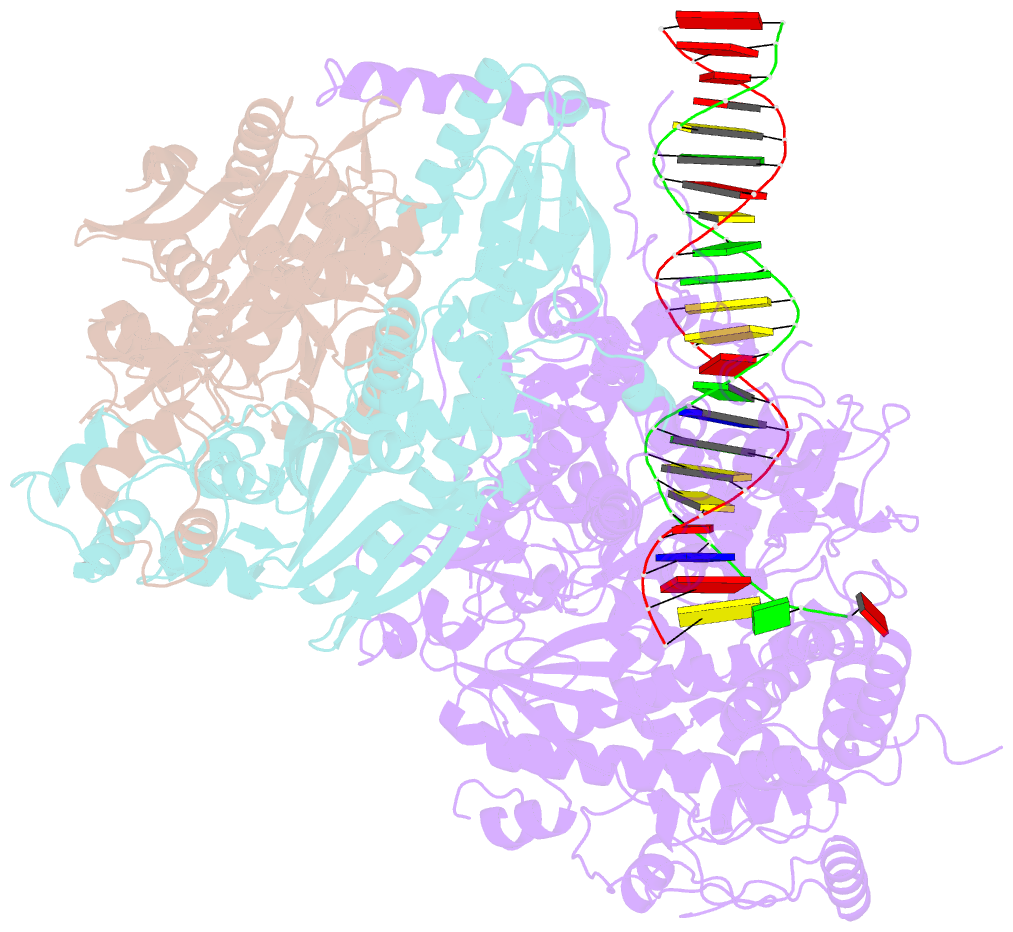
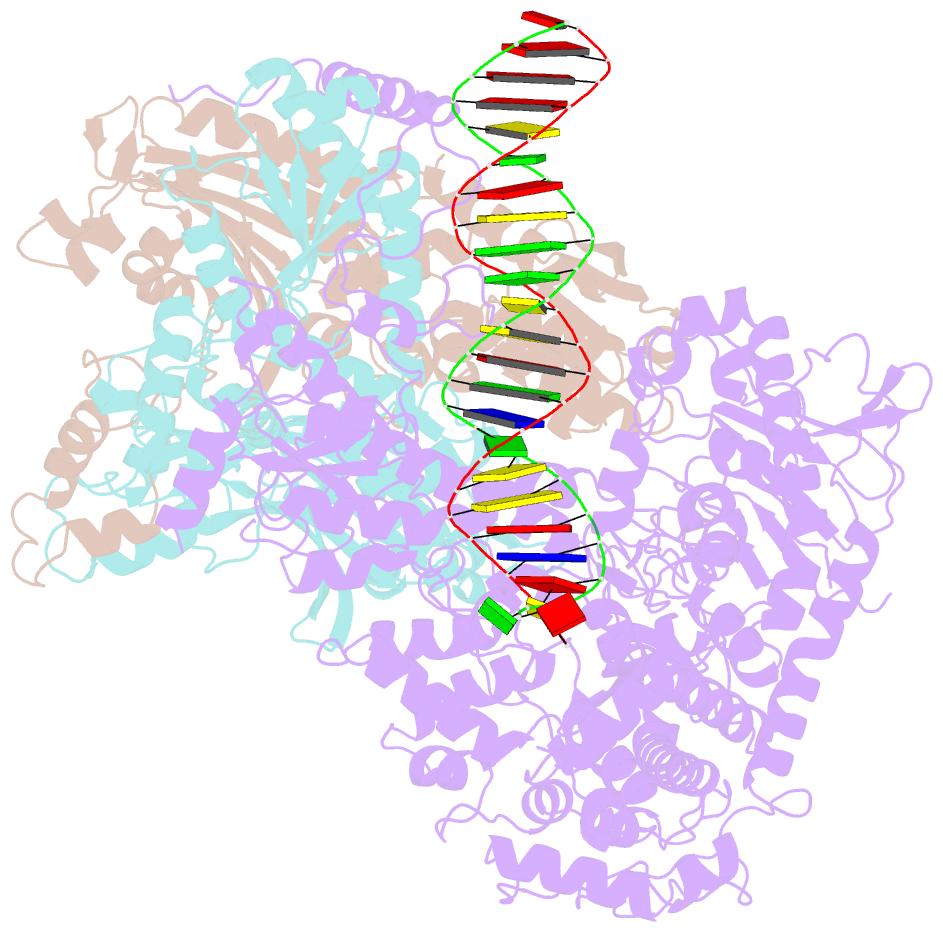
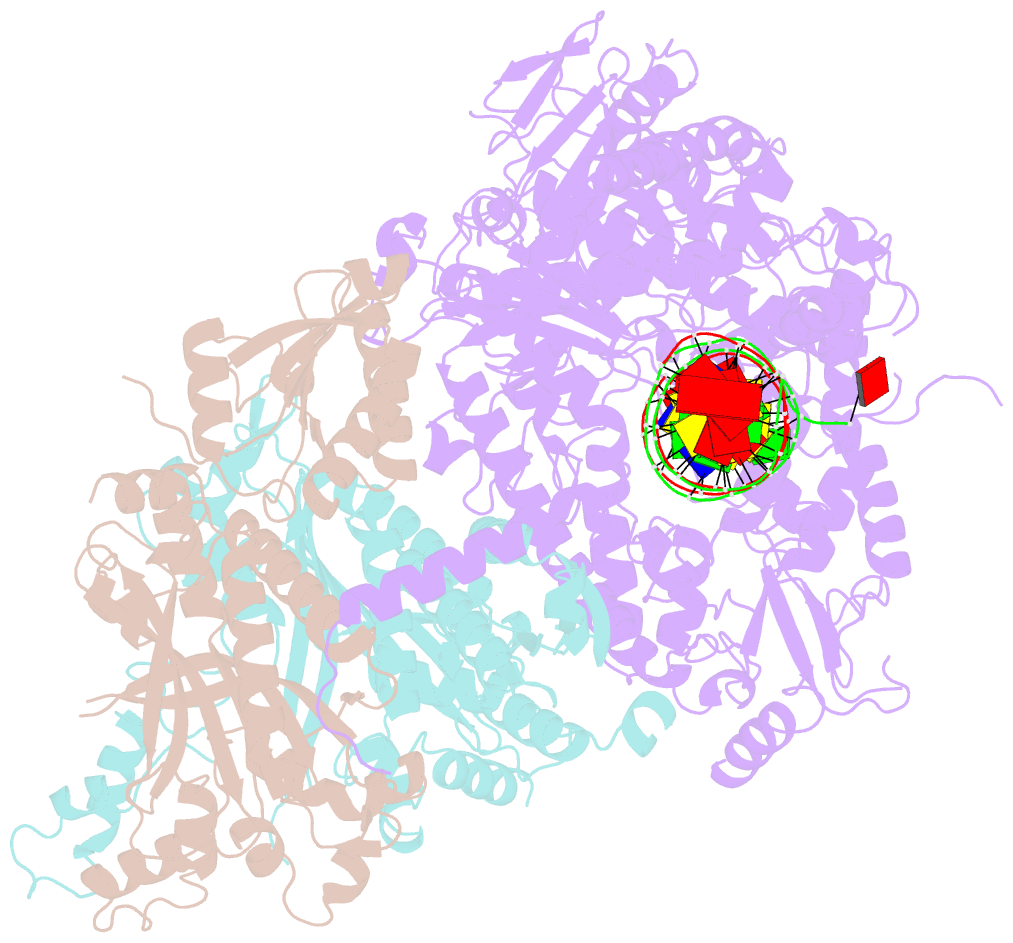
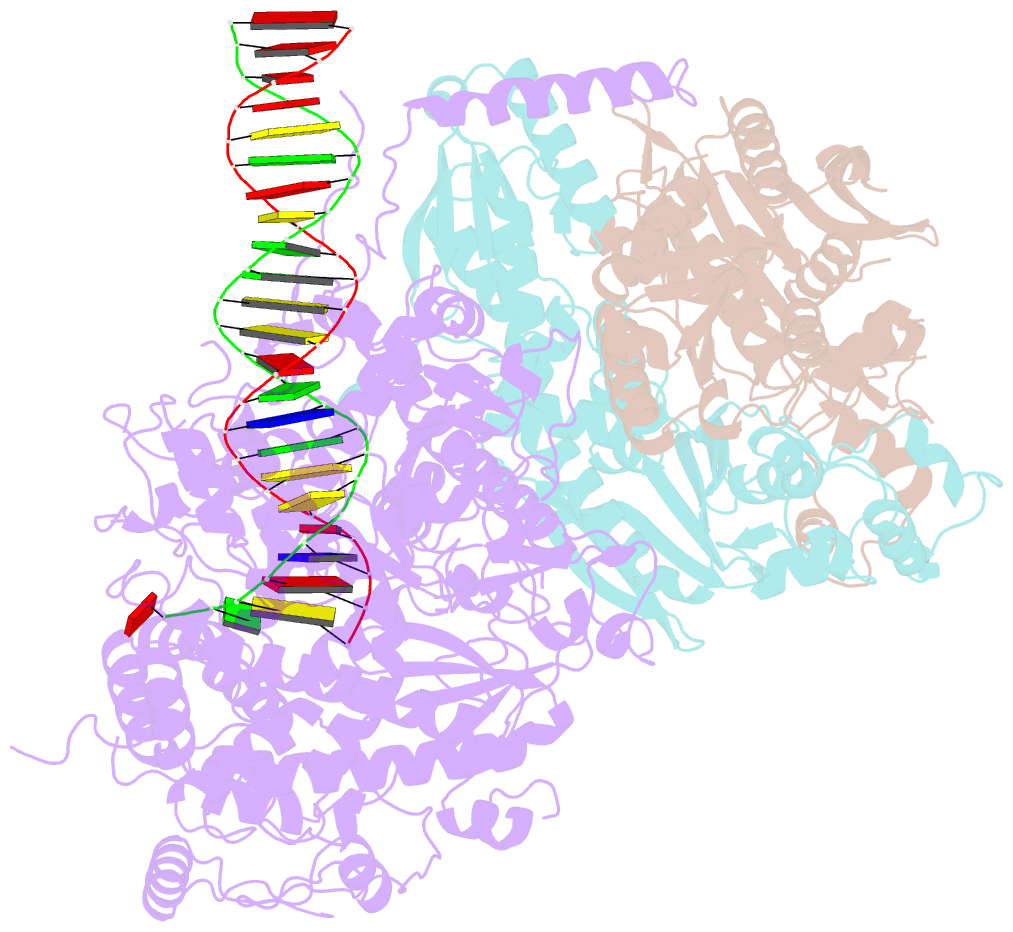
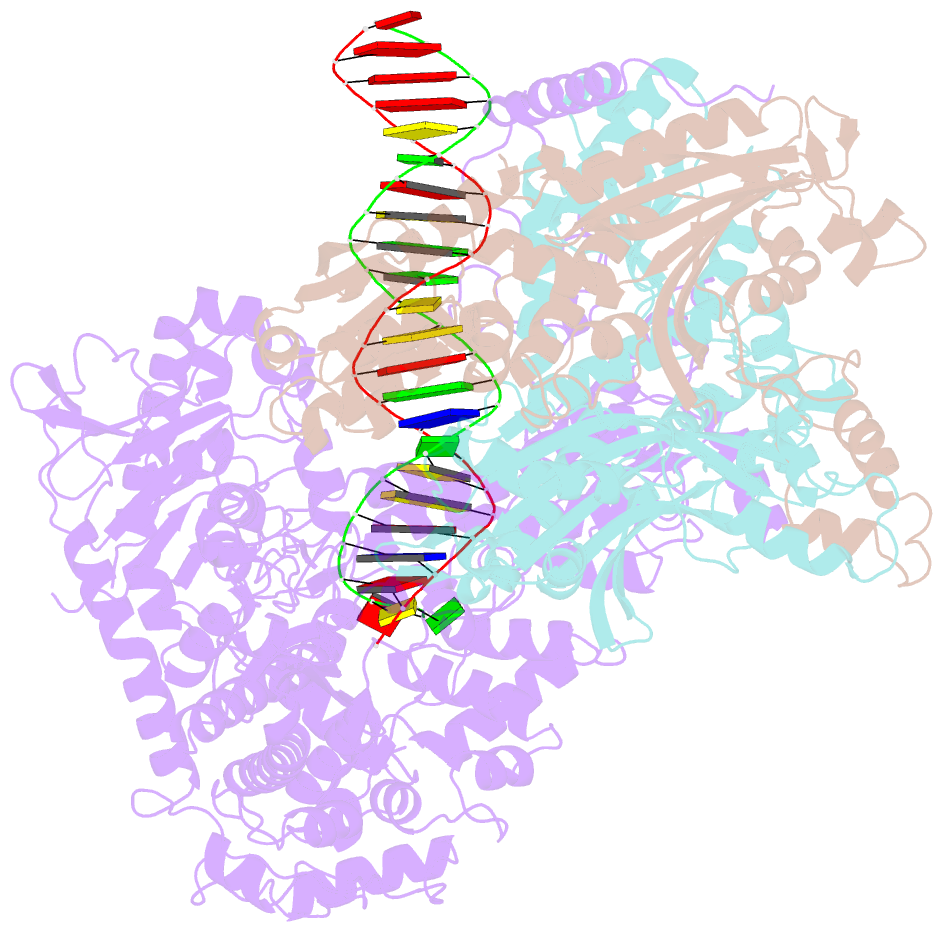
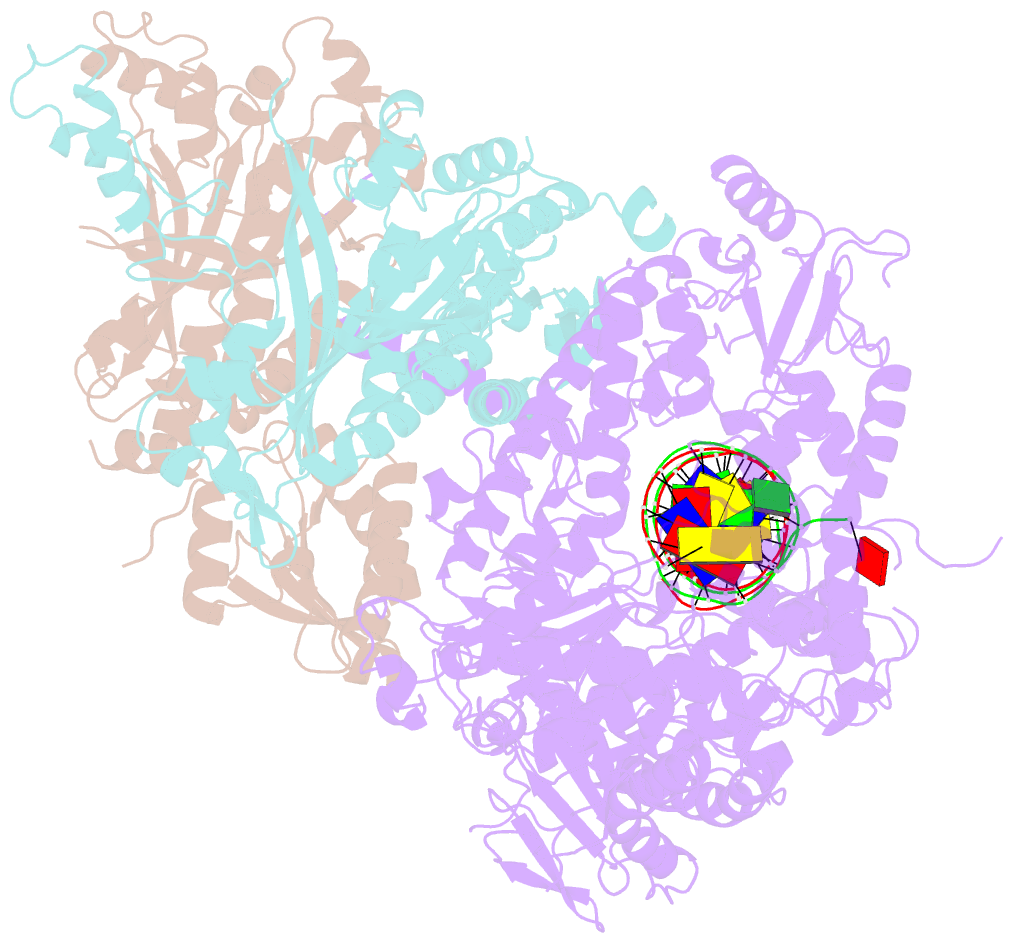
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8udl; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.37 Å)
- Summary
- Human mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma binary complex
- Reference
- Park J, Herrmann GK, Roy A, Shumate CK, Cisneros GA, Yin YW (2024): "An interaction network in the polymerase active site is a prerequisite for Watson-Crick base pairing in Pol gamma." Sci Adv, 10, eadl3214. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adl3214.
- Abstract
- The replication accuracy of DNA polymerase gamma (Pol γ) is essential for mitochondrial genome integrity. Mutation of human Pol γ arginine-853 has been linked to neurological diseases. Although not a catalytic residue, Pol γ arginine-853 mutants are void of polymerase activity. To identify the structural basis for the disease, we determined a crystal structure of the Pol γ mutant ternary complex with correct incoming nucleotide 2'-deoxycytidine 5'-triphosphate (dCTP). Opposite to the wild type that undergoes open-to-closed conformational changes when bound to a correct nucleotide that is essential for forming a catalytically competent active site, the mutant complex failed to undergo the conformational change, and the dCTP did not base pair with its Watson-Crick complementary templating residue. Our studies revealed that arginine-853 coordinates an interaction network that aligns the 3'-end of primer and dCTP with the catalytic residues. Disruption of the network precludes the formation of Watson-Crick base pairing and closing of the active site, resulting in an inactive polymerase.