Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8u0p; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.9 Å)
- Summary
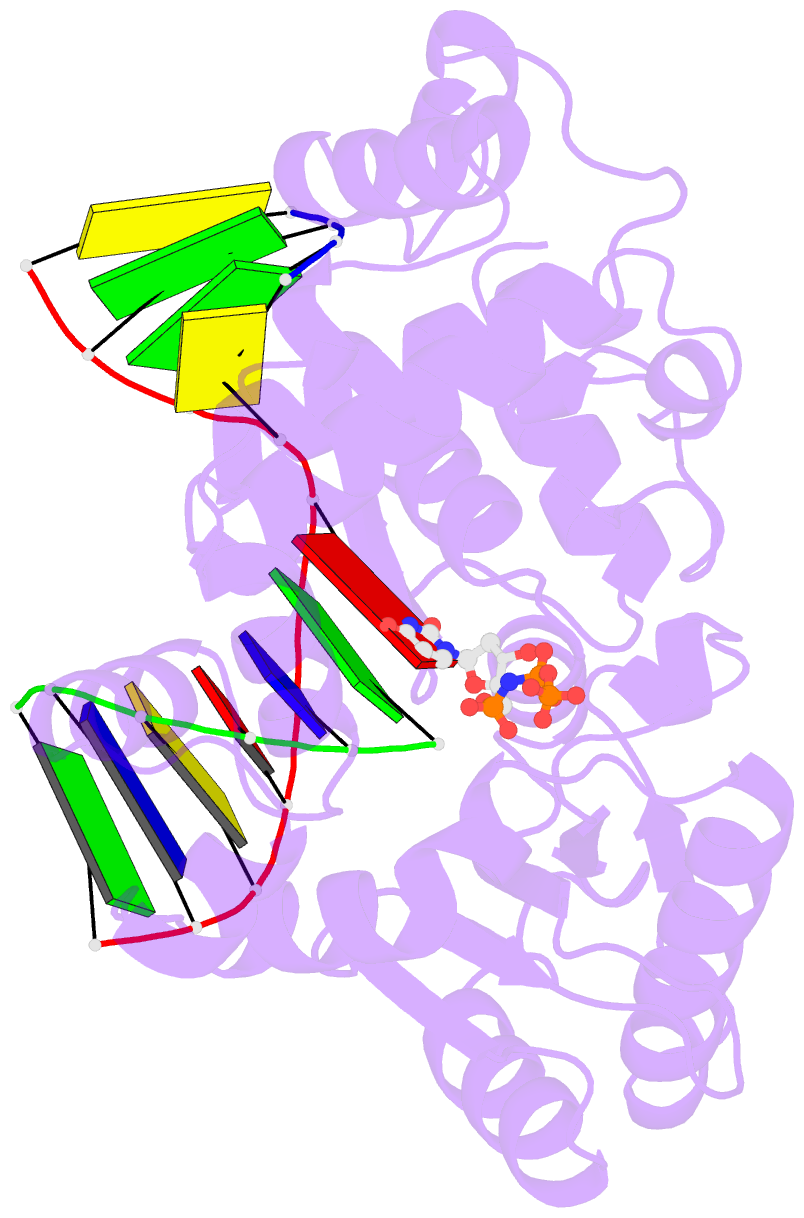
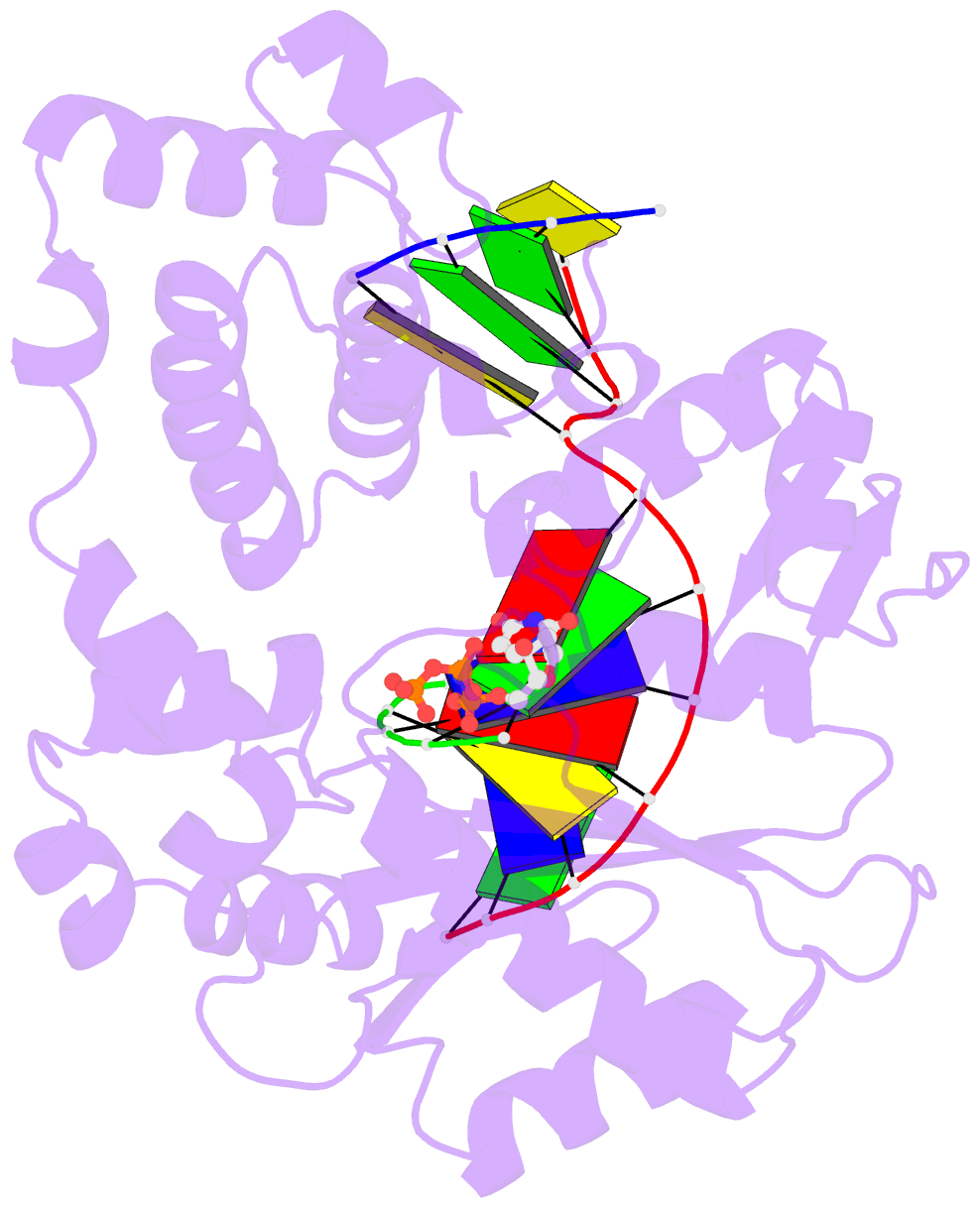
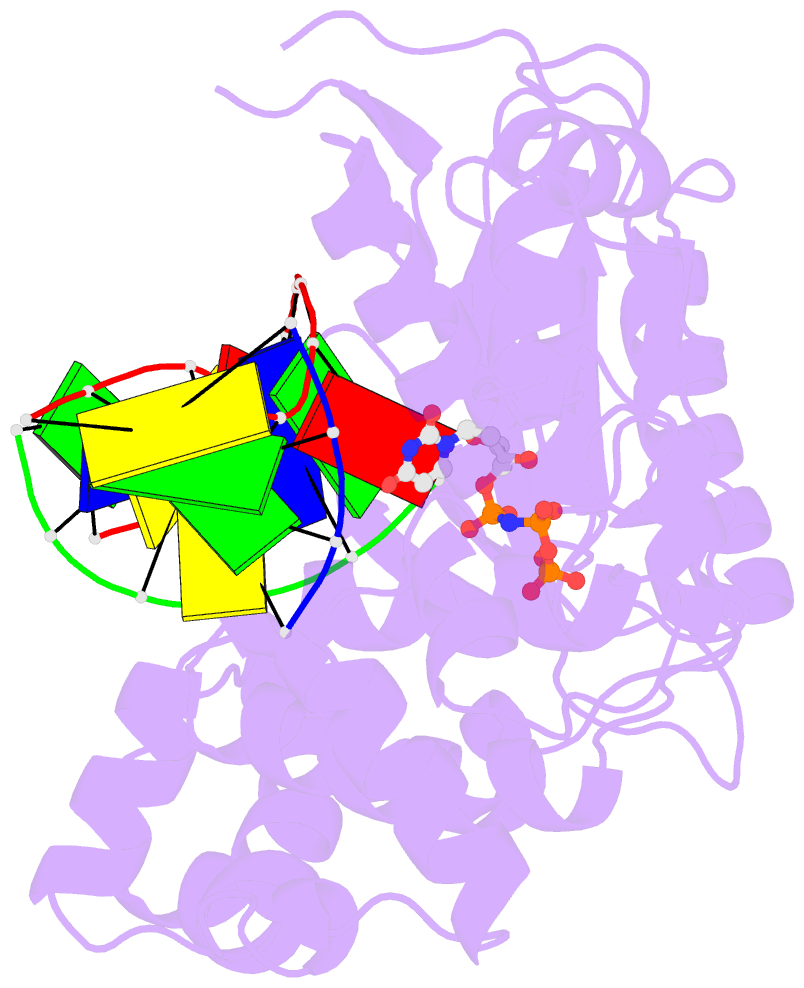
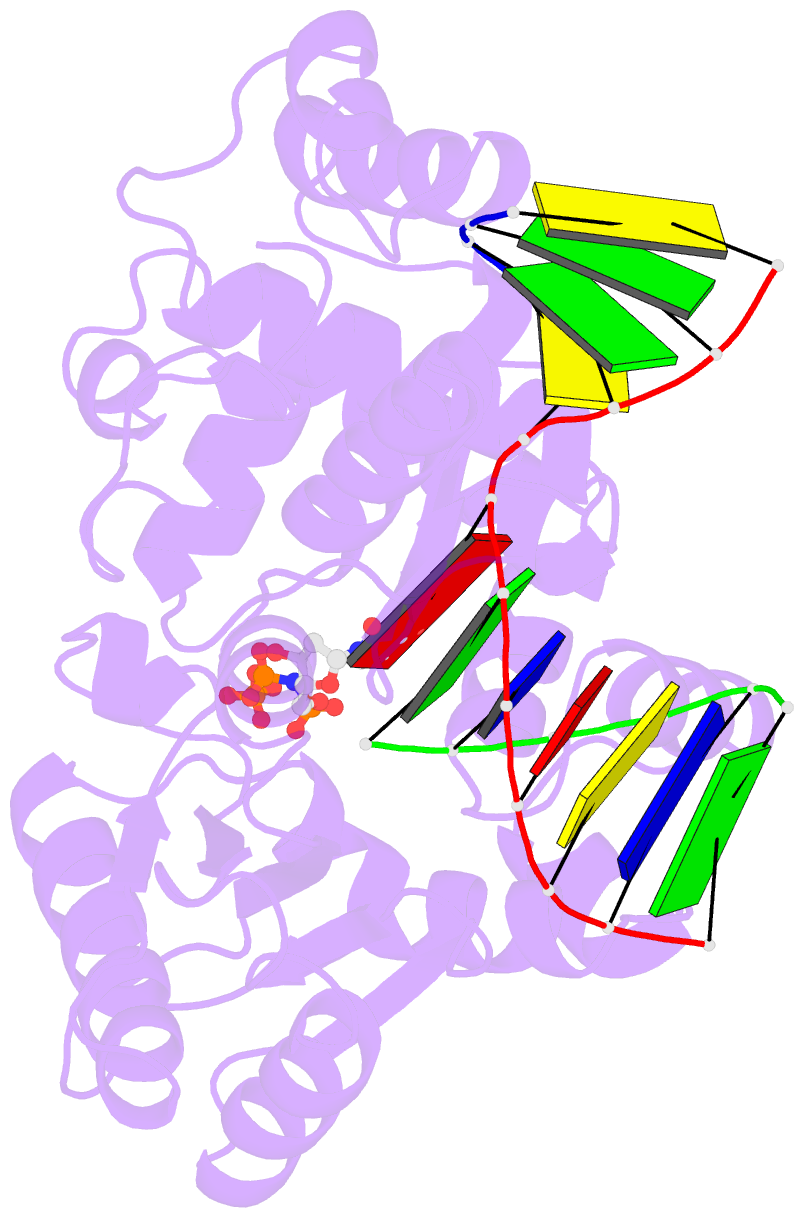
- Synaptic complex of human DNA polymerase lambda dl variant engaged on a noncomplementary DNA double-strand break
- Reference
- Kaminski AM, Chiruvella KK, Ramsden DA, Bebenek K, Kunkel TA, Pedersen LC (2024): "DNA polymerase lambda Loop1 variant yields unexpected gain-of-function capabilities in nonhomologous end-joining." DNA Repair (Amst), 136, 103645. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2024.103645.
- Abstract
- DNA polymerases lambda (Polλ) and mu (Polμ) are X-Family polymerases that participate in DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair by the nonhomologous end-joining pathway (NHEJ). Both polymerases direct synthesis from one DSB end, using template derived from a second DSB end. In this way, they promote the NHEJ ligation step and minimize the sequence loss normally associated with this pathway. The two polymerases differ in cognate substrate, as Polλ is preferred when synthesis must be primed from a base-paired DSB end, while Polμ is required when synthesis must be primed from an unpaired DSB end. We generated a Polλ variant (PolλKGET) that retained canonical Polλ activity on a paired end-albeit with reduced incorporation fidelity. We recently discovered that the variant had unexpectedly acquired the activity previously unique to Polμ-synthesis from an unpaired primer terminus. Though the sidechains of the Loop1 region make no contact with the DNA substrate, PolλKGET Loop1 amino acid sequence is surprisingly essential for its unique activity during NHEJ. Taken together, these results underscore that the Loop1 region plays distinct roles in different Family X polymerases.