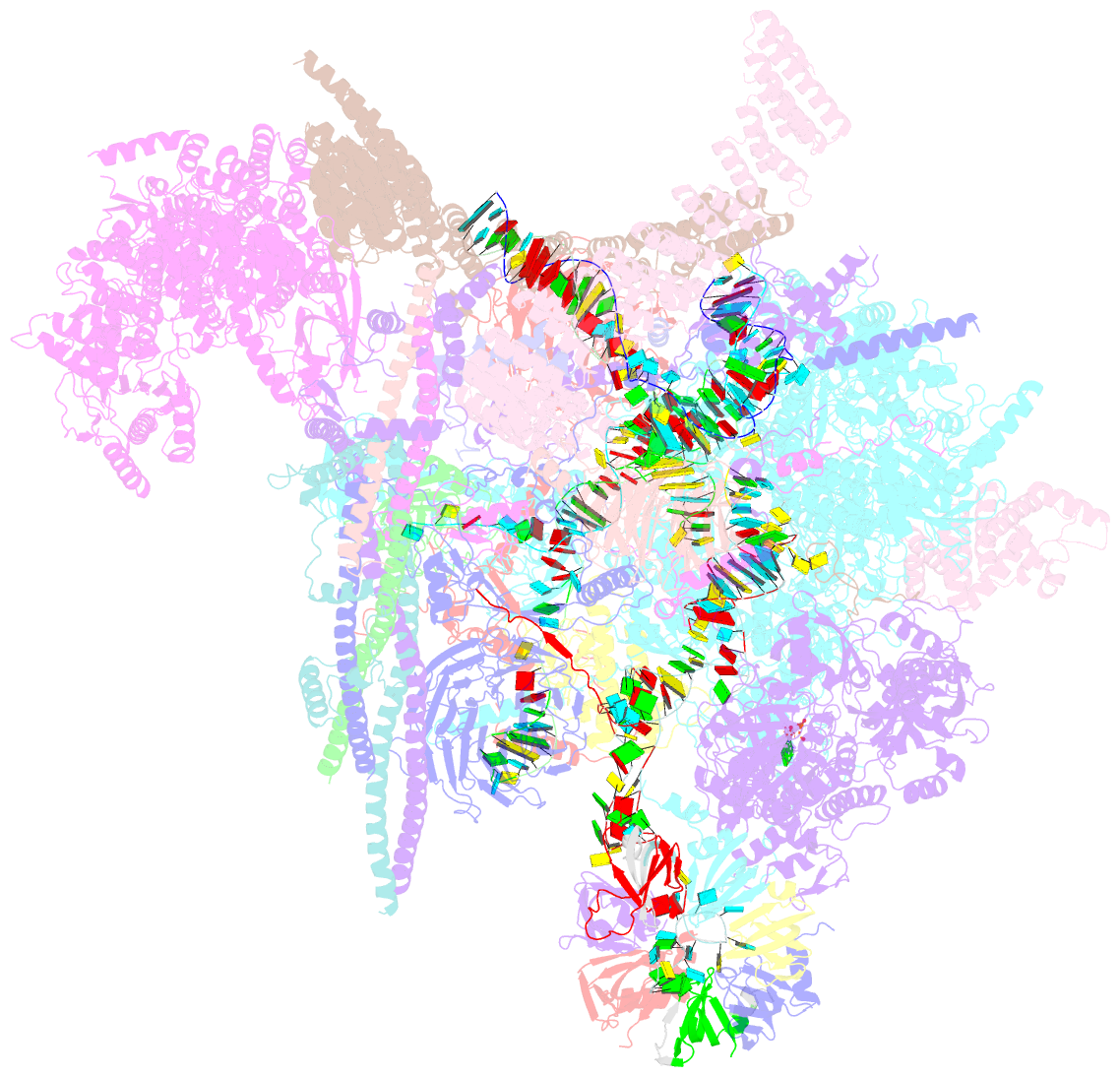
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8xi2; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- splicing
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.6 Å)
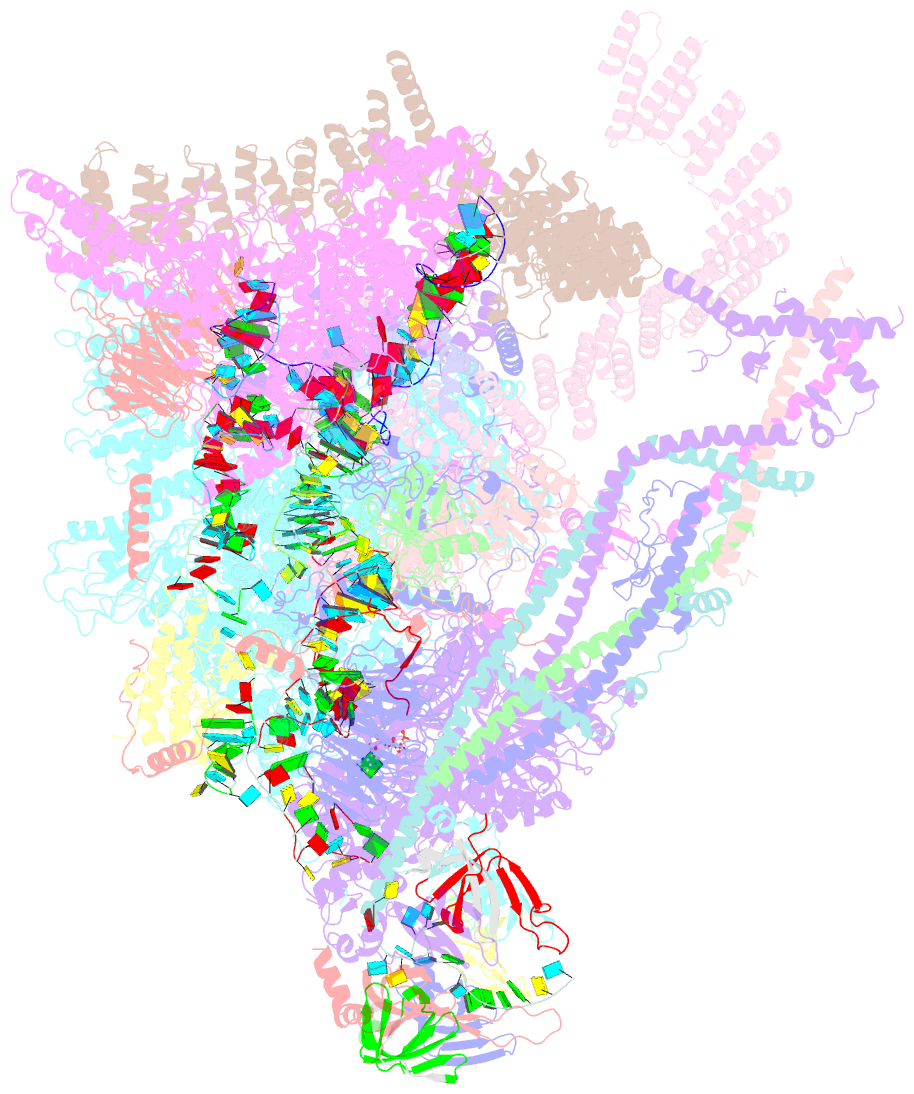
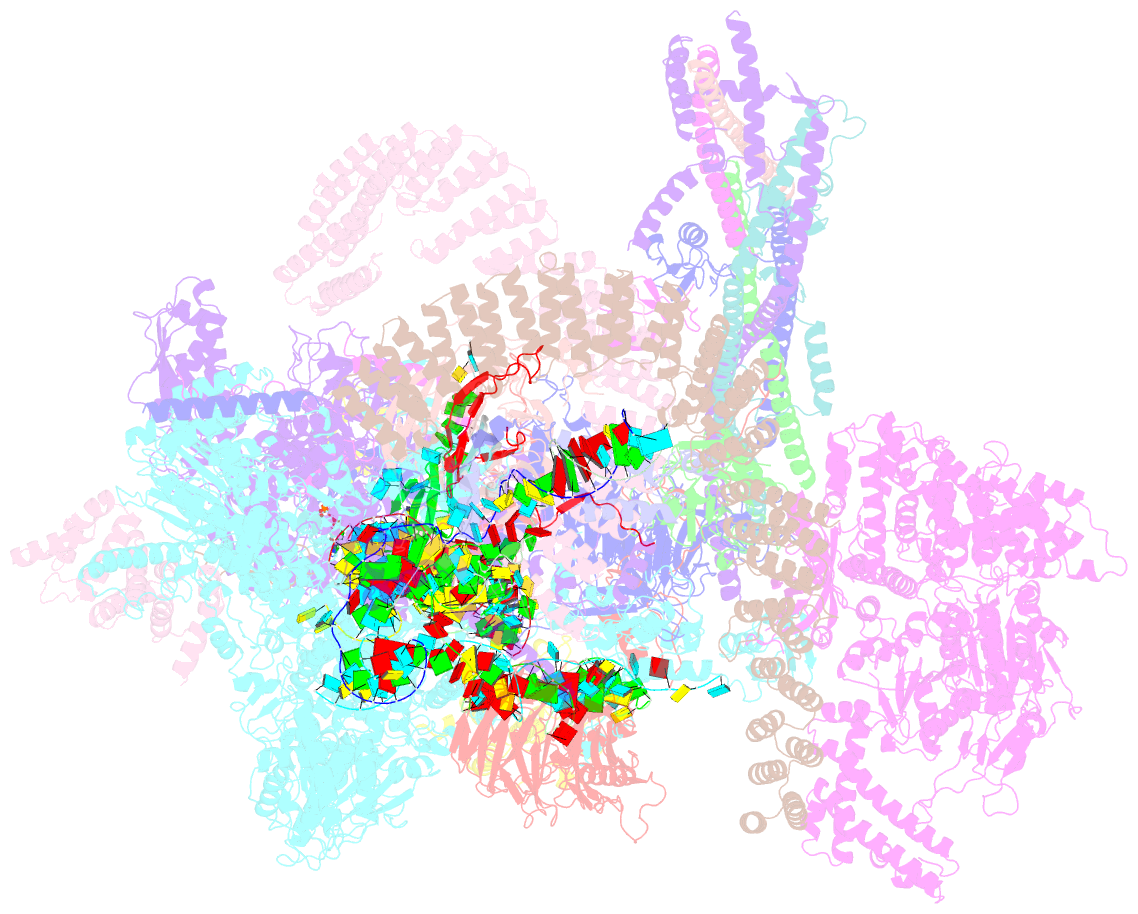
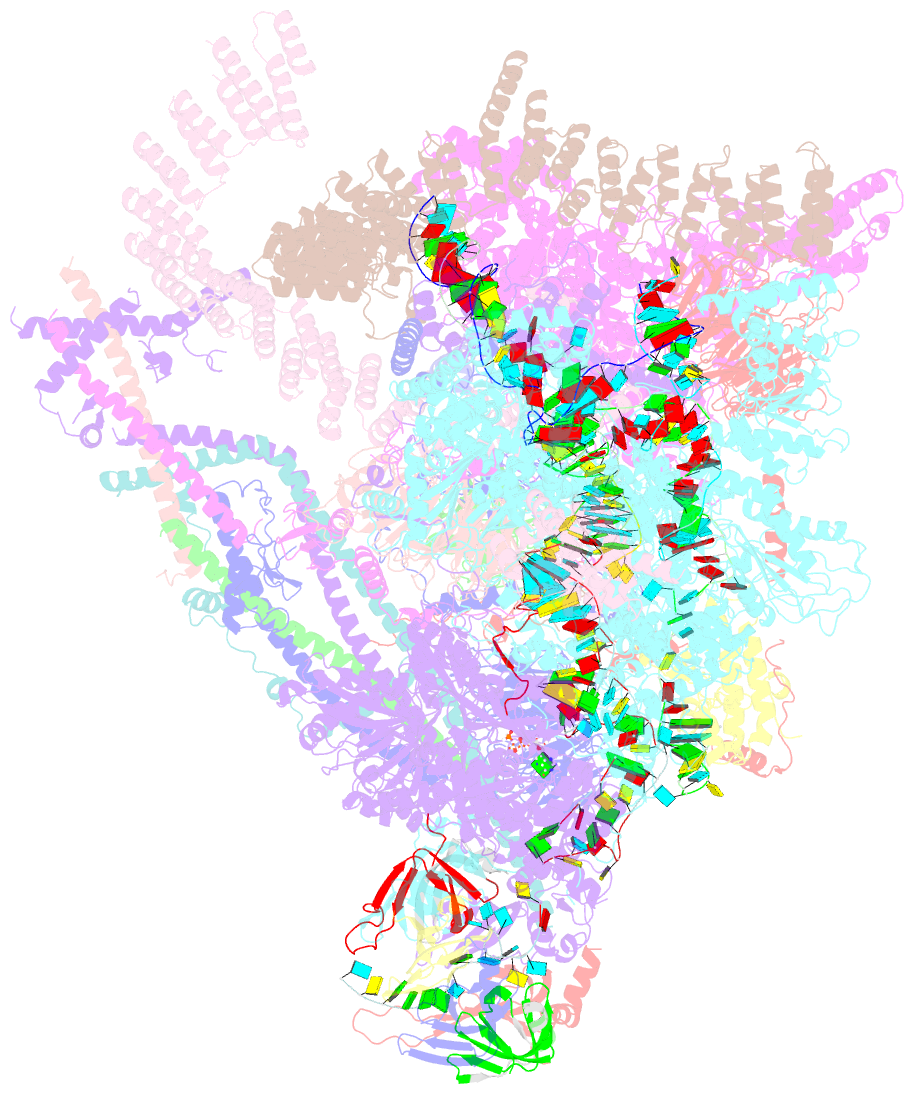
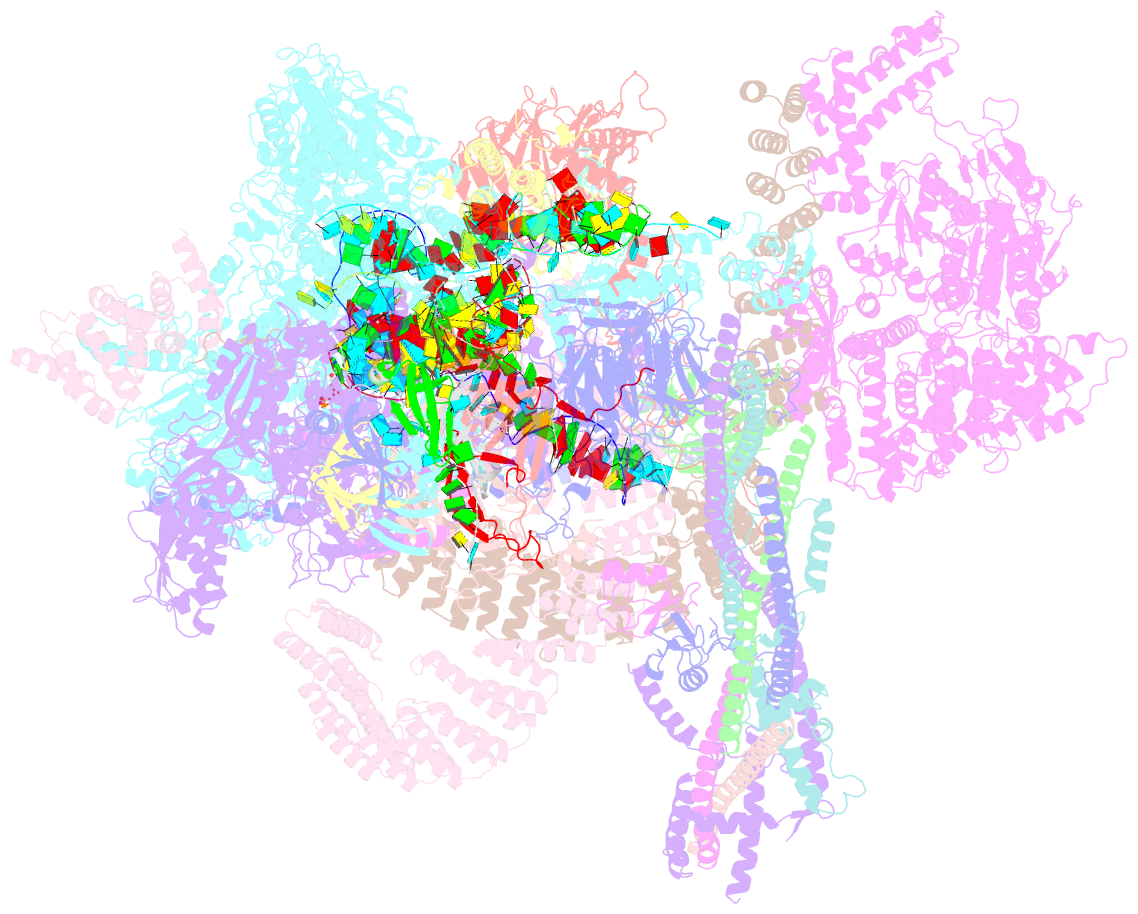
- Summary
- cryo-EM structure of the chlamydomonas c* complex
- Reference
- Lu Y, Liang K, Zhan X (2024): "Structure of a step II catalytically activated spliceosome from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii." Embo J. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00274-3.
- Abstract
- Pre-mRNA splicing, a fundamental step in eukaryotic gene expression, is executed by the spliceosomes. While there is extensive knowledge of the composition and structure of spliceosomes in yeasts and humans, the structural diversity of spliceosomes in non-canonical organisms remains unclear. Here, we present a cryo-EM structure of a step II catalytically activated spliceosome (C* complex) derived from the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii at 2.6 Å resolution. This Chlamydomonas C* complex comprises 29 proteins and four RNA elements, creating a dynamic assembly that shares a similar overall architecture with yeast and human counterparts but also has unique features of its own. Distinctive structural characteristics include variations in protein compositions as well as some noteworthy RNA features. The splicing factor Prp17, with four fragments and a WD40 domain, is engaged in intricate interactions with multiple protein and RNA components. The structural elucidation of Chlamydomonas C* complex provides insights into the molecular mechanism of RNA splicing in plants and understanding splicing evolution in eukaryotes.