Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8whb; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- gene regulation
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.17 Å)
- Summary
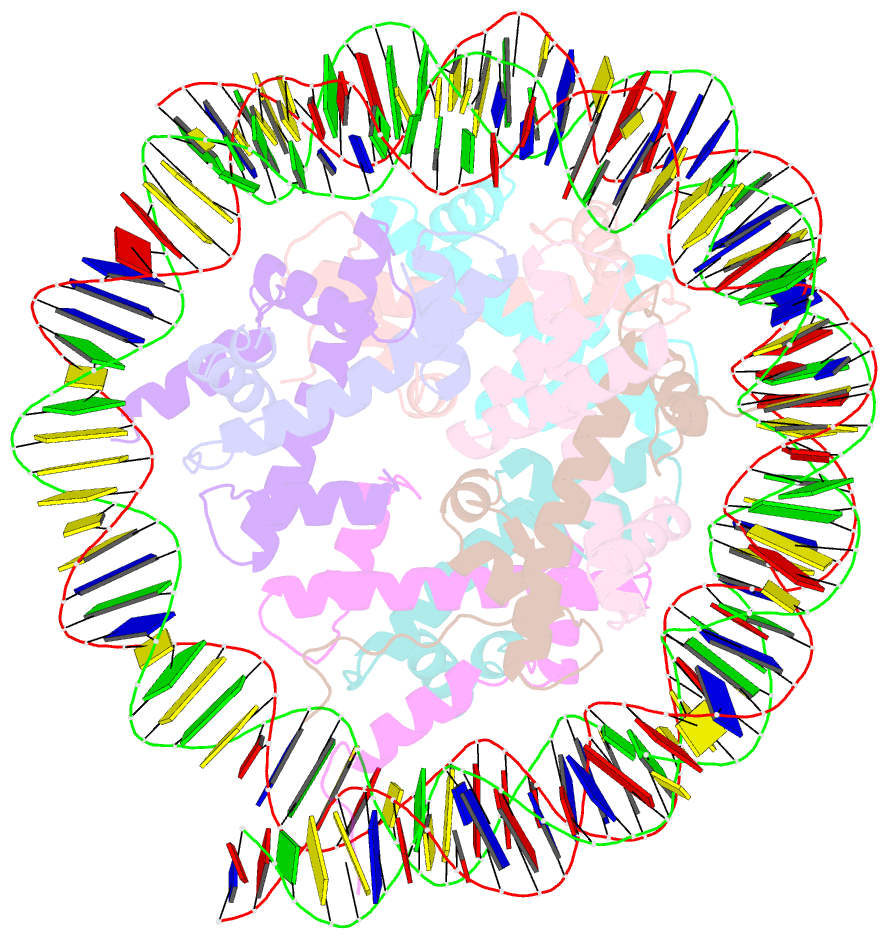
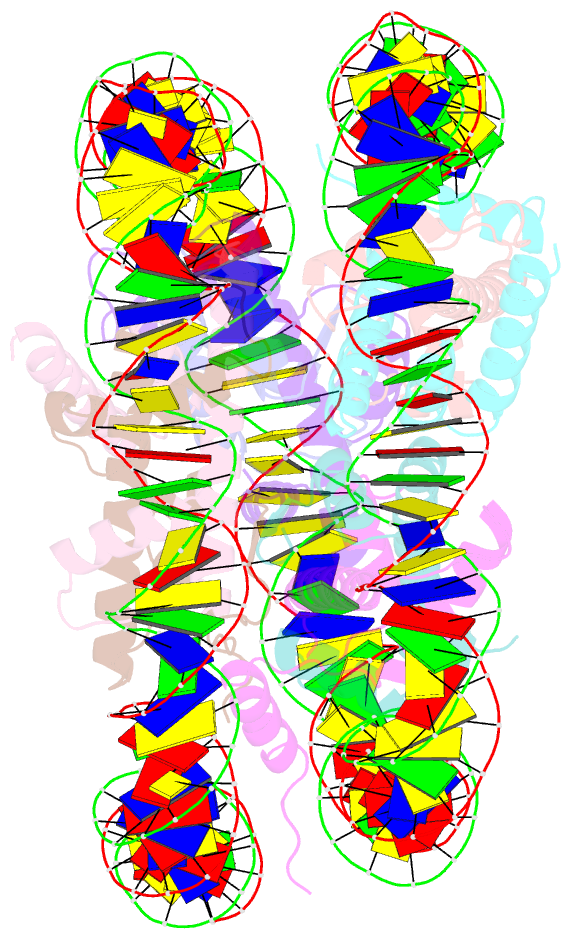
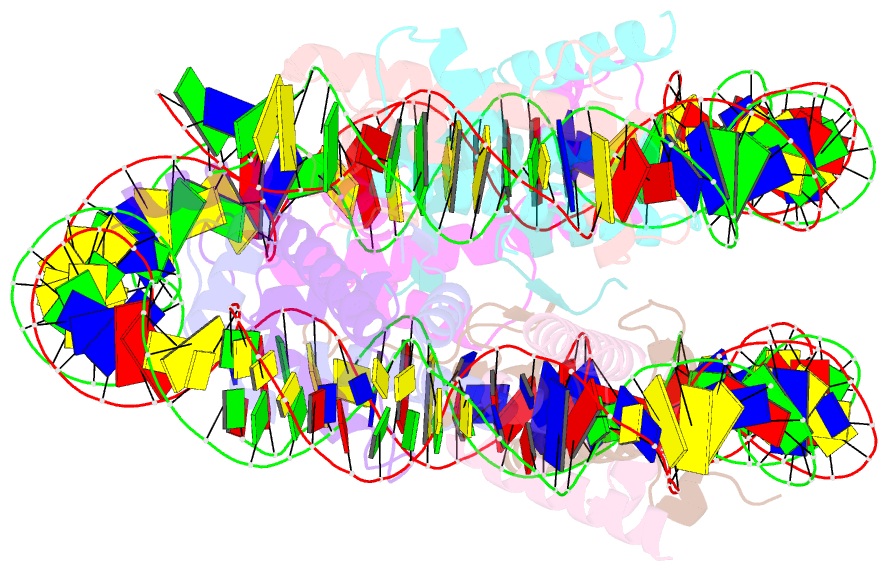
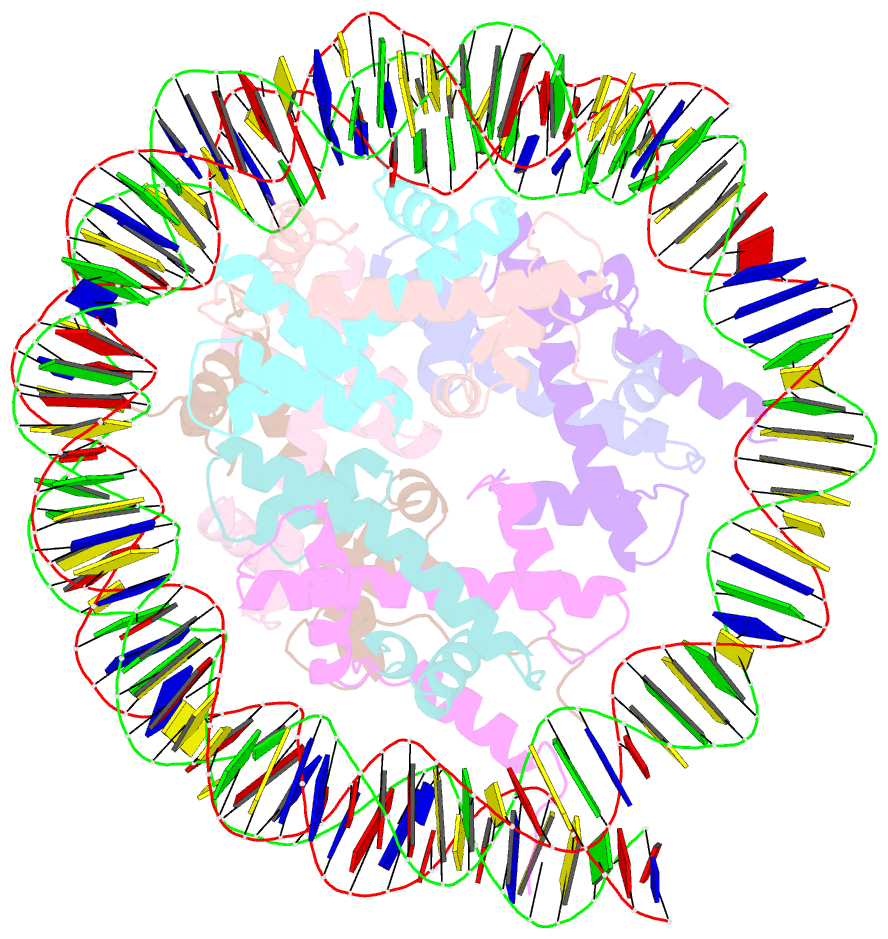
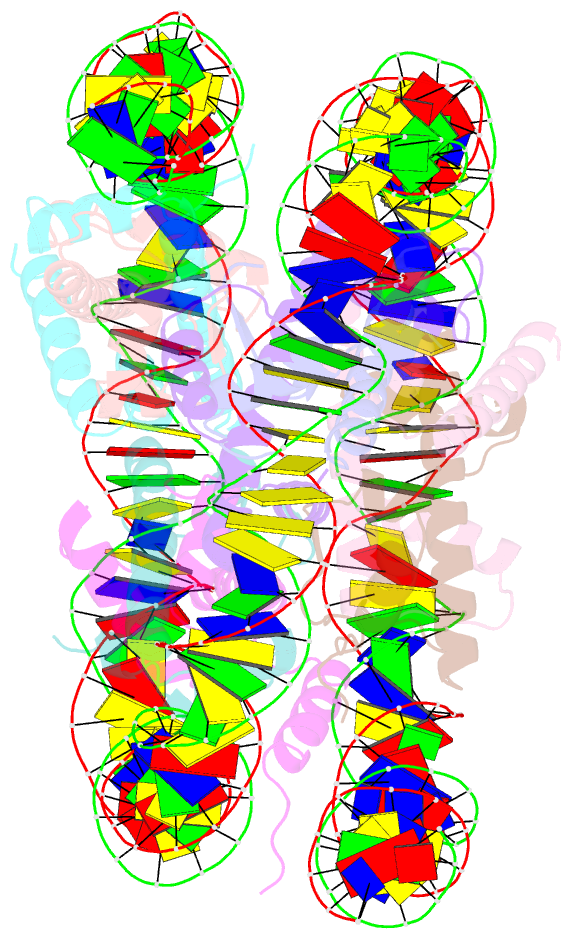
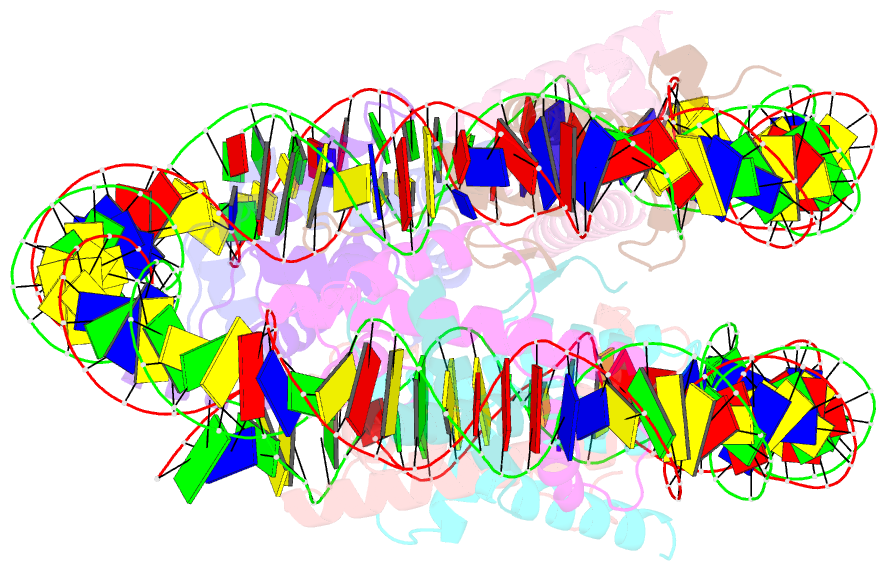
- Structure of nucleosome core particle of arabidopsis thaliana
- Reference
- Liu Y, Zhang Z, Hu H, Chen W, Zhang F, Wang Q, Wang C, Yan K, Du J (2024): "Molecular basis of chromatin remodelling by DDM1 involved in plant DNA methylation." Nat.Plants, 10, 374-380. doi: 10.1038/s41477-024-01640-z.
- Abstract
- Eukaryotic gene regulation occurs at the chromatin level, which requires changing the chromatin structure by a group of ATP-dependent DNA translocases-namely, the chromatin remodellers1. In plants, chromatin remodellers function in various biological processes and possess both conserved and plant-specific components2-5. DECREASE IN DNA METHYLATION 1 (DDM1) is a plant chromatin remodeller that plays a key role in the maintenance DNA methylation6-11. Here we determined the structures of Arabidopsis DDM1 in complex with nucleosome in ADP-BeFx-bound, ADP-bound and nucleotide-free conformations. We show that DDM1 specifically recognizes the H4 tail and nucleosomal DNA. The conformational differences between ADP-BeFx-bound, ADP-bound and nucleotide-free DDM1 suggest a chromatin remodelling cycle coupled to ATP binding, hydrolysis and ADP release. This, in turn, triggers conformational changes in the DDM1-bound nucleosomal DNA, which alters the nucleosome structure and promotes DNA sliding. Together, our data reveal the molecular basis of chromatin remodelling by DDM1.