Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8tas; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- gene regulation
- Method
- cryo-EM (4.1 Å)
- Summary
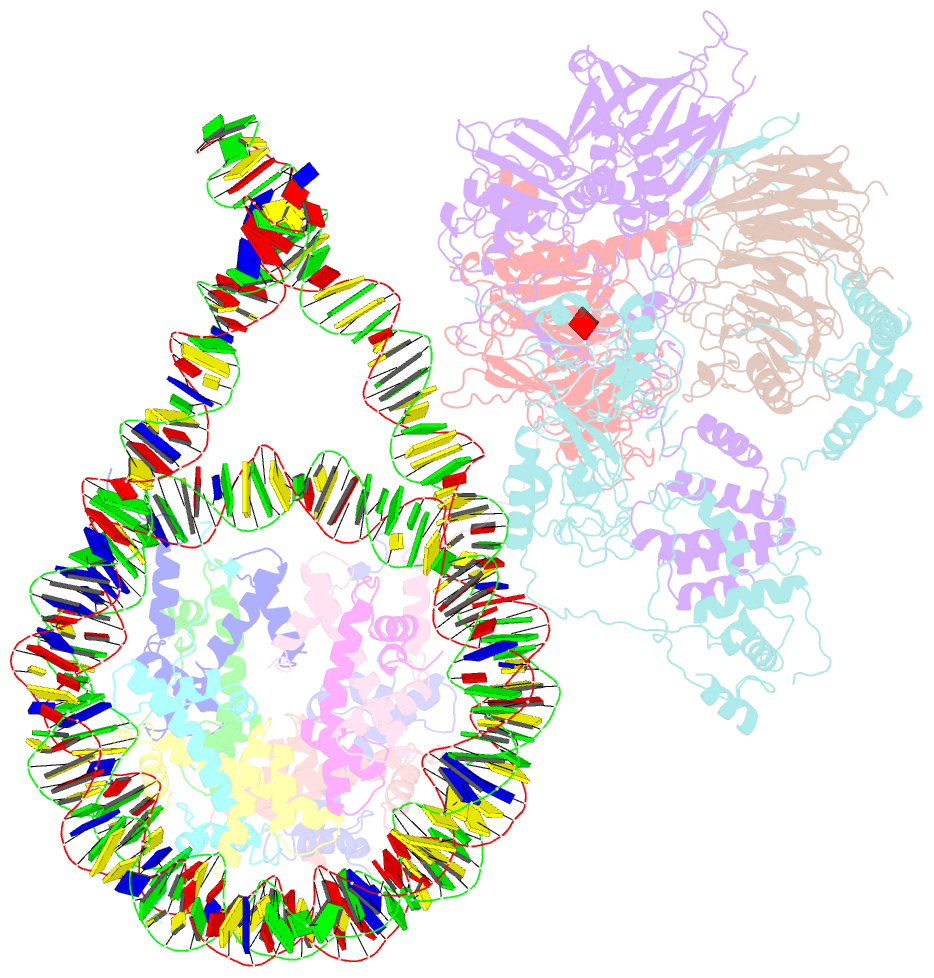
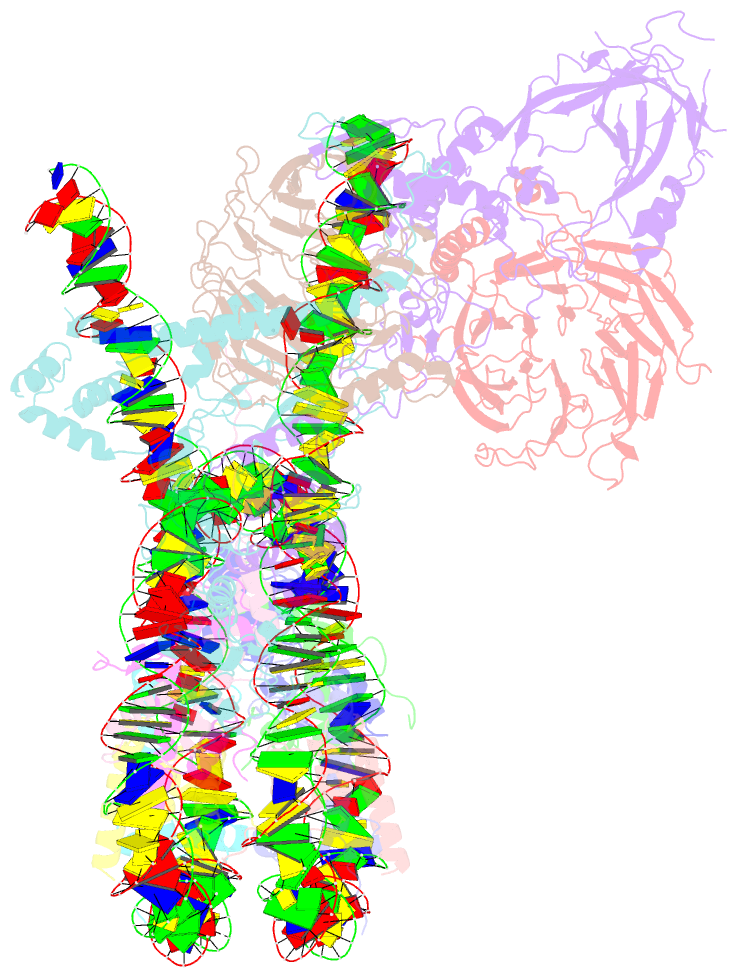
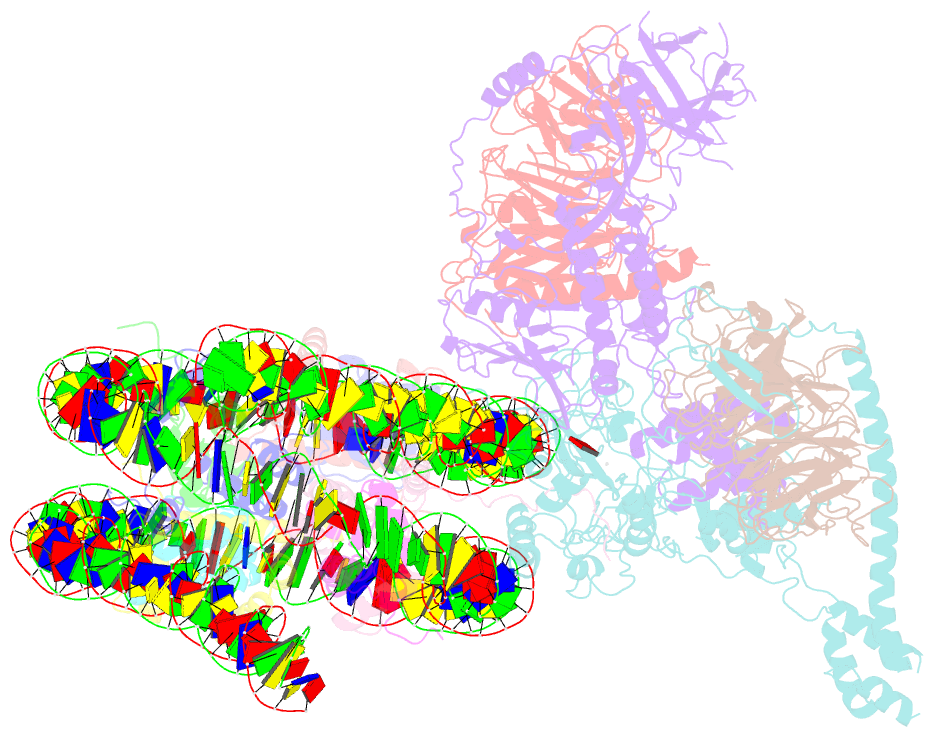
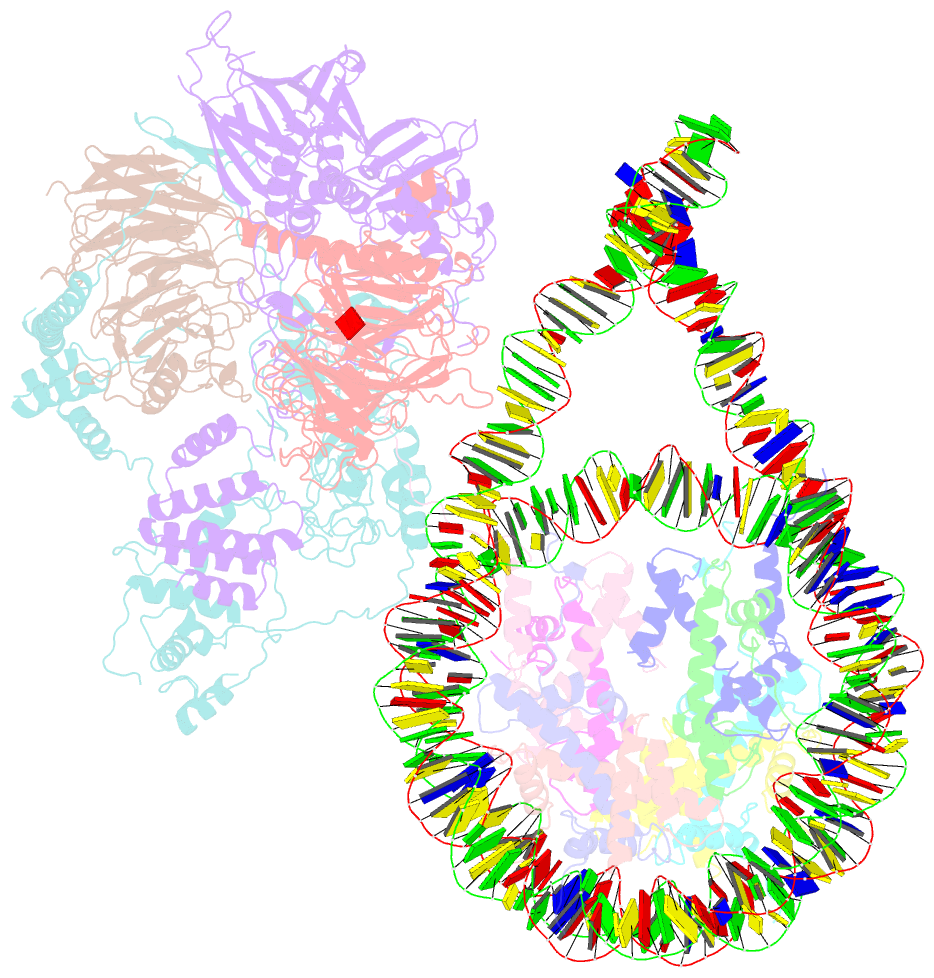
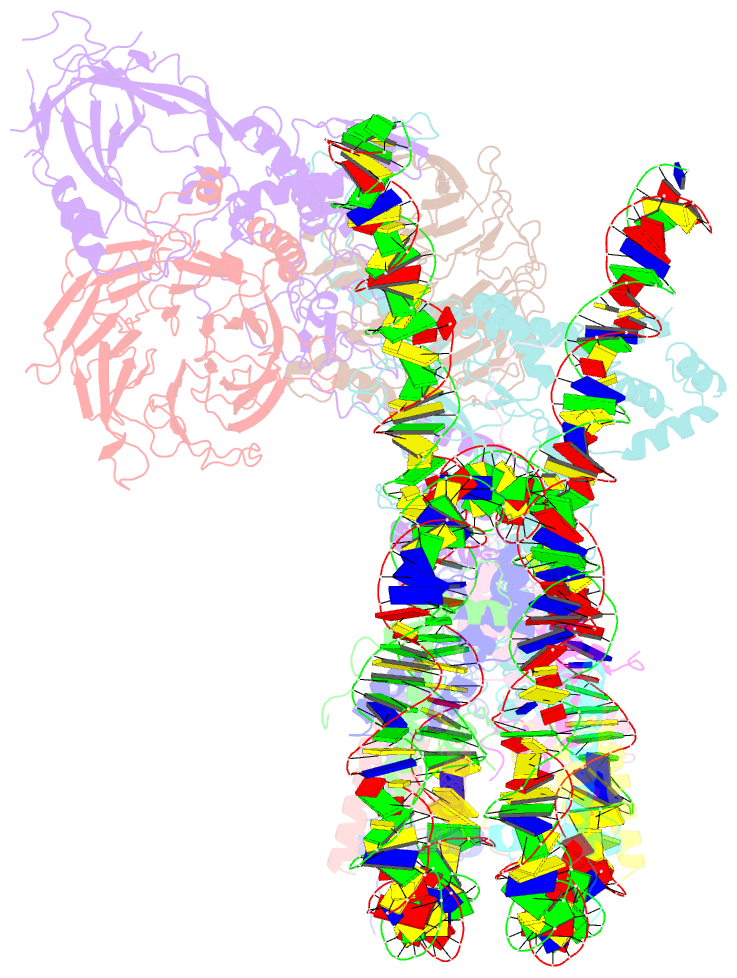
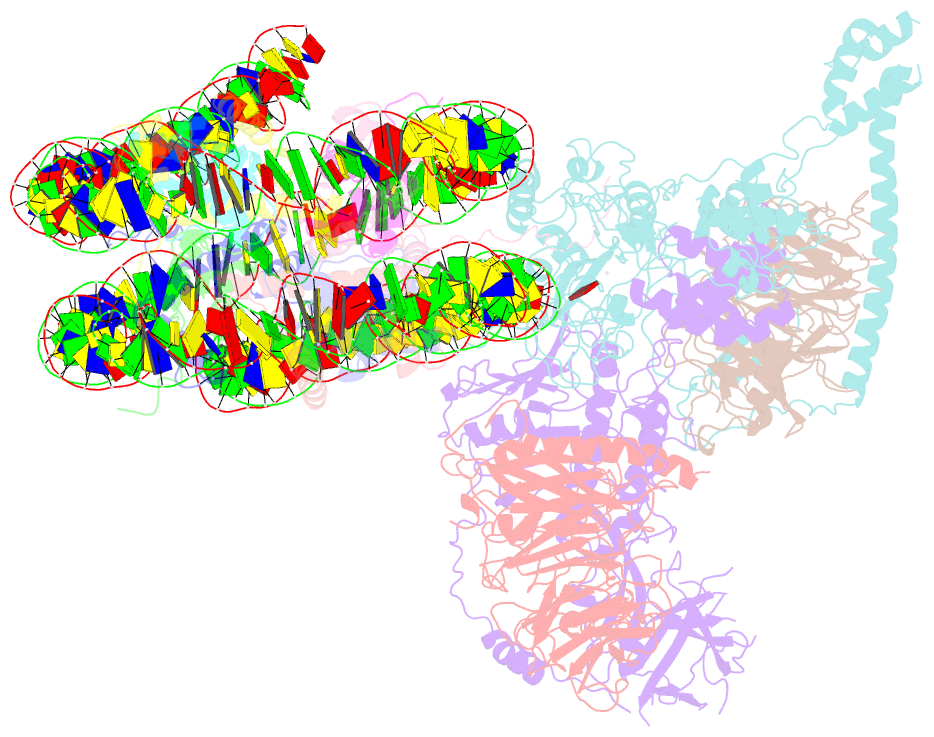
- Prc2 monomer bound to nucleosome
- Reference
- Sauer PV, Pavlenko E, Cookis T, Zirden LC, Renn J, Singhal A, Hunold P, Hoehne-Wiechmann MN, van Ray O, Kaschani F, Kaiser M, Hansel-Hertsch R, Sanbonmatsu KY, Nogales E, Poepsel S (2024): "Activation of automethylated PRC2 by dimerization on chromatin." Mol.Cell, 84, 3885-3898.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.08.025.
- Abstract
- Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) is an epigenetic regulator that trimethylates lysine 27 of histone 3 (H3K27me3) and is essential for embryonic development and cellular differentiation. H3K27me3 is associated with transcriptionally repressed chromatin and is established when PRC2 is allosterically activated upon methyl-lysine binding by the regulatory subunit EED. Automethylation of the catalytic subunit enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) stimulates its activity by an unknown mechanism. Here, we show that human PRC2 forms a dimer on chromatin in which an inactive, automethylated PRC2 protomer is the allosteric activator of a second PRC2 that is poised to methylate H3 of a substrate nucleosome. Functional assays support our model of allosteric trans-autoactivation via EED, suggesting a previously unknown mechanism mediating context-dependent activation of PRC2. Our work showcases the molecular mechanism of auto-modification-coupled dimerization in the regulation of chromatin-modifying complexes.