Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8wo8; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.78 Å)
- Summary
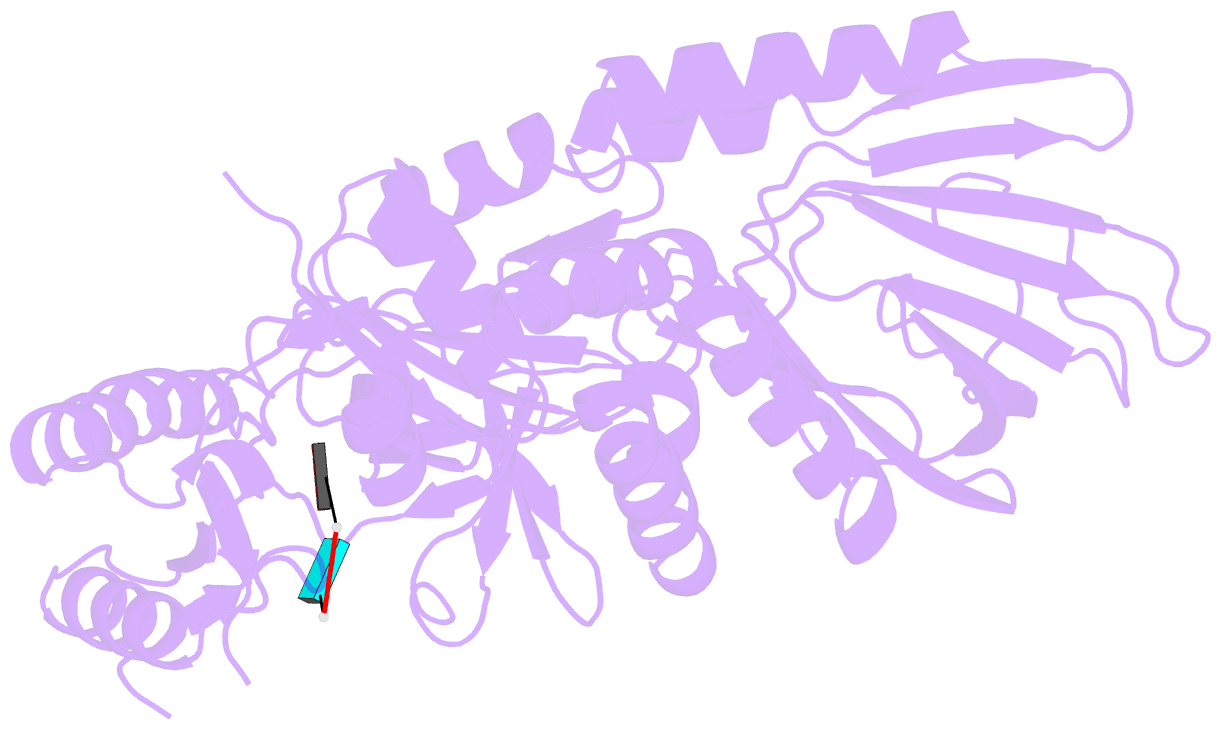
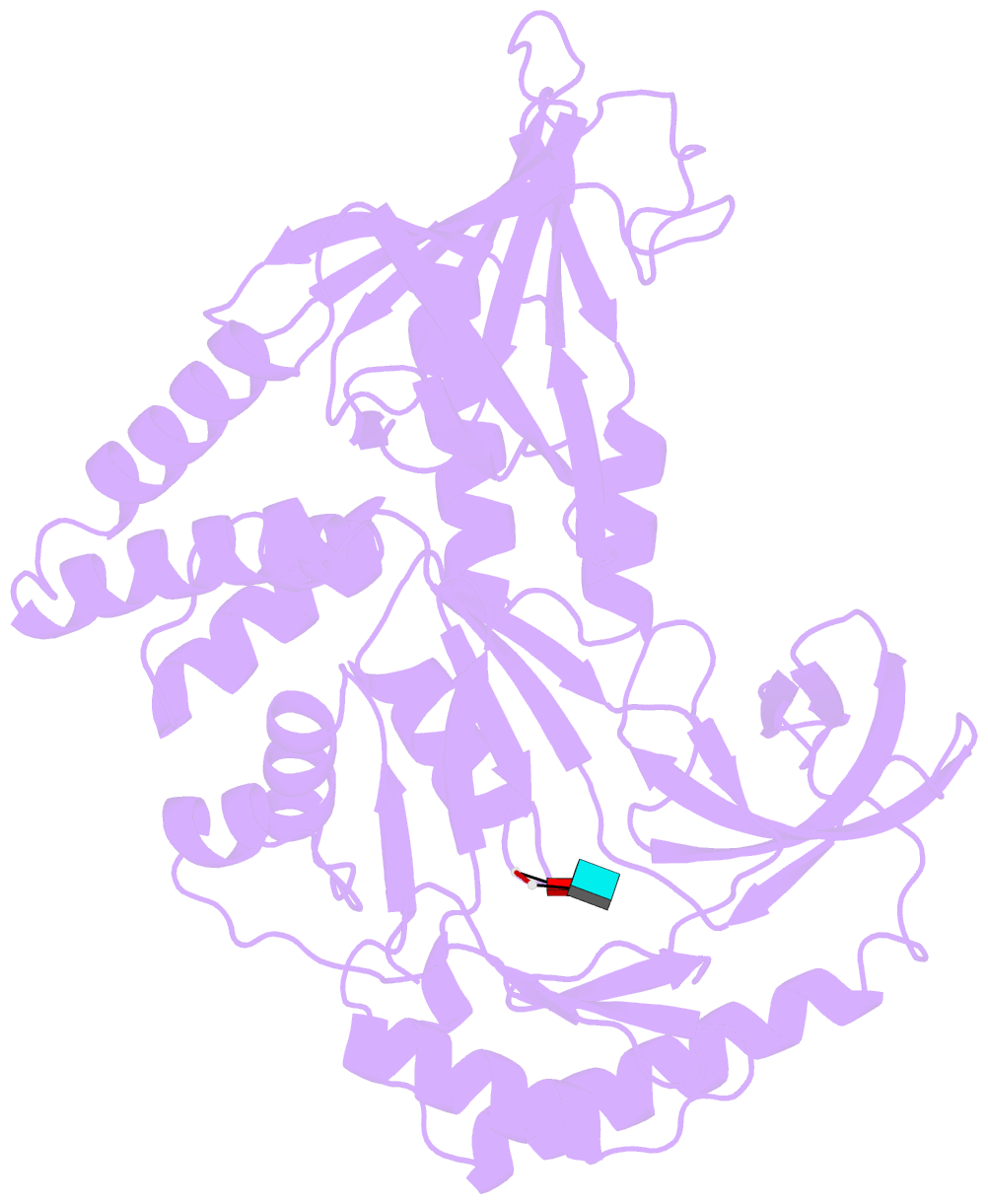
- Crystal structure of an RNA-binding protein, fau-1, from pyrococcus furiosus
- Reference
- Kawai G, Okada K, Baba S, Sato A, Sakamoto T, Kanai A (2024): "Homo-trimeric structure of the ribonuclease for rRNA processing, FAU-1, from Pyrococcus furiosus." J.Biochem., 175, 671-676. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvae010.
- Abstract
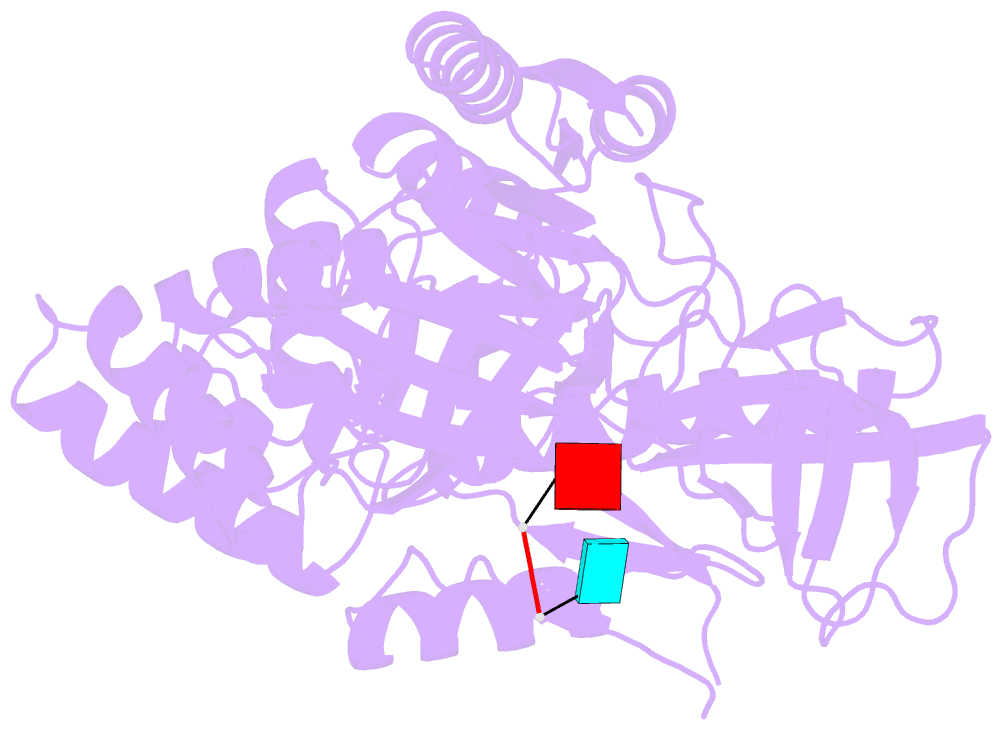
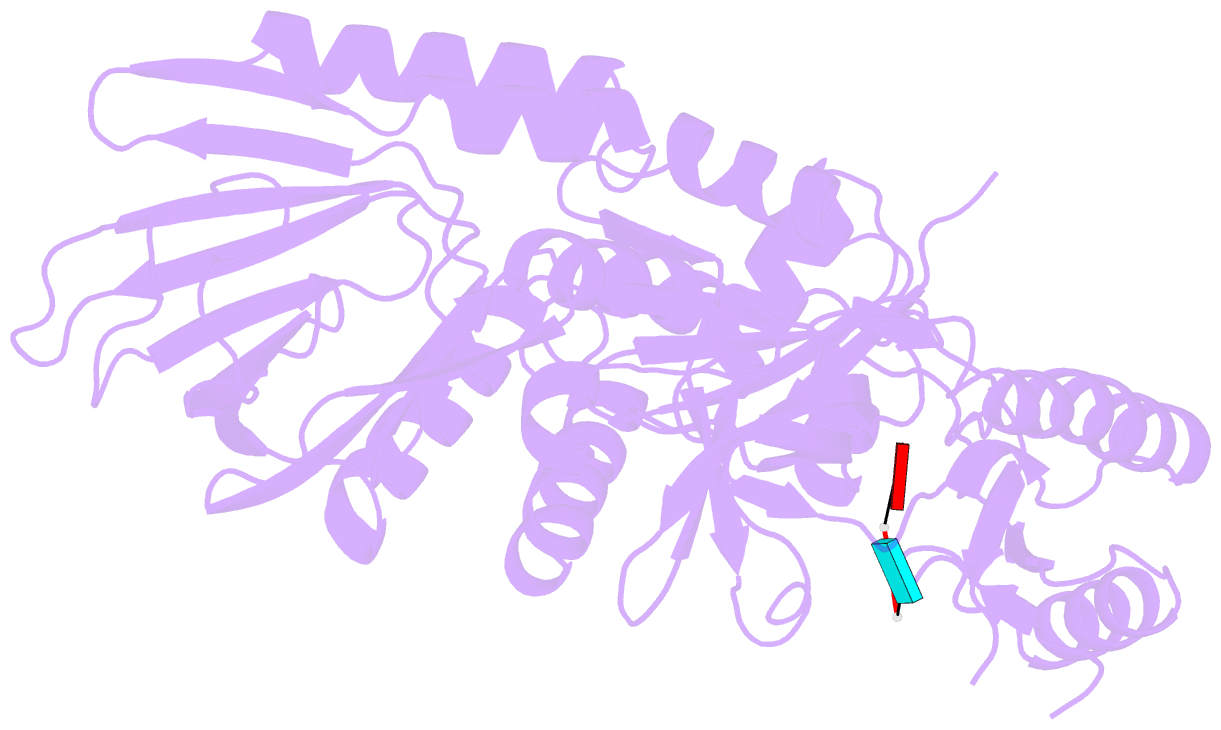
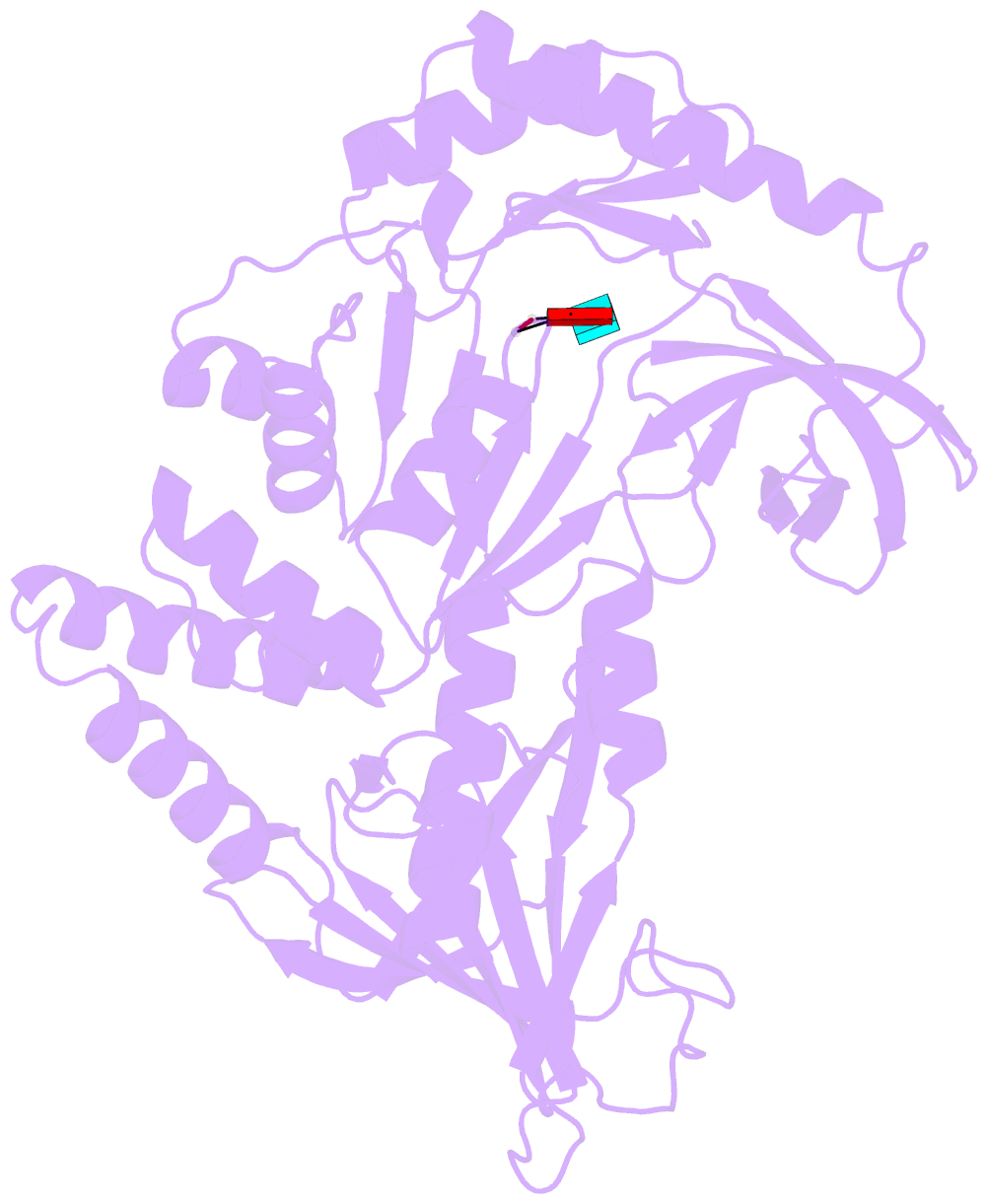
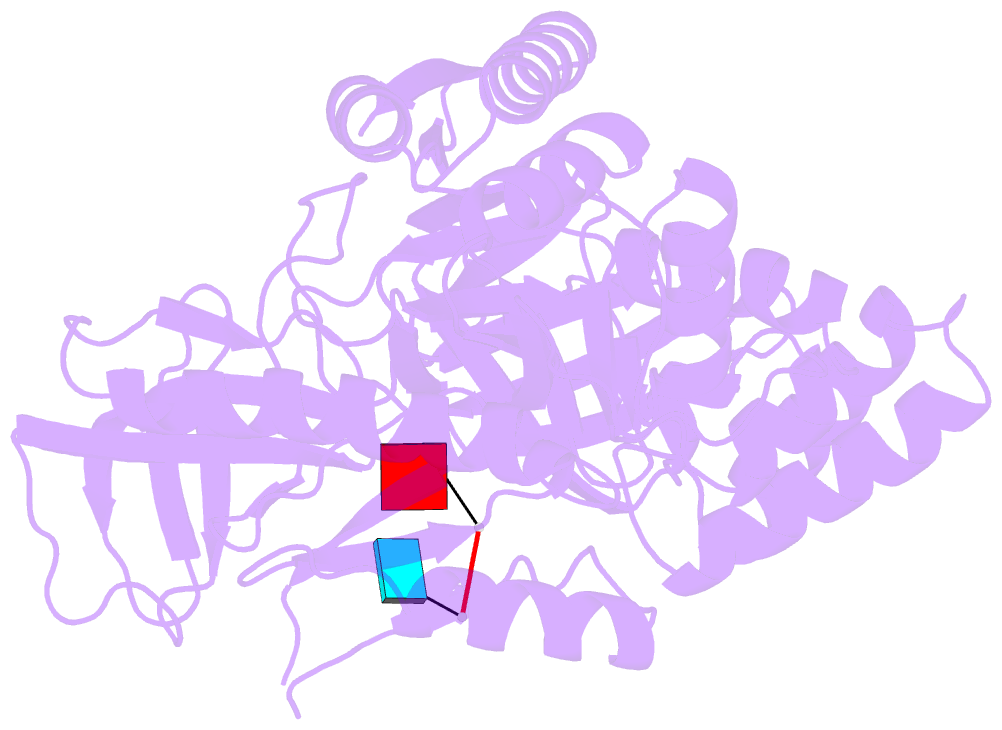
- Crystal structure of a ribonuclease for rRNA processing, FAU-1, from Pyrococcus furiosus was determined with the resolution of 2.57 Å in a homo-trimeric form. The monomer structure consists of two domains, N-terminal and C-terminal domains. C-terminal domain forms trimer and each N-terminal domain locates outside of the trimer core. In the obtained crystal, a dinucleotide, pApUp, was bound to the N-terminal domain, indicating that N-terminal domain has the RNA-binding ability. The affinities to RNA of FAU-1 and a fragment corresponding to the N-terminal domain, FAU-ΔC, were confirmed by PAGE and NMR. Interestingly, well dispersed NMR signals were observed at 318 K, indicating that the FAU-ΔC-F18 complex form an ordered structure at higher temperature. As predicted in our previous works, FAU-1 and RNase E show a structural similarity in their RNA binding regions. However, structural similarity between RNase E and FAU-1 could be found in the limited regions of the N-terminal domain. On the other hand, structural similarity between C-terminal domain and some proteins including a phosphatase was found. Thus, it is possible that the catalytic site is located in C-terminal domain.