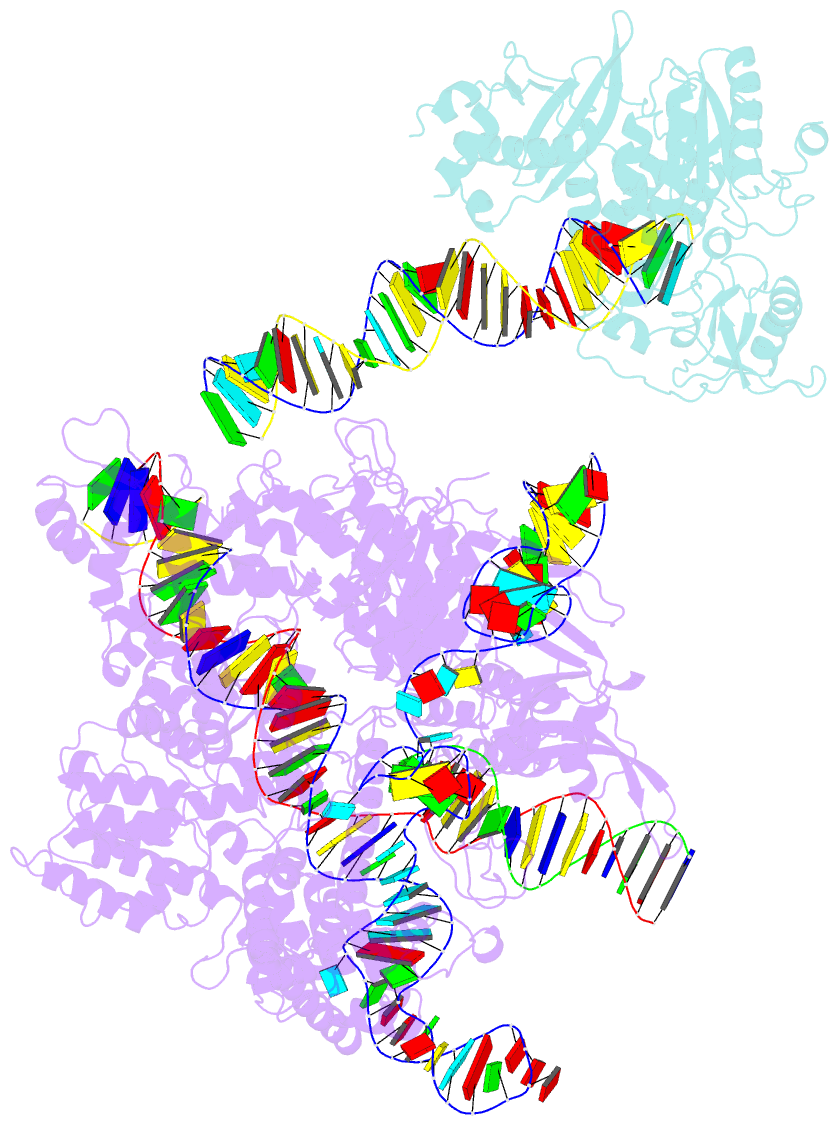
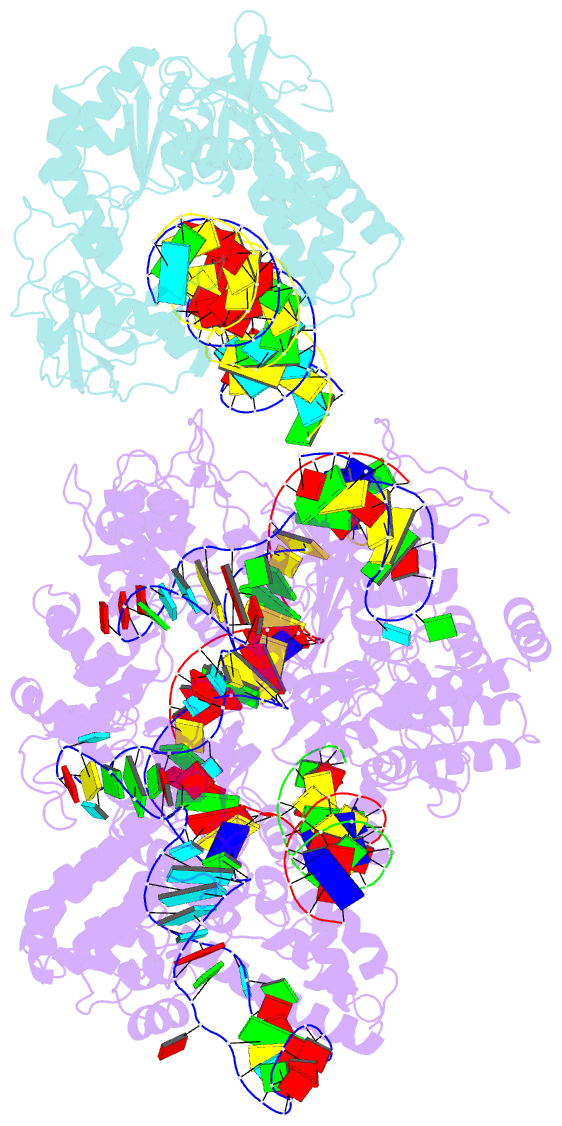
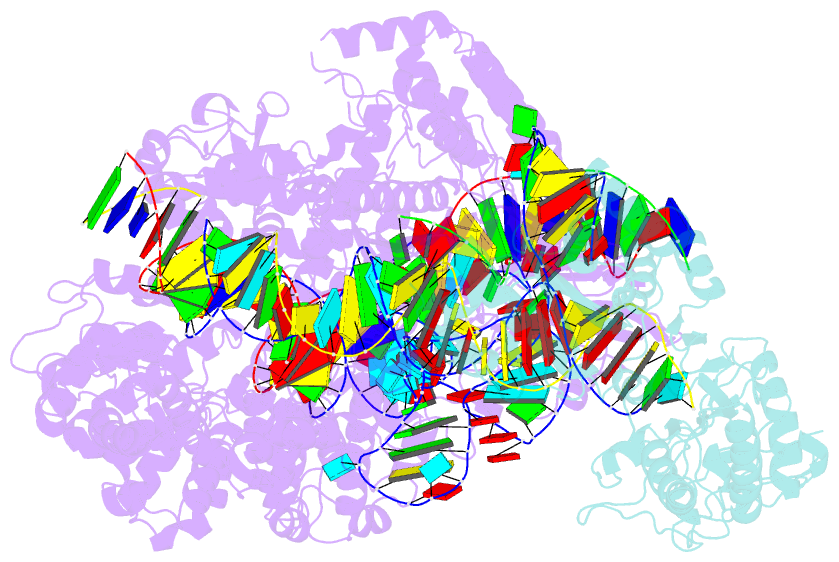
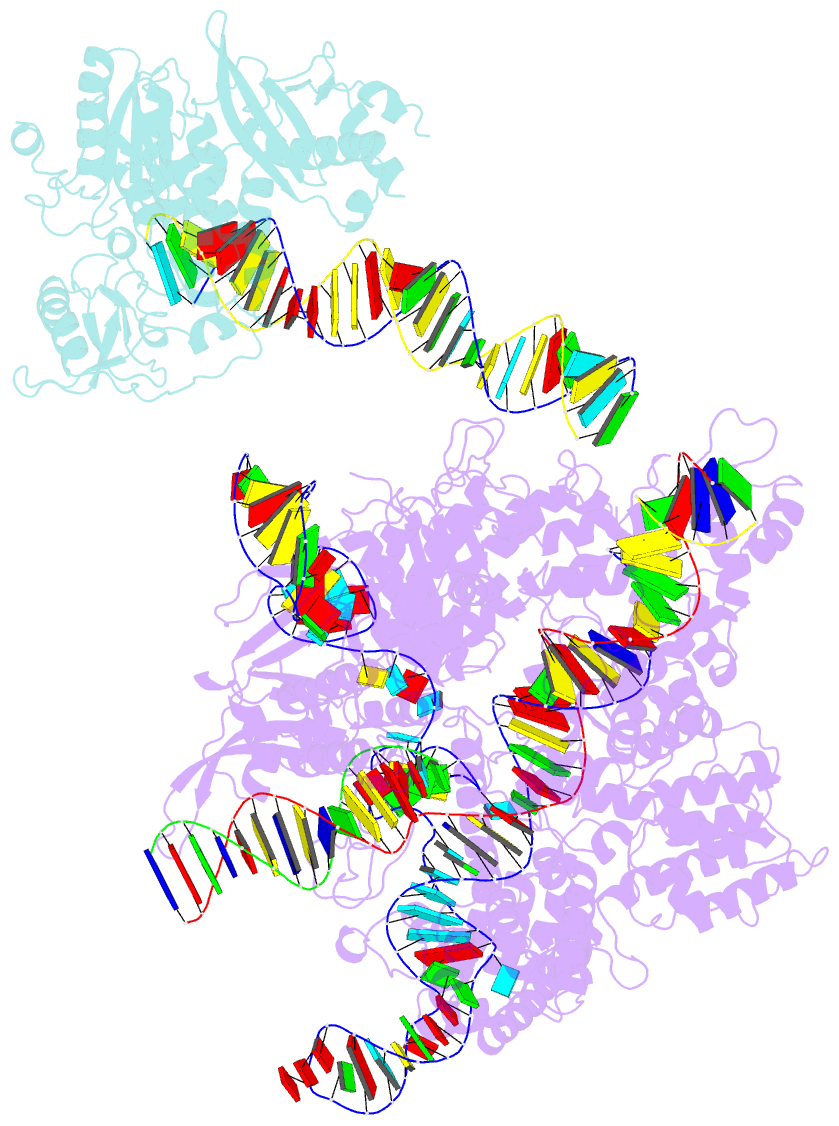
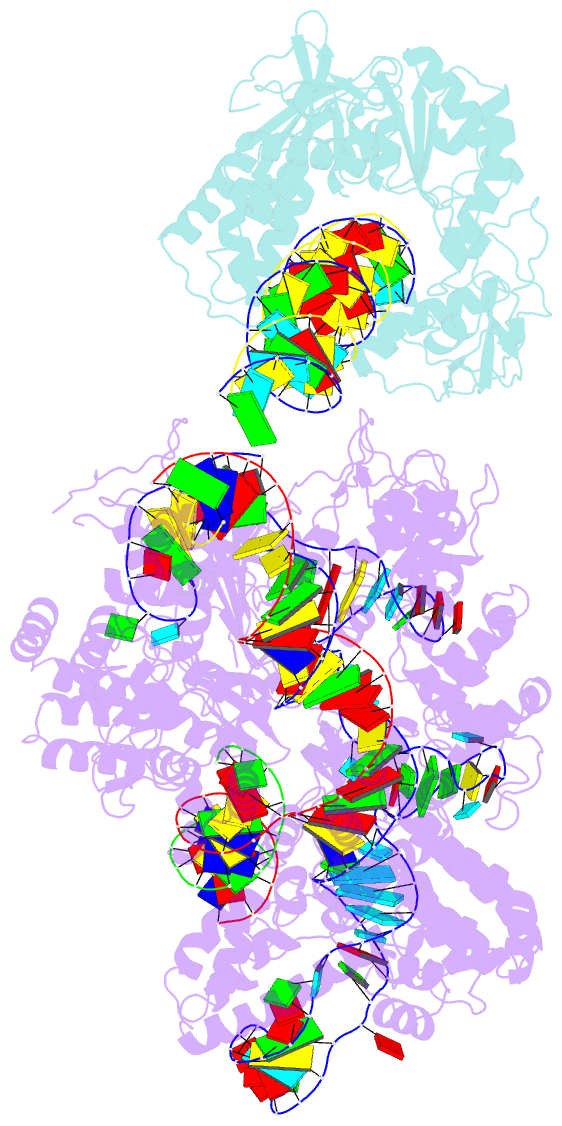
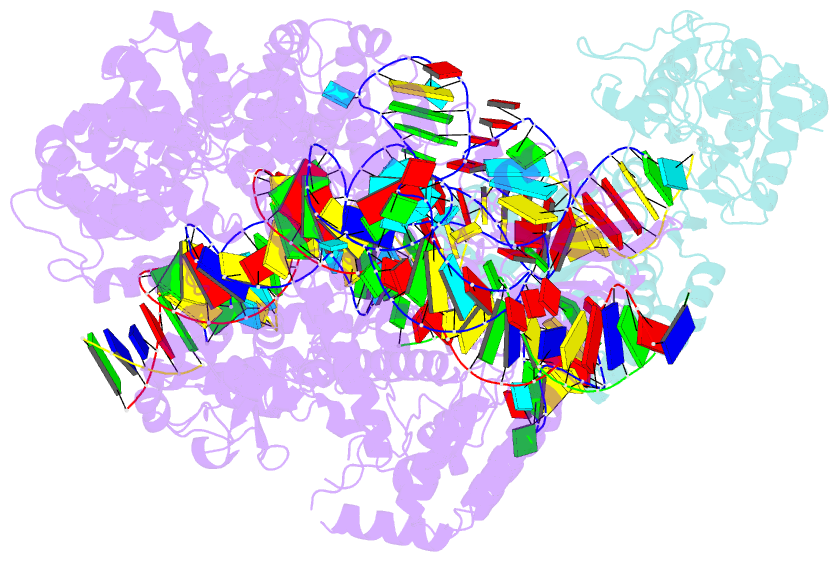
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8wuv; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.0 Å)
- Summary
- Spcas9-mmlv rt-pegrna-target DNA complex (elongation 16-nt)
- Reference
- Shuto Y, Nakagawa R, Zhu S, Hoki M, Omura SN, Hirano H, Itoh Y, Zhang F, Nureki O (2024): "Structural basis for pegRNA-guided reverse transcription by a prime editor." Nature, 631, 224-231. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07497-8.
- Abstract
- The prime editor system composed of Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 nickase (nSpCas9) and engineered Moloney murine leukaemia virus reverse transcriptase (M-MLV RT) collaborates with a prime editing guide RNA (pegRNA) to facilitate a wide variety of precise genome edits in living cells1. However, owing to a lack of structural information, the molecular mechanism of pegRNA-guided reverse transcription by the prime editor remains poorly understood. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of the SpCas9-M-MLV RTΔRNaseH-pegRNA-target DNA complex in multiple states. The termination structure, along with our functional analysis, reveals that M-MLV RT extends reverse transcription beyond the expected site, resulting in scaffold-derived incorporations that cause undesired edits at the target loci. Furthermore, structural comparisons among the pre-initiation, initiation and elongation states show that M-MLV RT remains in a consistent position relative to SpCas9 during reverse transcription, whereas the pegRNA-synthesized DNA heteroduplex builds up along the surface of SpCas9. On the basis of our structural insights, we rationally engineered pegRNA variants and prime-editor variants in which M-MLV RT is fused within SpCas9. Collectively, our findings provide structural insights into the stepwise mechanism of prime editing, and will pave the way for the development of a versatile prime editing toolbox.