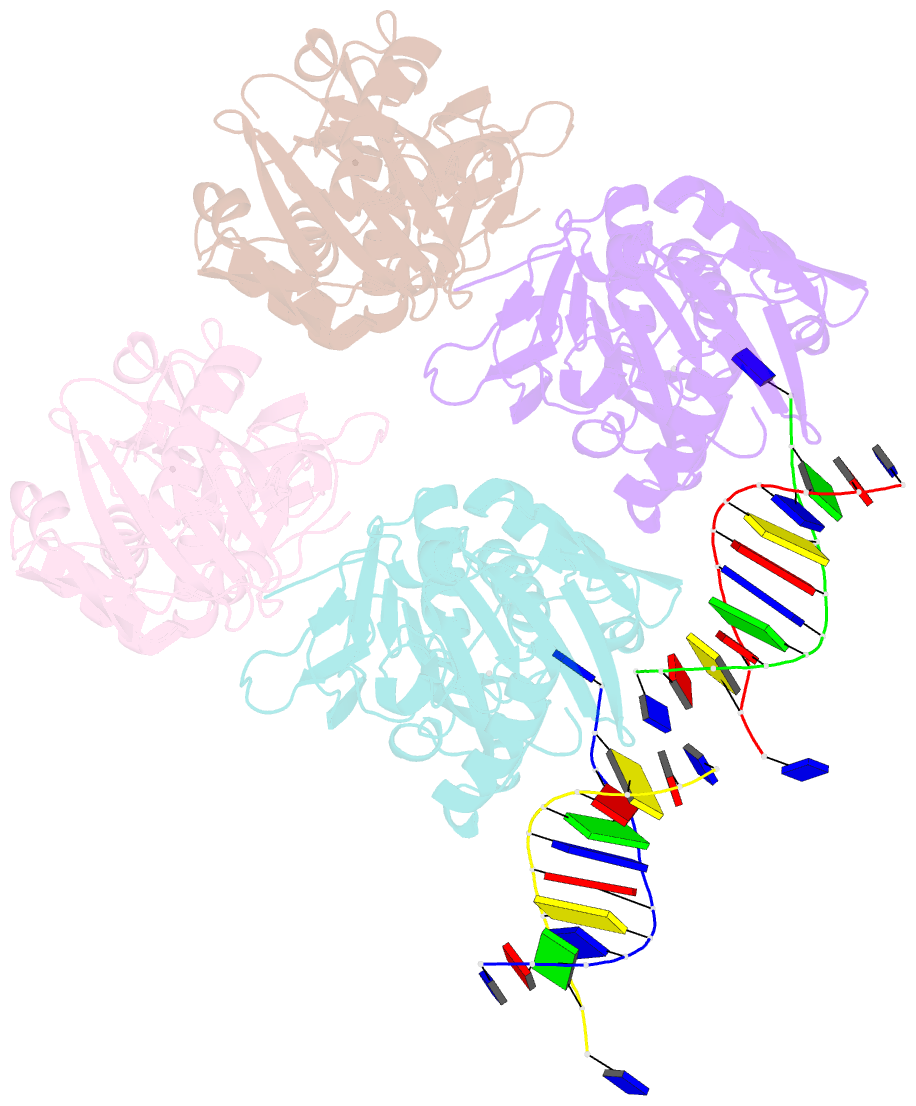
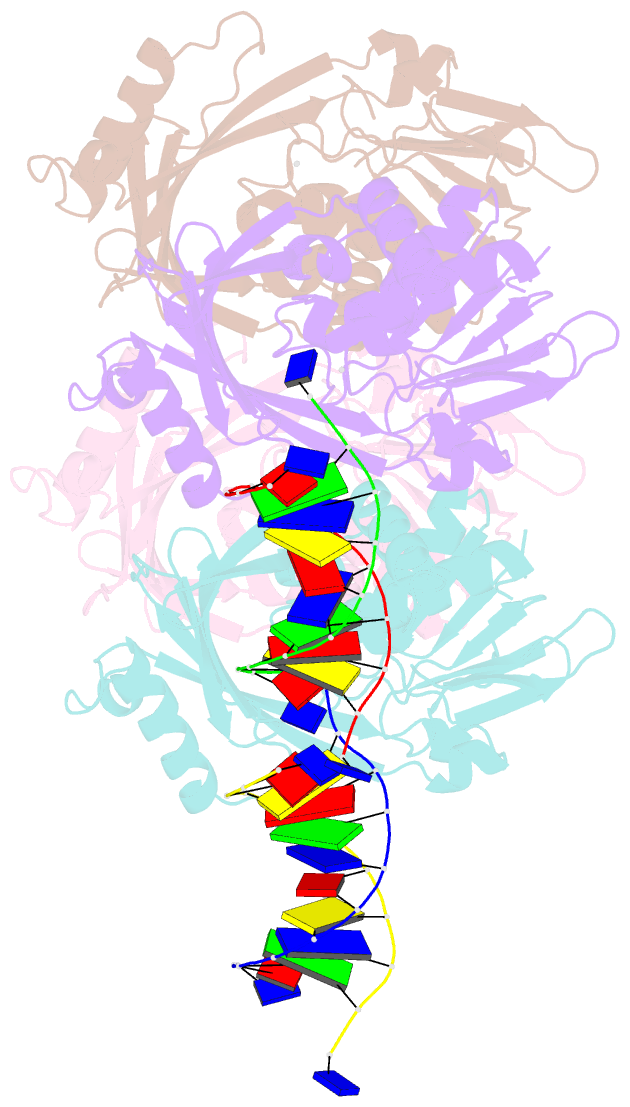
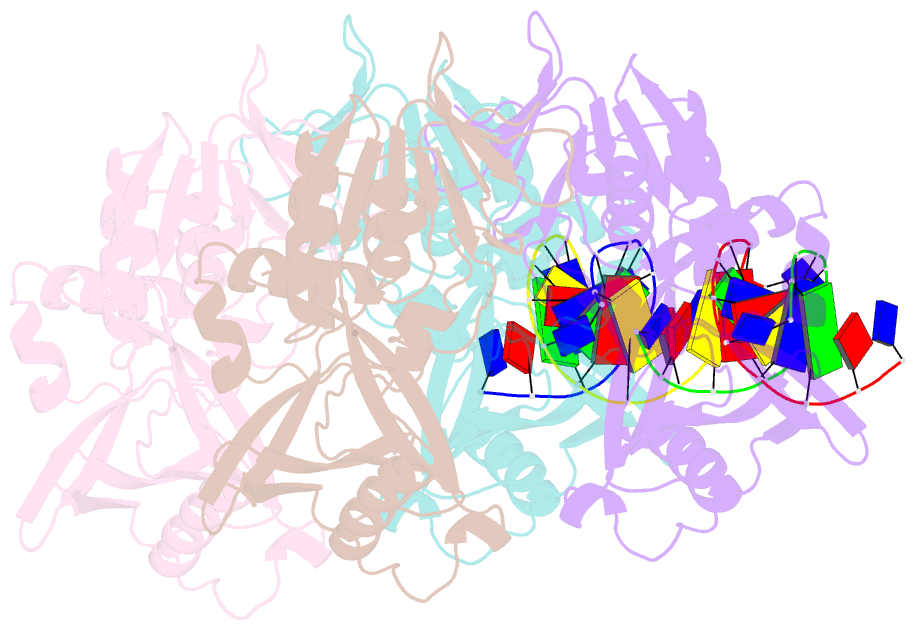
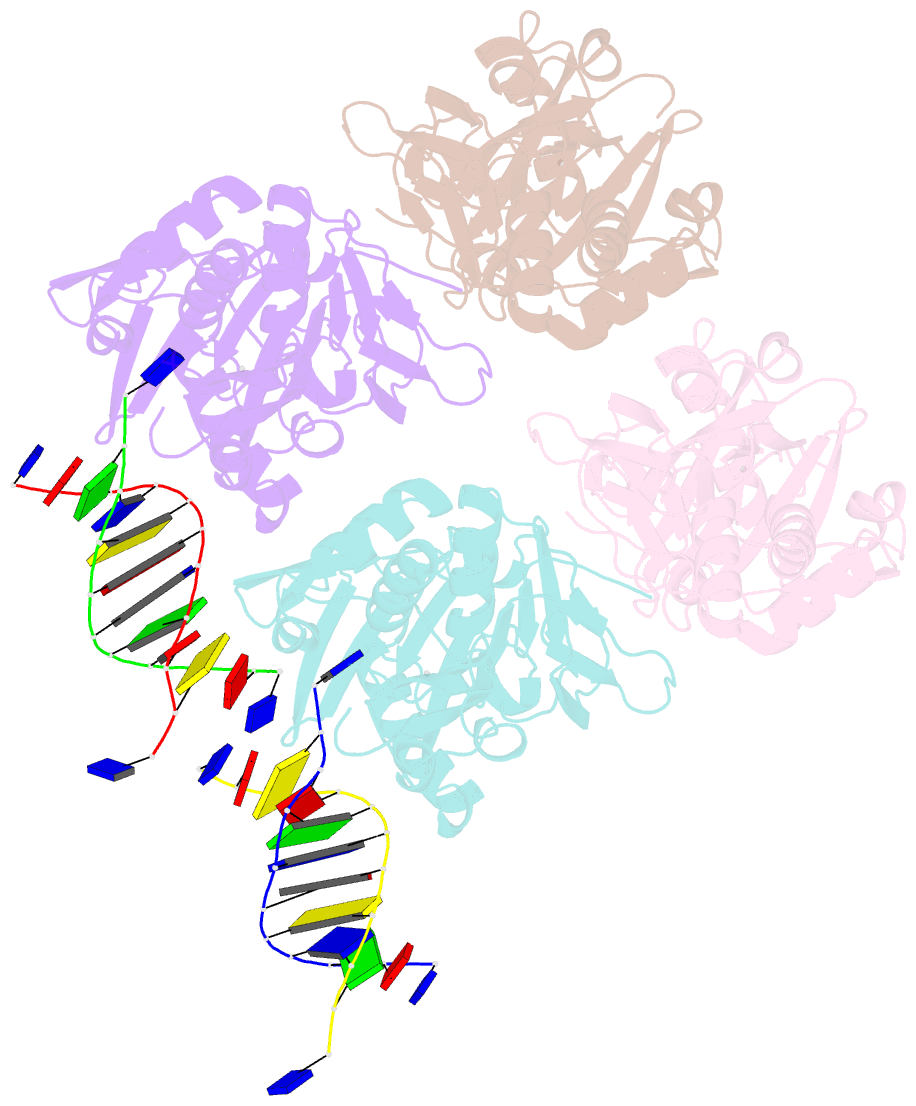
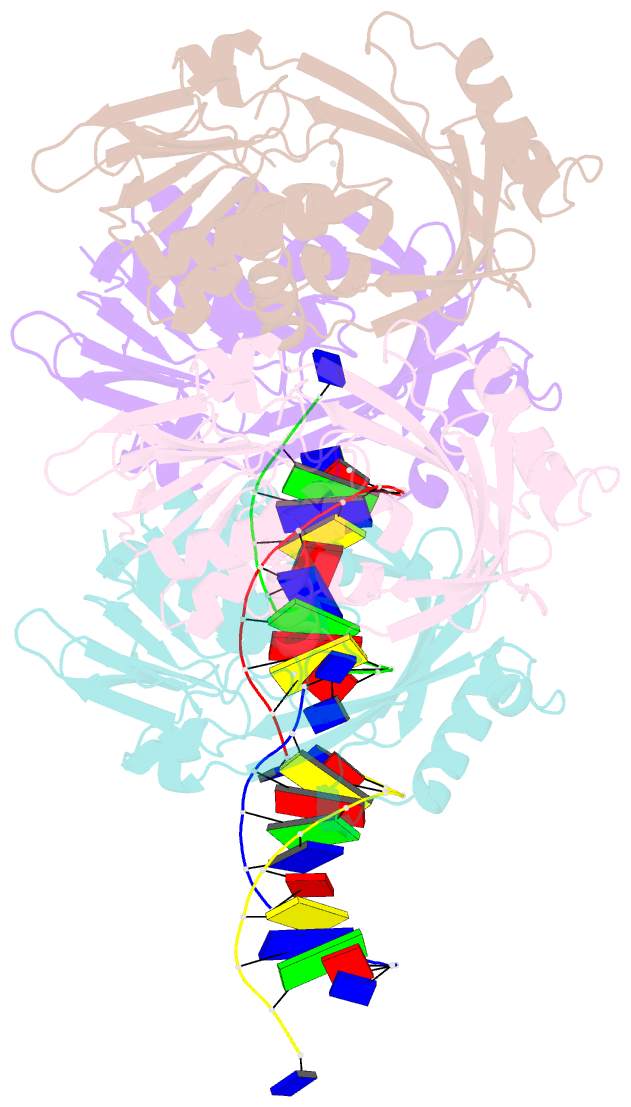
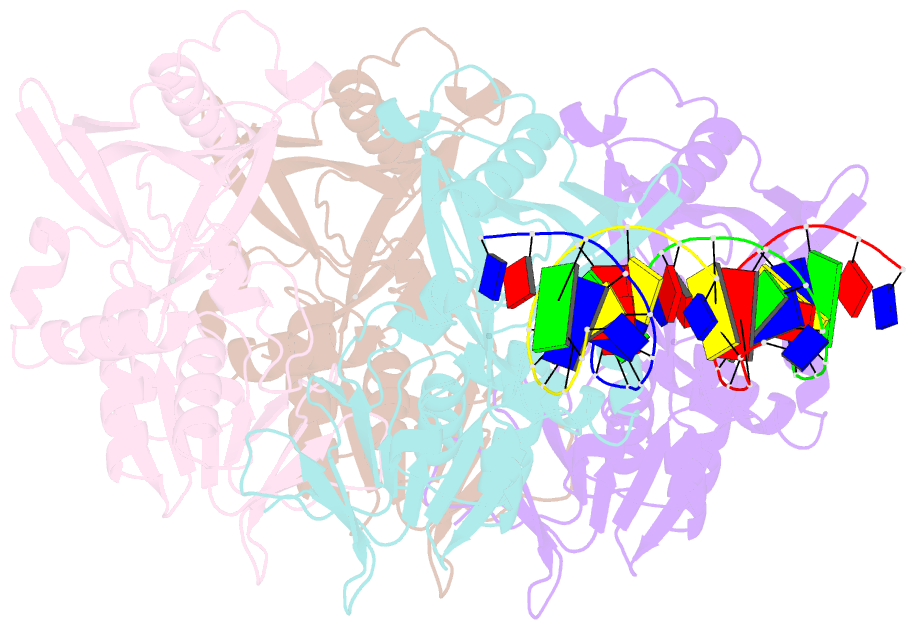
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
8z79;
DSSR-derived features in text and
JSON formats; DNAproDB
- Class
- oxidoreductase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.65 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of 5-n-alpha-glycinylthymidine
(n-alpha-glyt) fad-dependent lyase gp47-ngto from
pseudomonas phage pamx11 in complex with dsDNA
- Reference
-
Wen Y, Guo W, Meng C, Yang J, Xu S, Chen H, Gan J, Wu B
(2024): "Structural
insights into the biosynthetic mechanism of N alpha-GlyT
and 5-NmdU hypermodifications of DNA." Nucleic
Acids Res., 52, 11083-11097. doi:
10.1093/nar/gkae784.
- Abstract
- DNA hypermodifications are effective weapons for phages
to cope with the defense system of bacteria. The biogenesis
of DNA hypermodification in phages involves multiple
steps, from the modified deoxynucleotide monophosphates to
the final hypermodification on the DNA chains.
PseudomonasPaMx11 gp46 and gp47 encode the enzymes for
sequentially converting 5-phosphomethyl-2'-deoxyuridine to
5-Nα-glycinylthymidine and 5-aminomethyl-2'-deoxyuridine.
Here, we have determined the crystal structures of gp46 and
gp47 in their apo and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA)-bound
forms. We uncovered their dsDNA recognition properties and
identified the critical residues for the catalytic
reactions. Combined with in vitro biochemical studies, we
proposed a plausible reaction scheme for gp46 and gp47 in
converting these DNA hypermodifications. Our studies will
provide the structural basis for future bioengineering of
the synthetic pathway of hypermodification and identifying
new modifications in mammals by enzyme-assisted sequencing
methods.