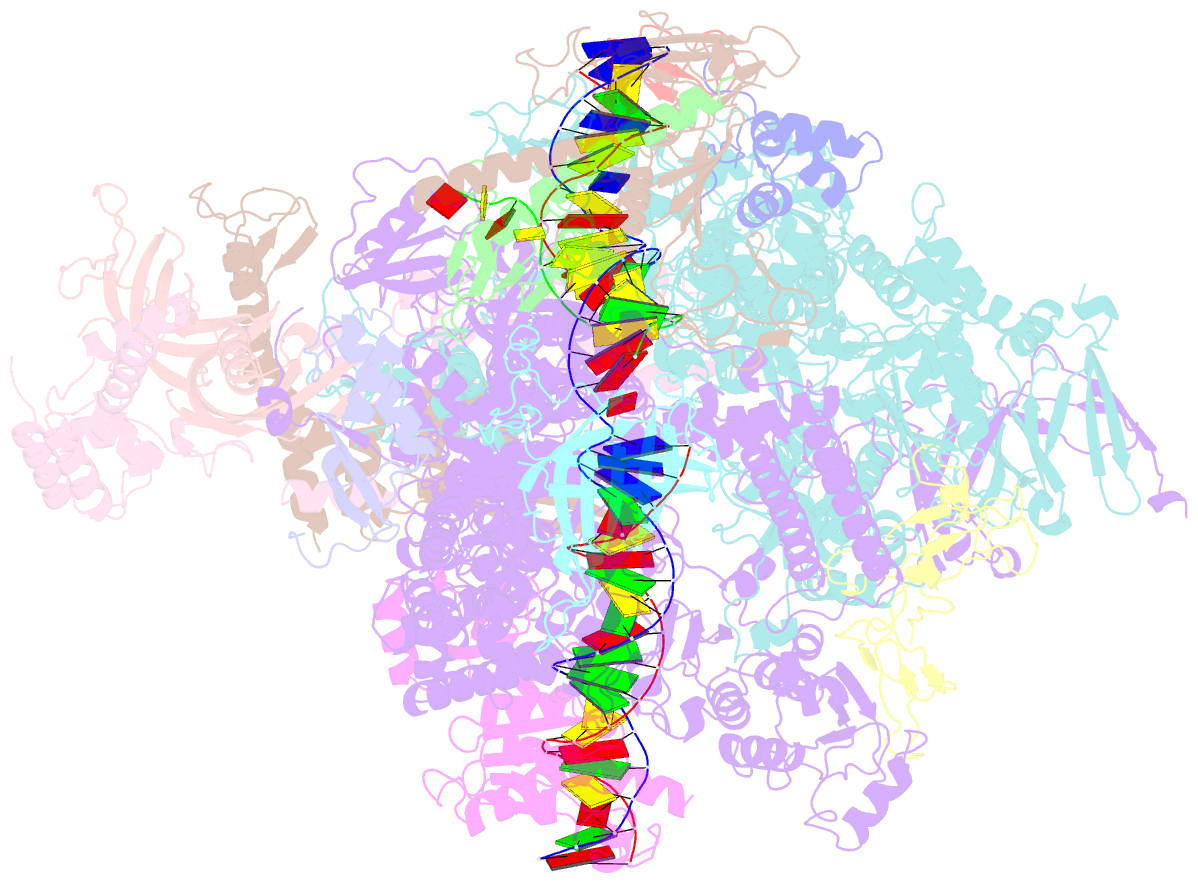
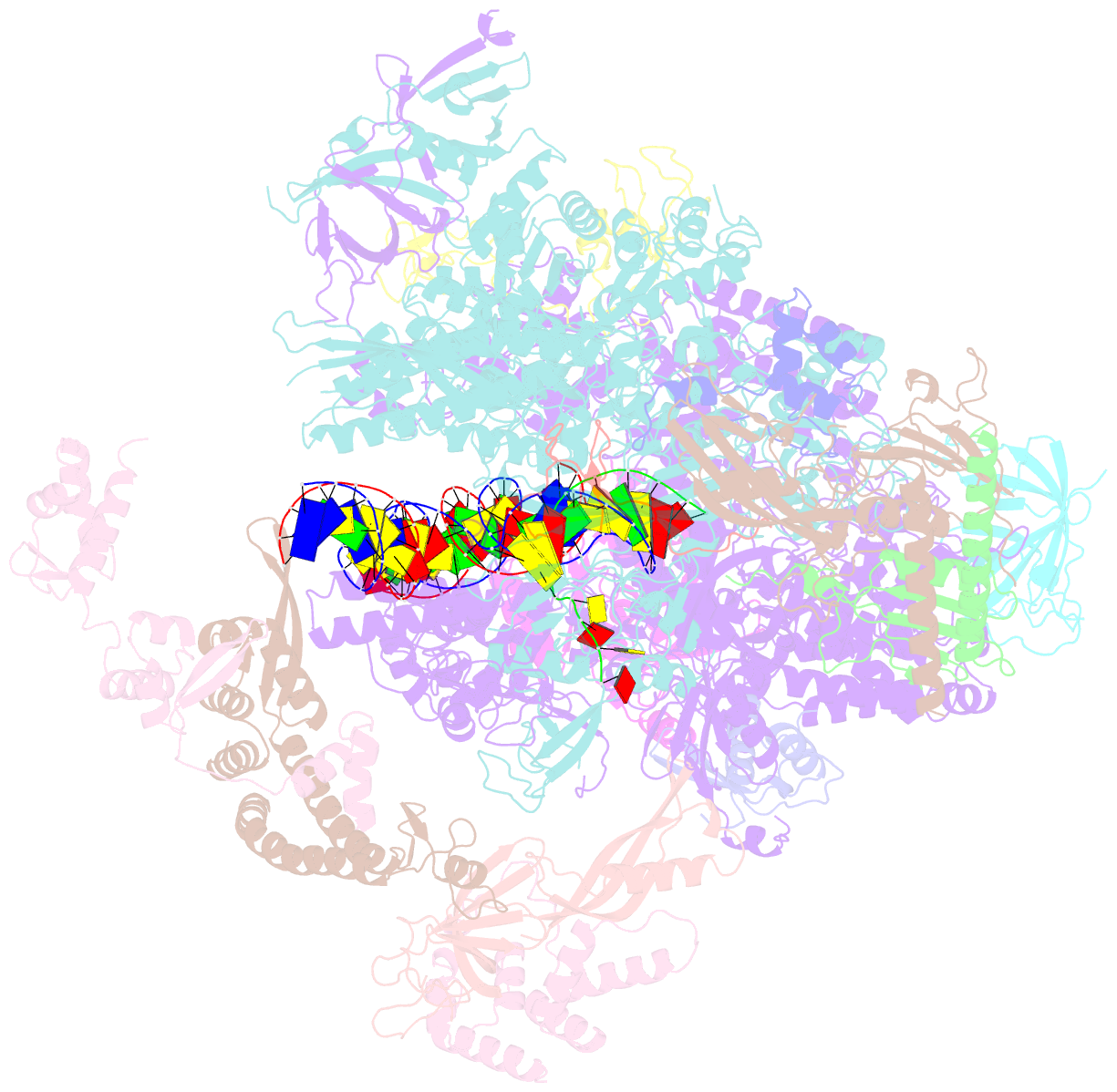
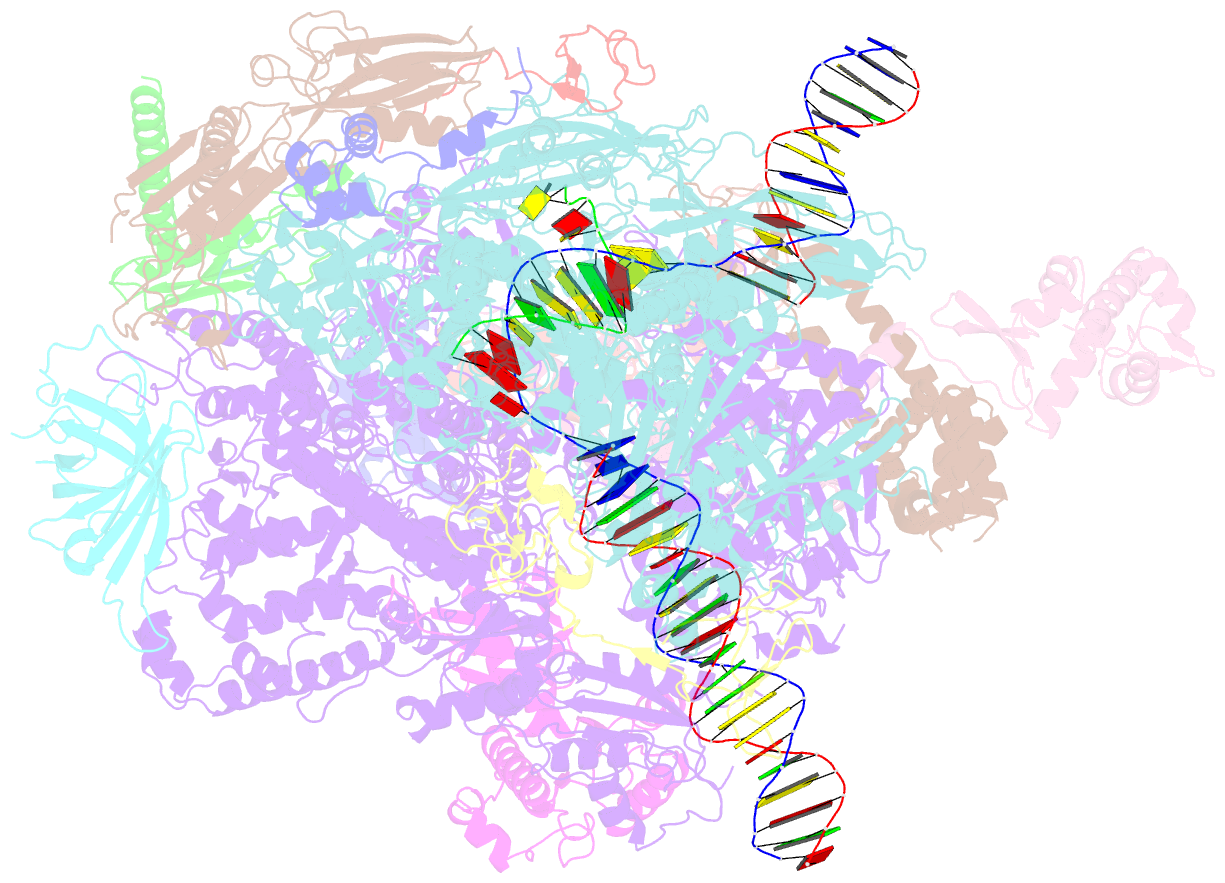
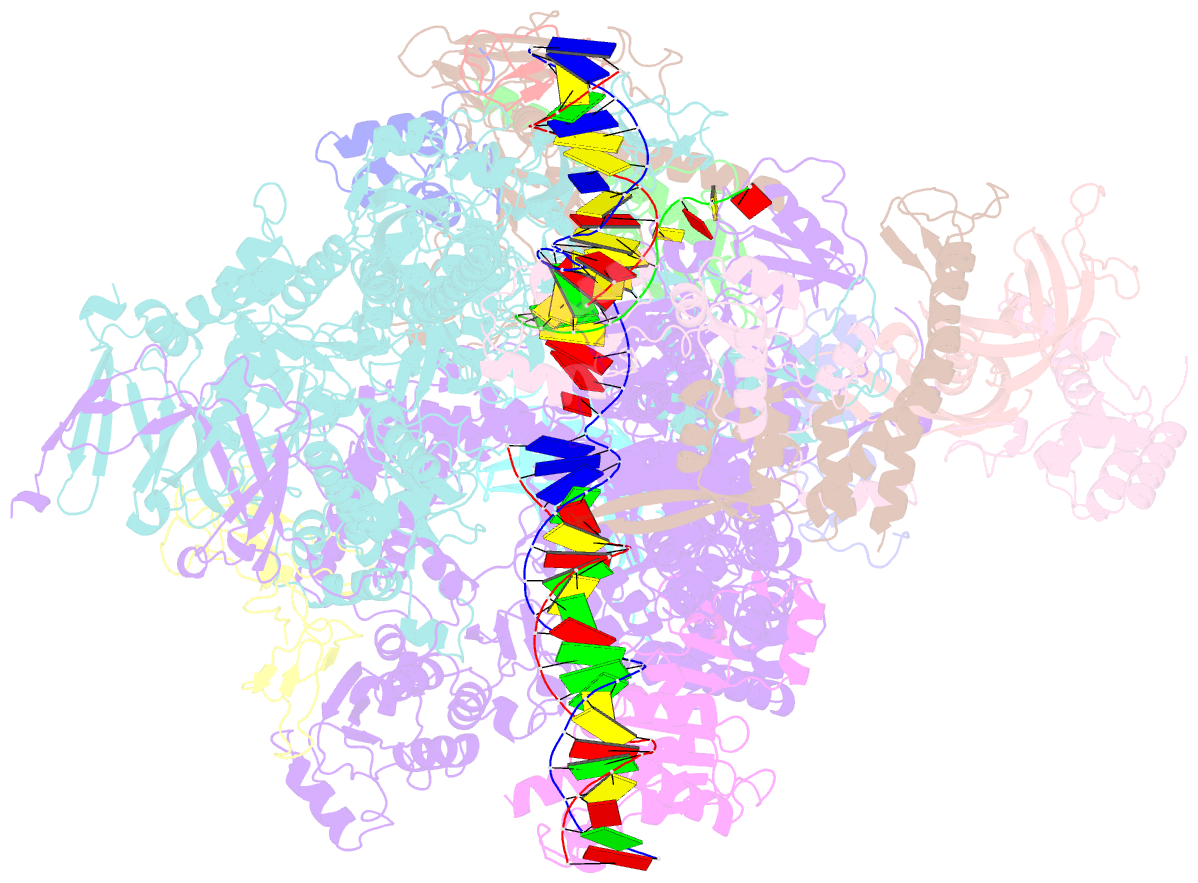
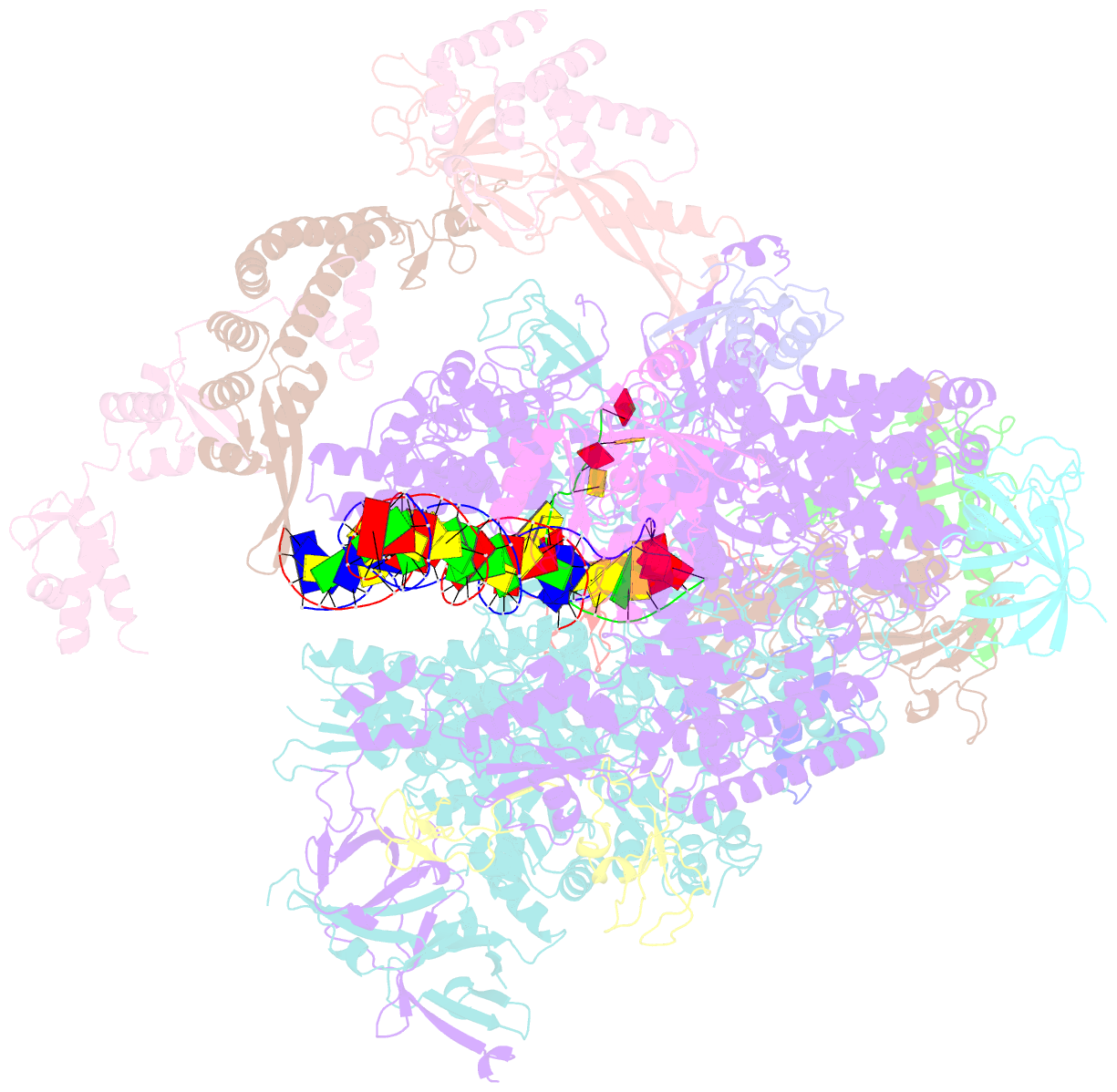
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8s55; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.4 Å)
- Summary
- RNA polymerase ii early elongation complex bound to tfiie and tfiif - state a (composite structure)
- Reference
- Zhan Y, Grabbe F, Oberbeckmann E, Dienemann C, Cramer P (2024): "Three-step mechanism of promoter escape by RNA polymerase II." Mol.Cell, 84, 1699-1710.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.03.016.
- Abstract
- The transition from transcription initiation to elongation is highly regulated in human cells but remains incompletely understood at the structural level. In particular, it is unclear how interactions between RNA polymerase II (RNA Pol II) and initiation factors are broken to enable promoter escape. Here, we reconstitute RNA Pol II promoter escape in vitro and determine high-resolution structures of initially transcribing complexes containing 8-, 10-, and 12-nt ordered RNAs and two elongation complexes containing 14-nt RNAs. We suggest that promoter escape occurs in three major steps. First, the growing RNA displaces the B-reader element of the initiation factor TFIIB without evicting TFIIB. Second, the rewinding of the transcription bubble coincides with the eviction of TFIIA, TFIIB, and TBP. Third, the binding of DSIF and NELF facilitates TFIIE and TFIIH dissociation, establishing the paused elongation complex. This three-step model for promoter escape fills a gap in our understanding of the initiation-elongation transition of RNA Pol II transcription.