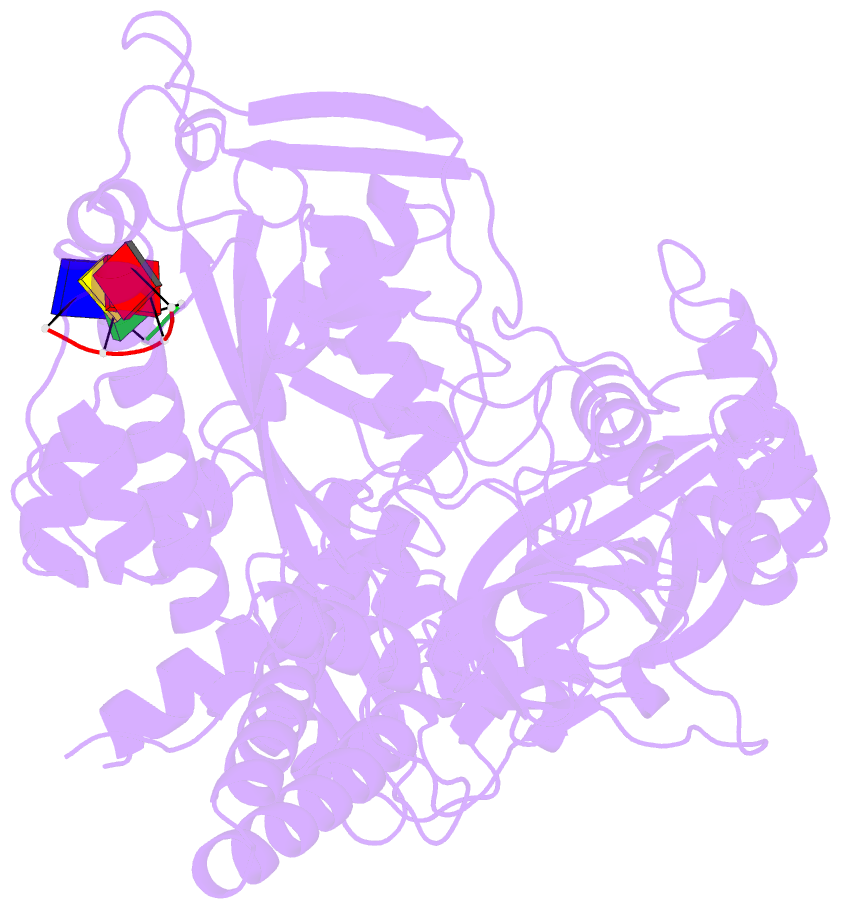
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 9enq; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.12 Å)
- Summary
- Hsv-1 DNA polymerase-processivity factor complex in exonuclease state active site with 1-bp DNA mismatch
- Reference
- Gustavsson E, Grunewald K, Elias P, Hallberg BM (2024): "Dynamics of the Herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase holoenzyme during DNA synthesis and proof-reading revealed by Cryo-EM." Nucleic Acids Res., 52, 7292-7304. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae374.
- Abstract
- Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1), a double-stranded DNA virus, replicates using seven essential proteins encoded by its genome. Among these, the UL30 DNA polymerase, complexed with the UL42 processivity factor, orchestrates leading and lagging strand replication of the 152 kb viral genome. UL30 polymerase is a prime target for antiviral therapy, and resistance to current drugs can arise in immunocompromised individuals. Using electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM), we unveil the dynamic changes of the UL30/UL42 complex with DNA in three distinct states. First, a pre-translocation state with an open fingers domain ready for nucleotide incorporation. Second, a halted elongation state where the fingers close, trapping dATP in the dNTP pocket. Third, a DNA-editing state involving significant conformational changes to allow DNA realignment for exonuclease activity. Additionally, the flexible UL30 C-terminal domain interacts with UL42, forming an extended positively charged surface binding to DNA, thereby enhancing processive synthesis. These findings highlight substantial structural shifts in the polymerase and its DNA interactions during replication, offering insights for future antiviral drug development.