Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8wzc; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.925 Å)
- Summary
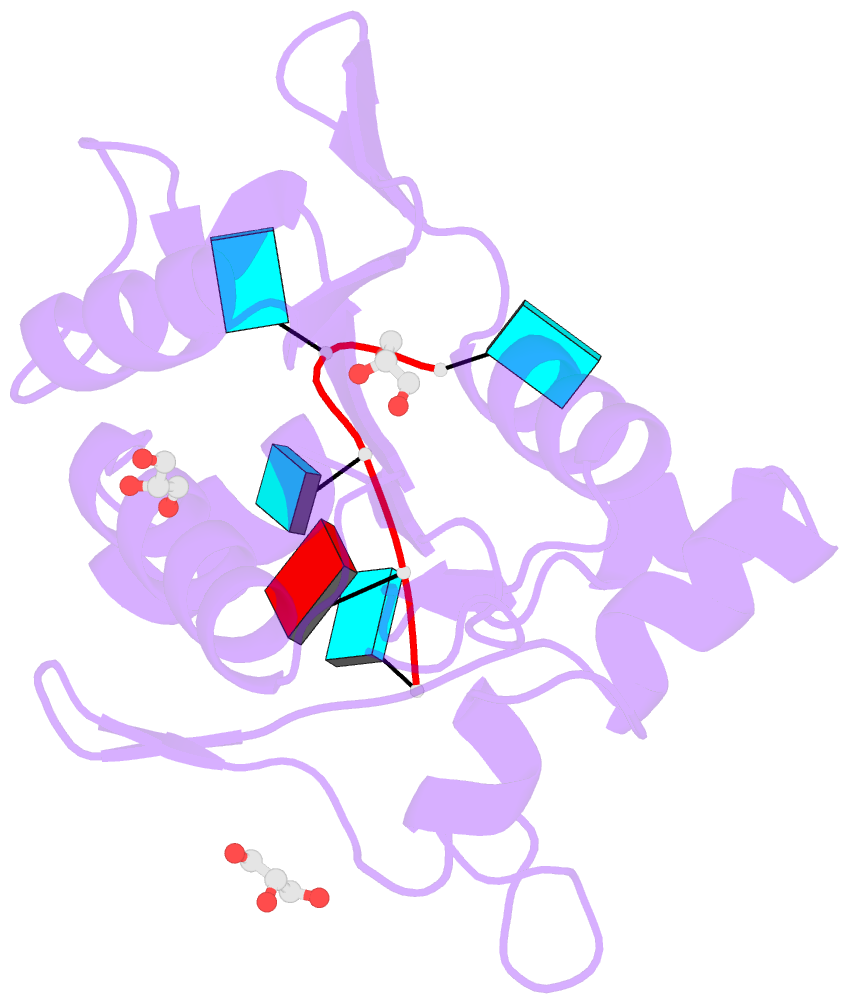
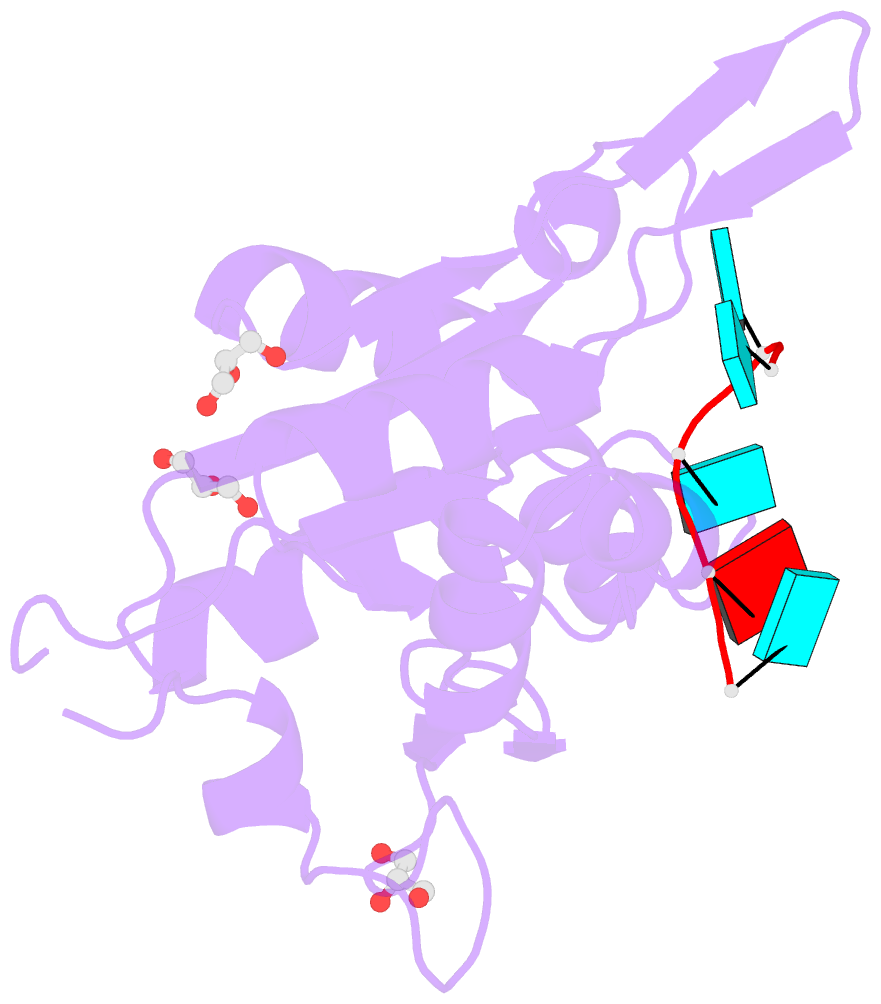
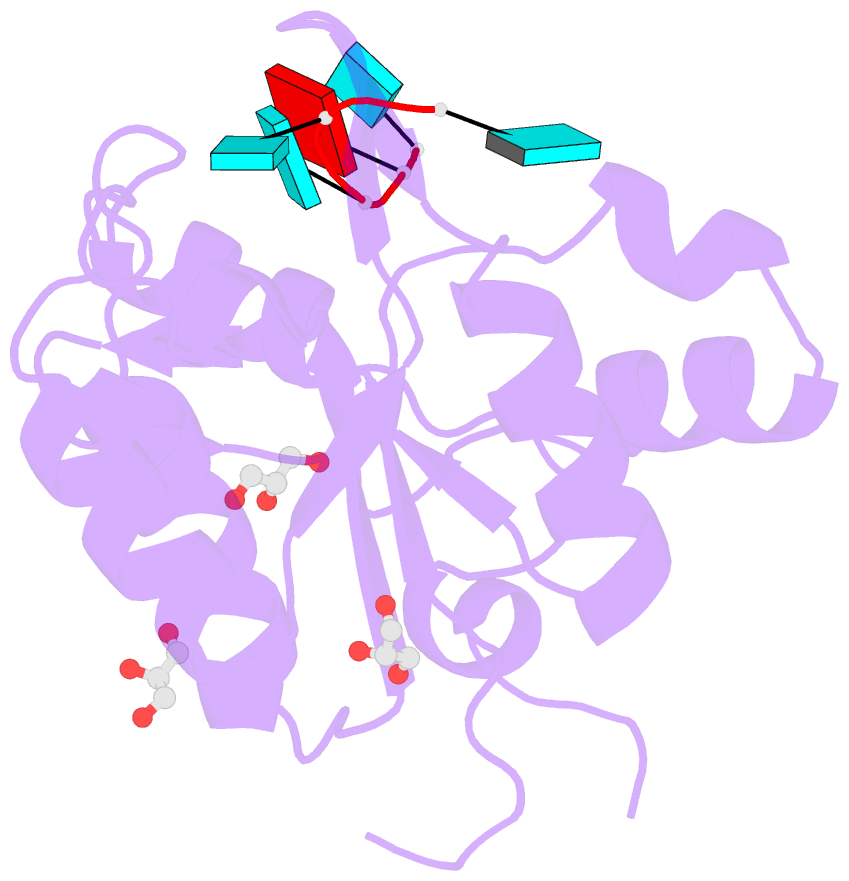
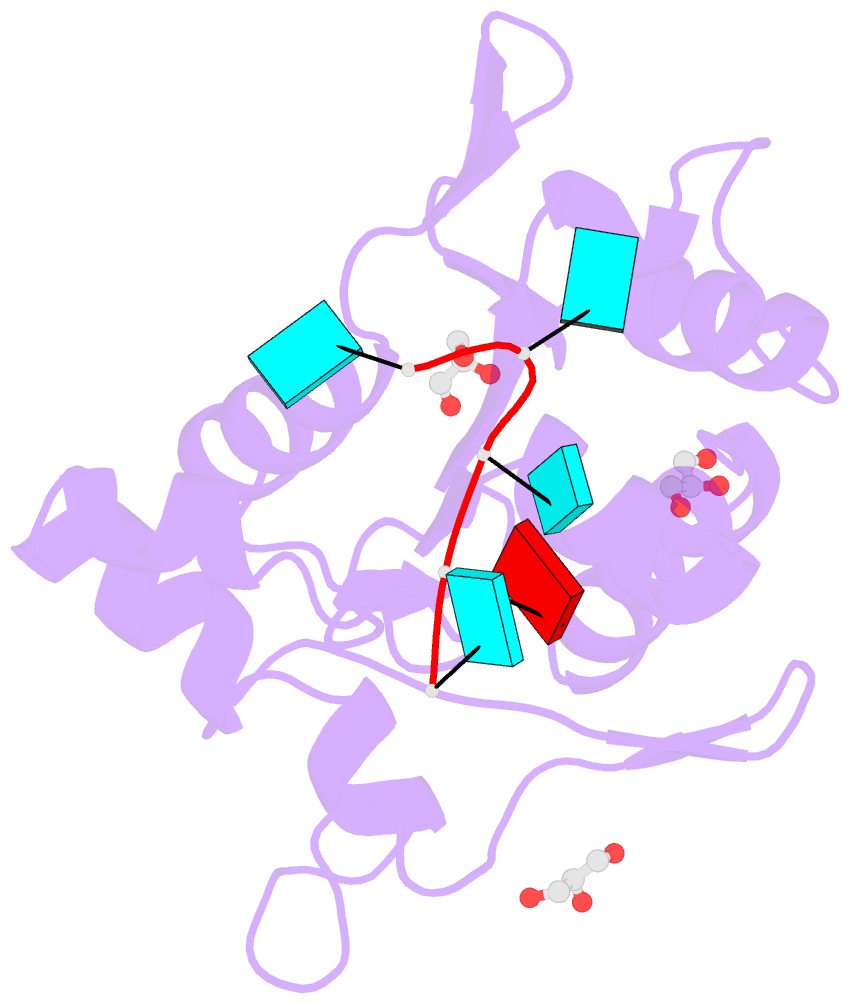
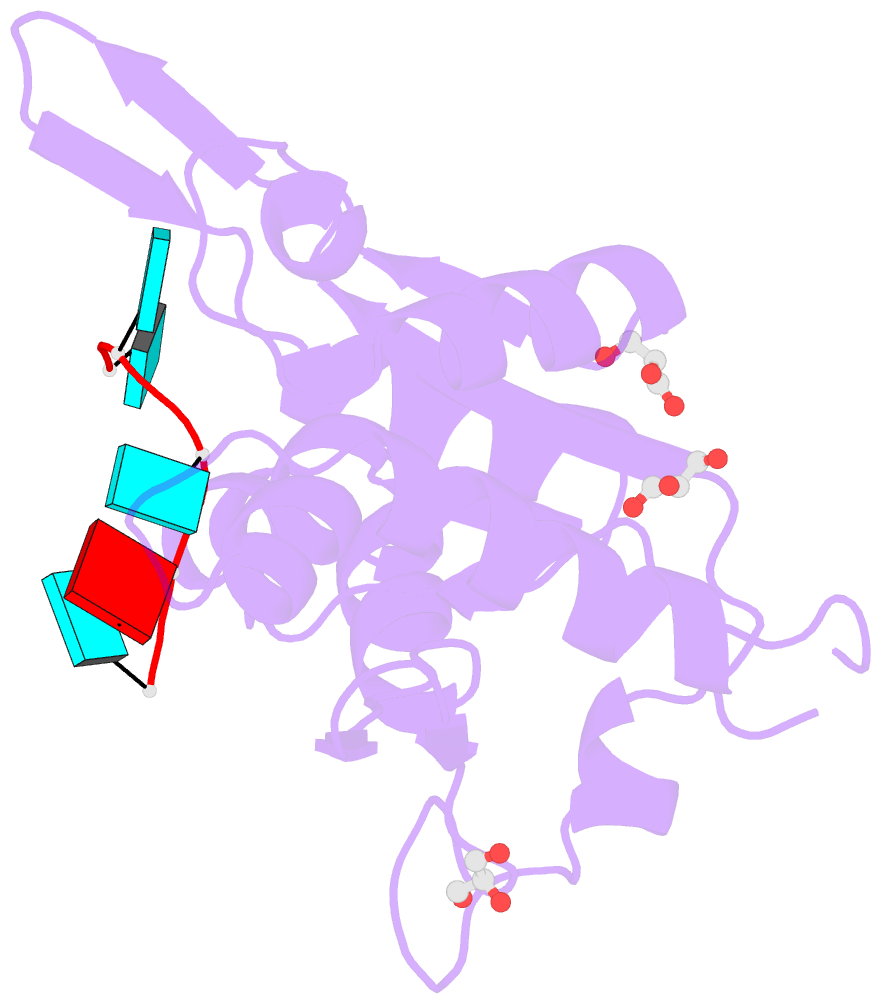
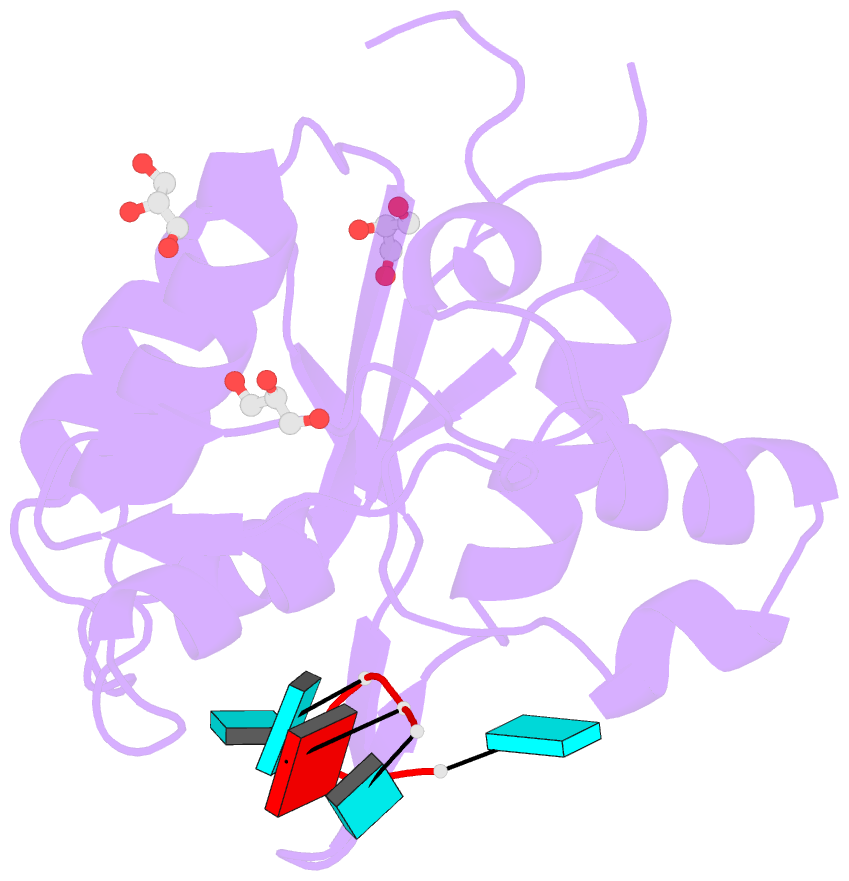
- Nyn domain of human khnyn complex with RNA
- Reference
- Hong S, Choe J (2024): "Crystal structure of NYN domain of Human KHNYN in complex with single strand RNA." Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun., 738, 150545. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150545.
- Abstract
- KHNYN protein with a KH-like domain and a NYN endoribonuclease domain interacts with Zinc-finger antiviral protein (ZAP). ZAP isoforms recognize viral or cellular RNAs and recruit KHNYN to form the ZAP: KHNYN complex. Although the structures of several PIN/NYN domains have been determined, the precise substrate RNA binding mode remains poorly understood. This study presents the crystal structure of a complex of the NYN domain of KHNYN and a 7mer RNA from interferon lambda3 (IFNL3). Our structural analysis reveals that NYN domain of human KHNYN shares structural similarities with other NYN domains of ZC3H12Ã C proteins. The RNA is bound in the central groove region of the protein, facilitated by interactions including coordination by two Mg2+ ions, hydrophobic interactions, and hydrogen bonds. In the observed RNA-protein complex, the U5, A6, and U7 bases are stacked on top of one another, while U3 and U4 bases adopt an "open" conformation (as opposed to base-stacked), forming a U-shaped overall structure. Mutagenesis studies underscore the significance of residues involved in RNA binding for RNase activity. Interestingly, NYN domain of human KHNYN forms a head-to-tail dimer in the crystal, a structural feature also observed in other homologous PIN/NYN proteins, with a residue from the symmetry mate contributing to hydrophobic interactions with the bound RNA.