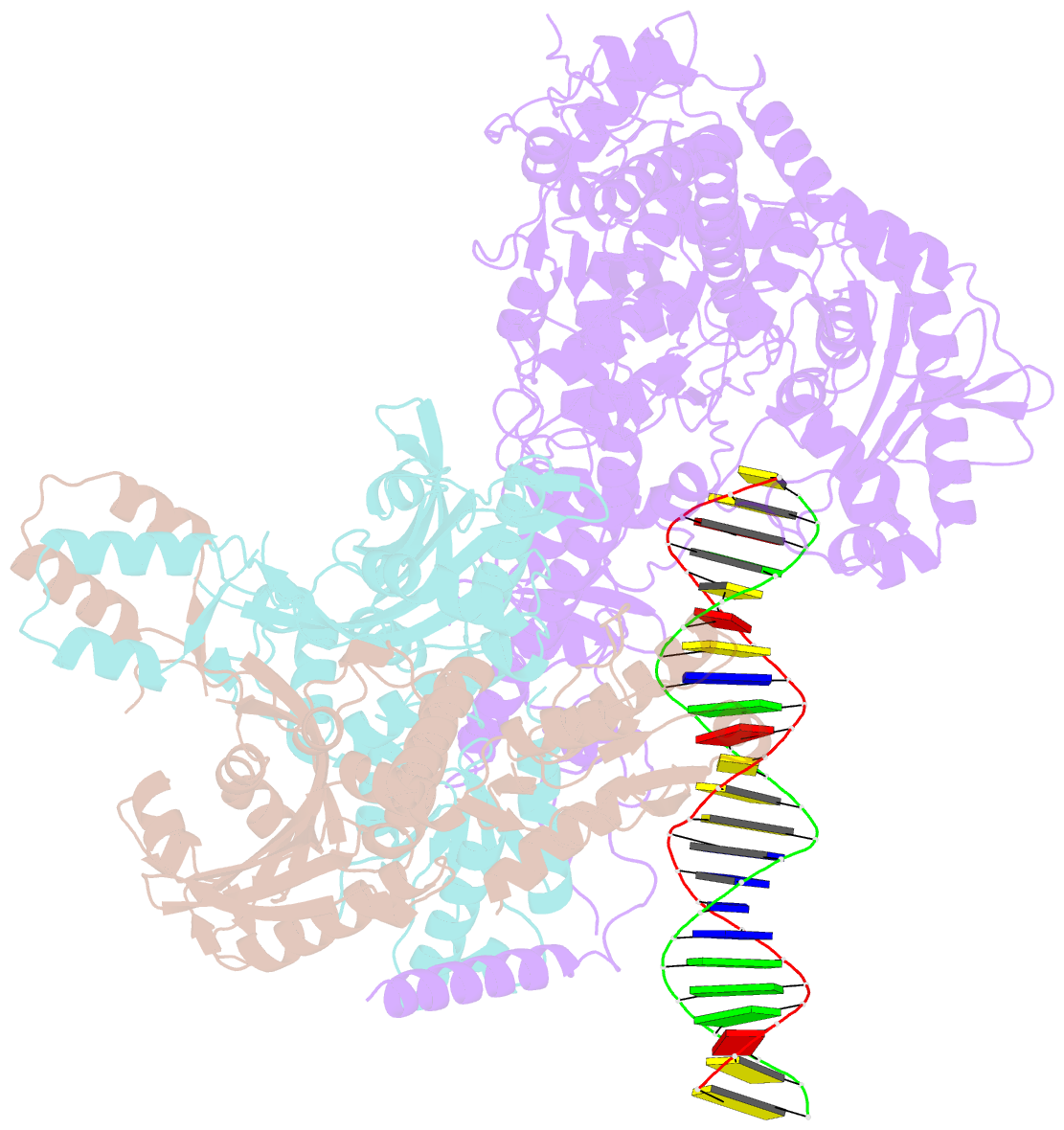
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8v55; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (4.2 Å)
- Summary
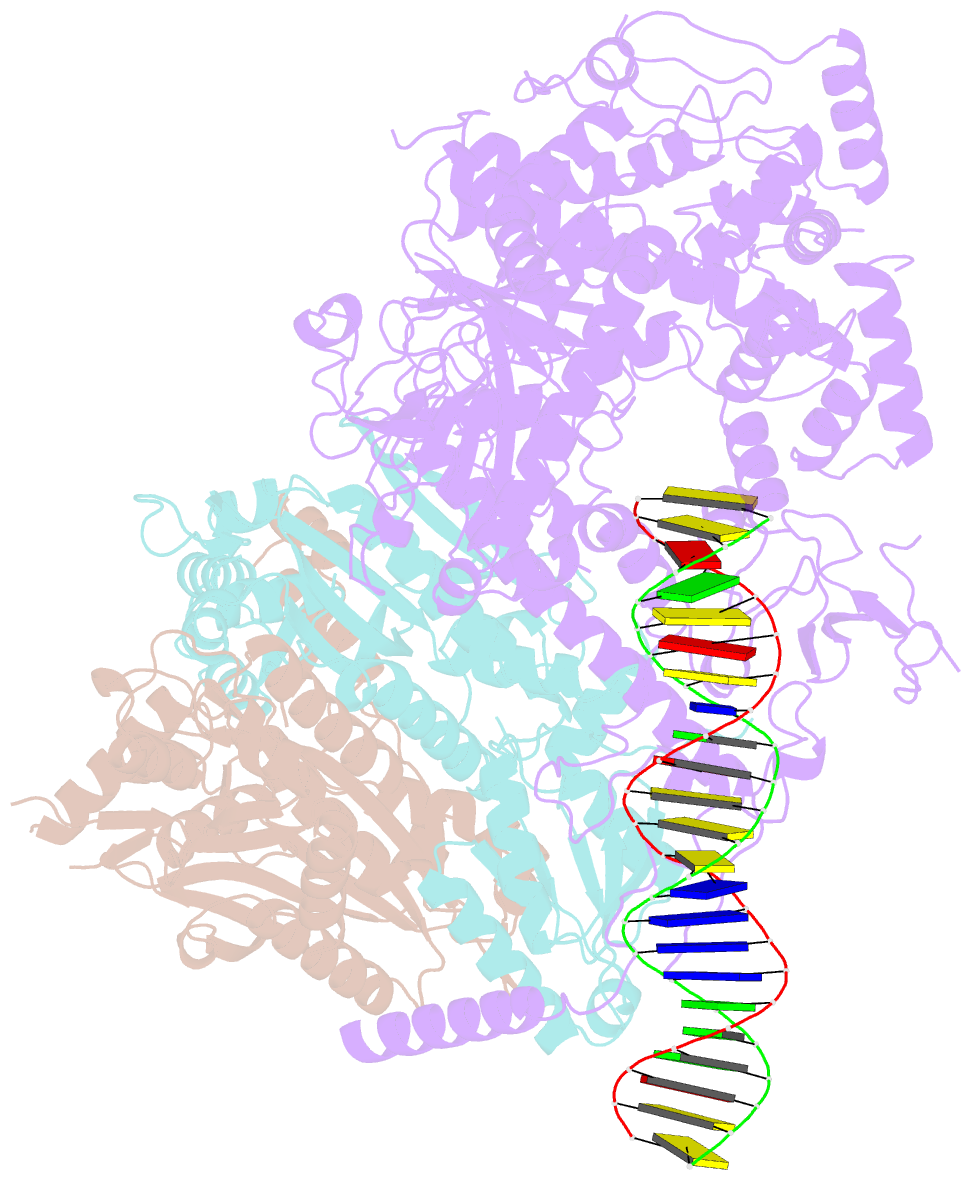
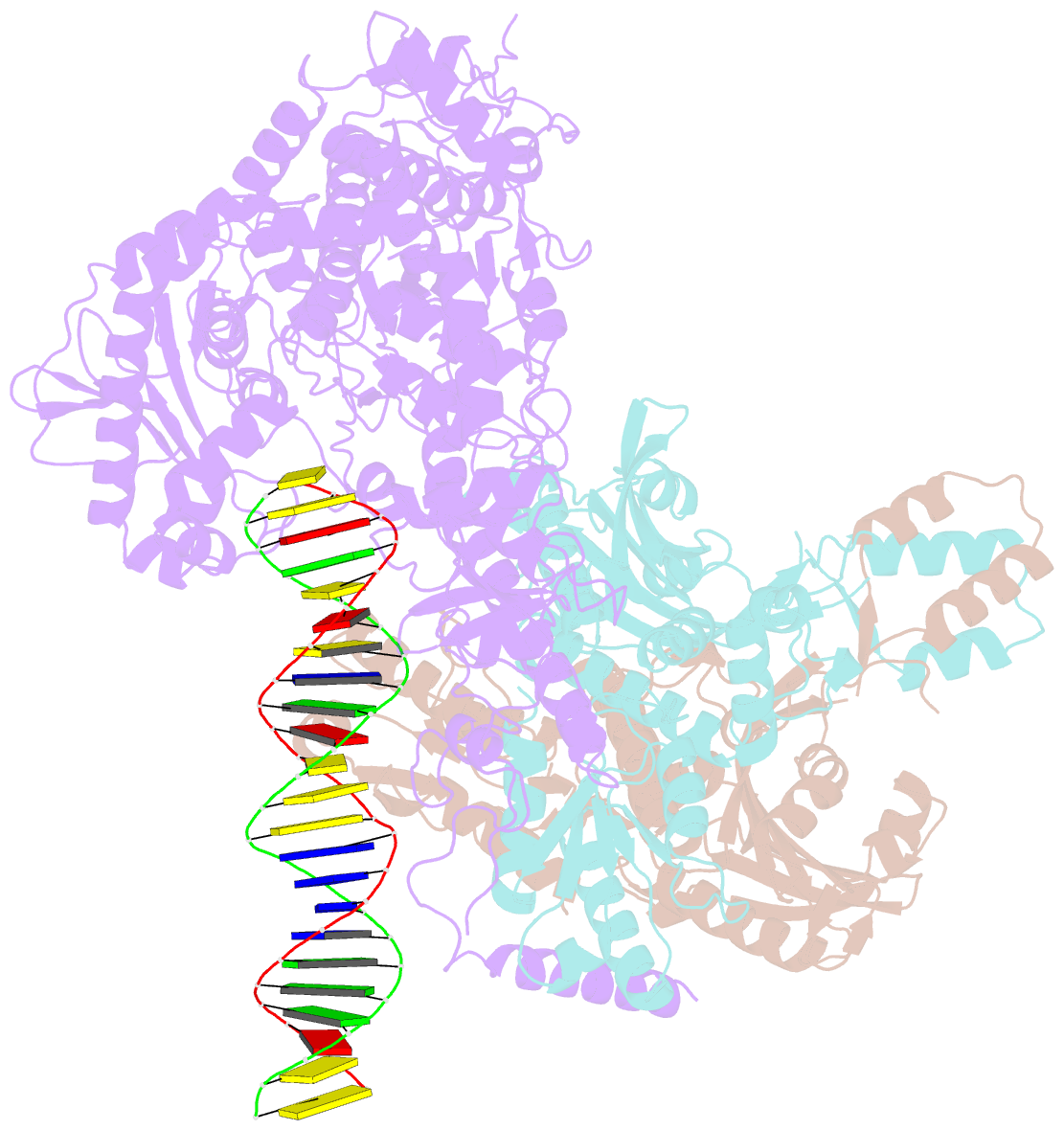
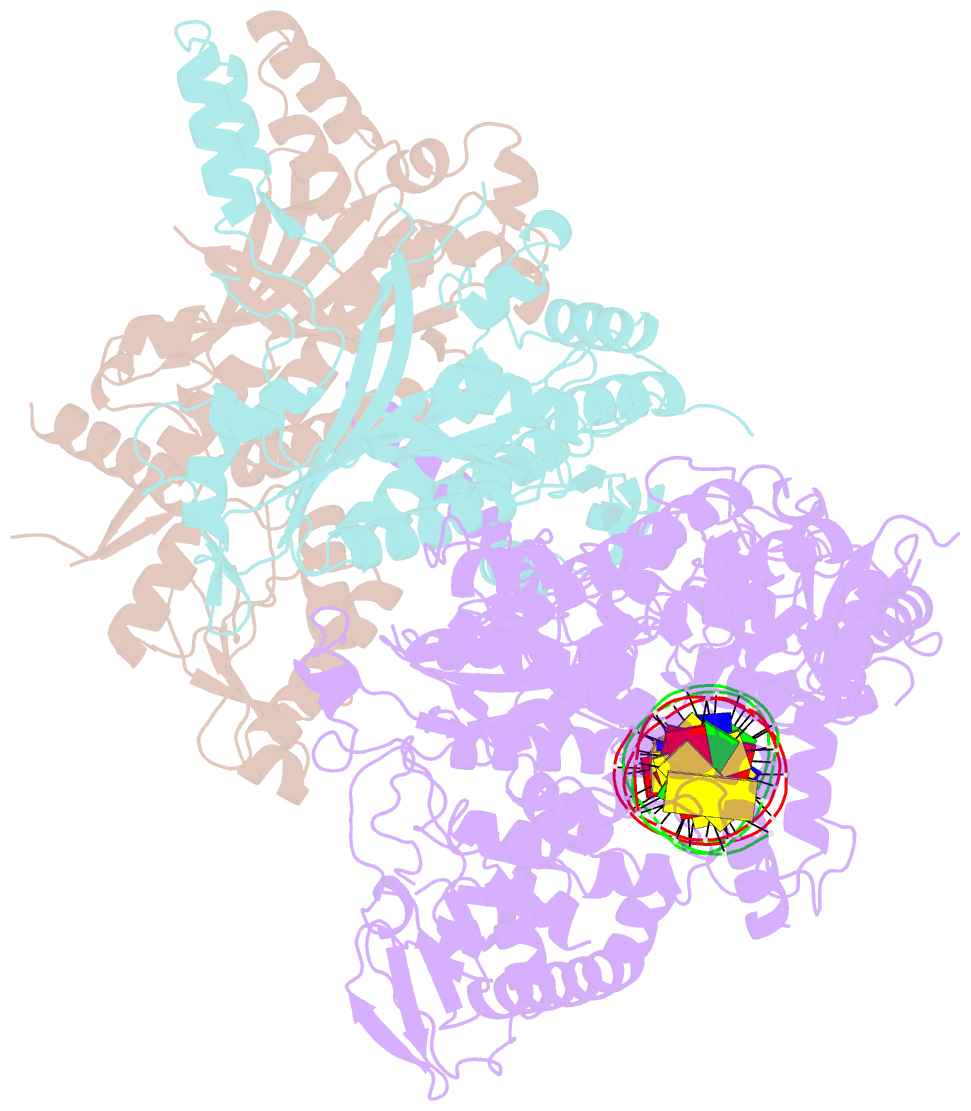
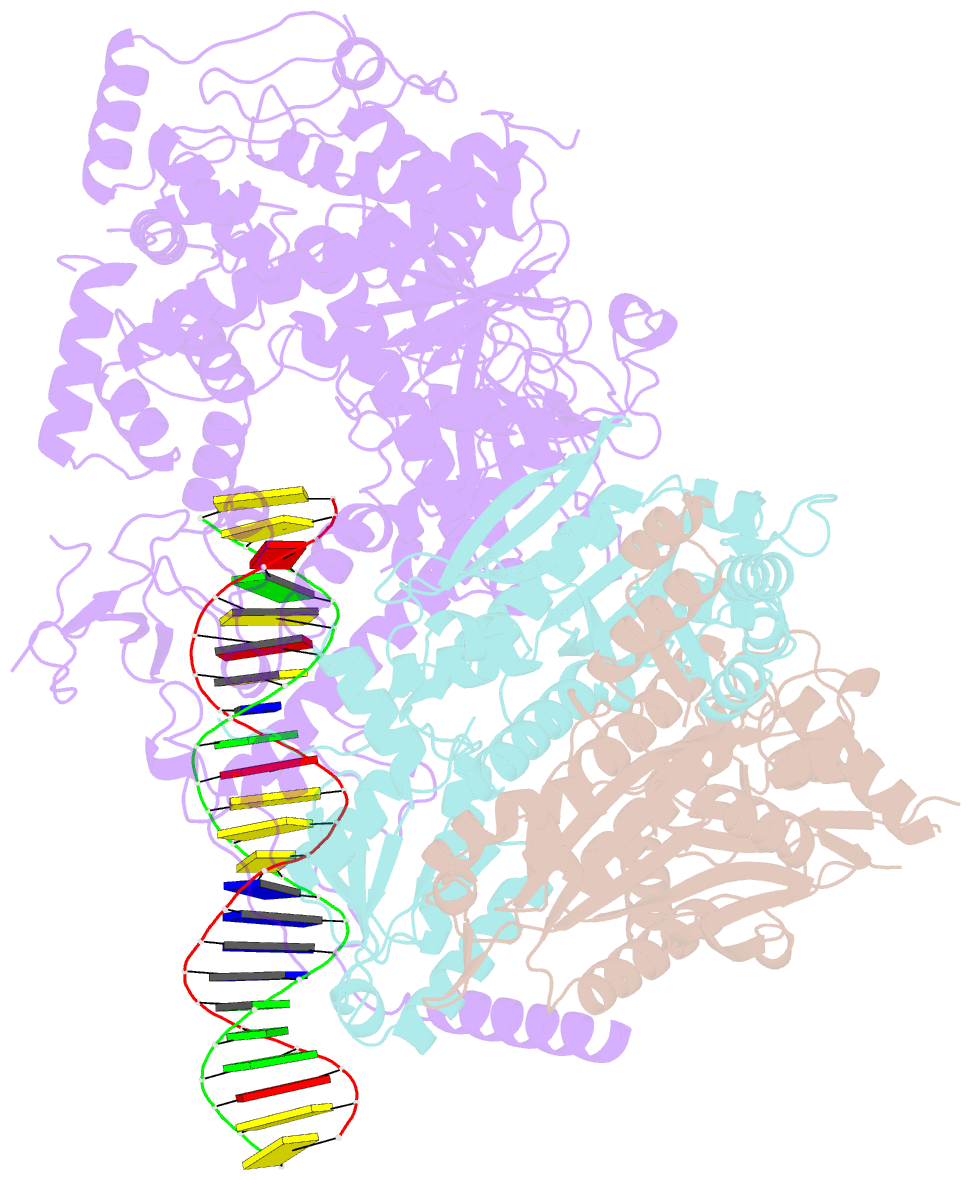
- Human mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma bound to a replication fork in an open conformation
- Reference
- Riccio AA, Brannon AJ, Krahn JM, Bouvette J, Williams JG, Borgnia MJ, Copeland WC (2024): "Coordinated DNA polymerization by Pol gamma and the region of LonP1 regulated proteolysis." Nucleic Acids Res., 52, 7863-7875. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae539.
- Abstract
- The replicative mitochondrial DNA polymerase, Polγ, and its protein regulation are essential for the integrity of the mitochondrial genome. The intricacies of Polγ regulation and its interactions with regulatory proteins, which are essential for fine-tuning polymerase function, remain poorly understood. Misregulation of the Polγ heterotrimer, consisting of (i) PolG, the polymerase catalytic subunit and (ii) PolG2, the accessory subunit, ultimately results in mitochondrial diseases. Here, we used single particle cryo-electron microscopy to resolve the structure of PolG in its apoprotein state and we captured Polγ at three intermediates within the catalytic cycle: DNA bound, engaged, and an active polymerization state. Chemical crosslinking mass spectrometry, and site-directed mutagenesis uncovered the region of LonP1 engagement of PolG, which promoted proteolysis and regulation of PolG protein levels. PolG2 clinical variants, which disrupted a stable Polγ complex, led to enhanced LonP1-mediated PolG degradation. Overall, this insight into Polγ aids in an understanding of mitochondrial DNA replication and characterizes how machinery of the replication fork may be targeted for proteolytic degradation when improperly functioning.