Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 9gd3; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.0 Å)
- Summary
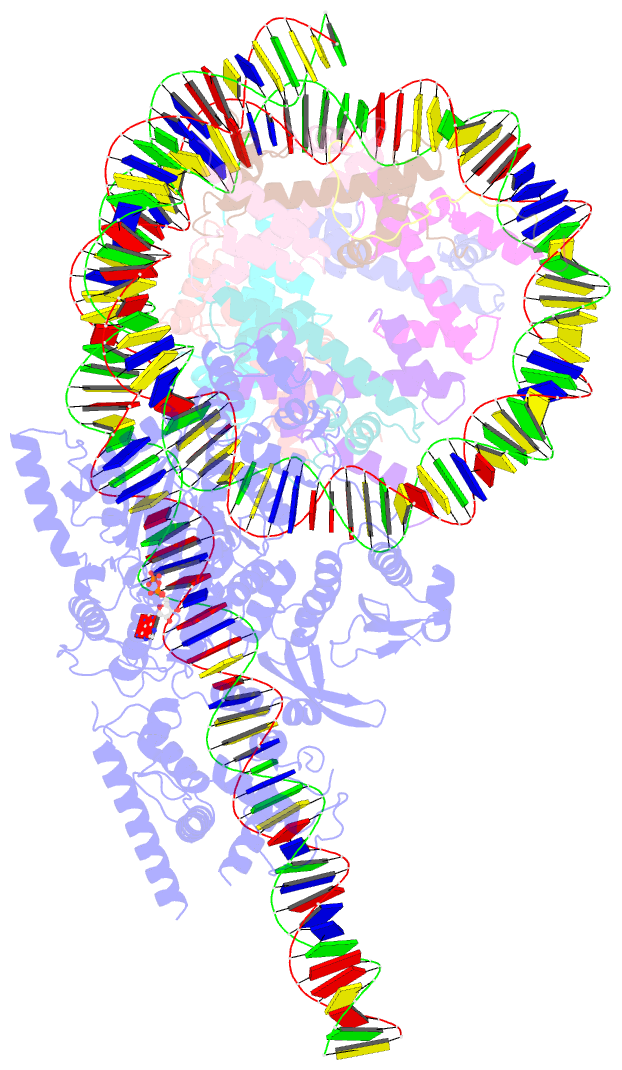
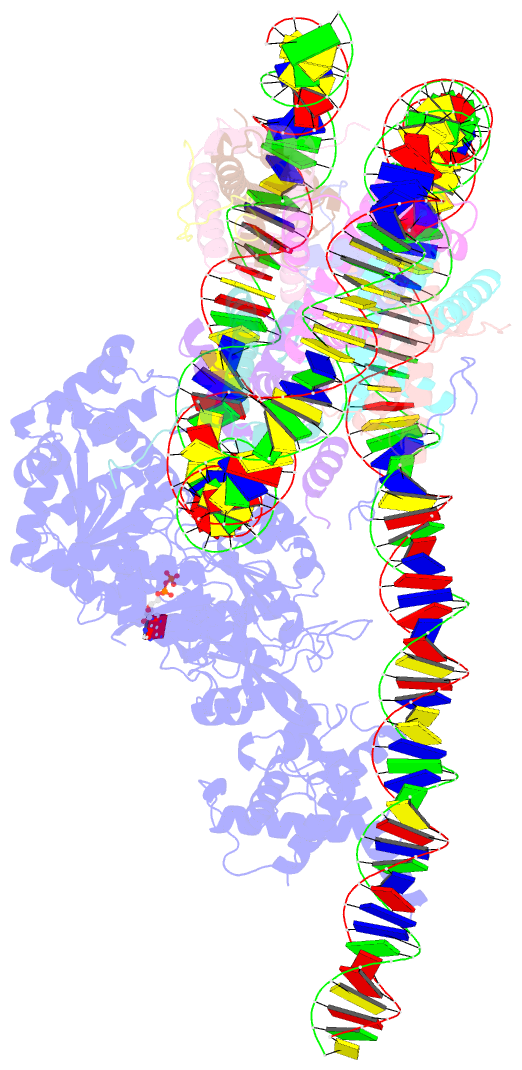
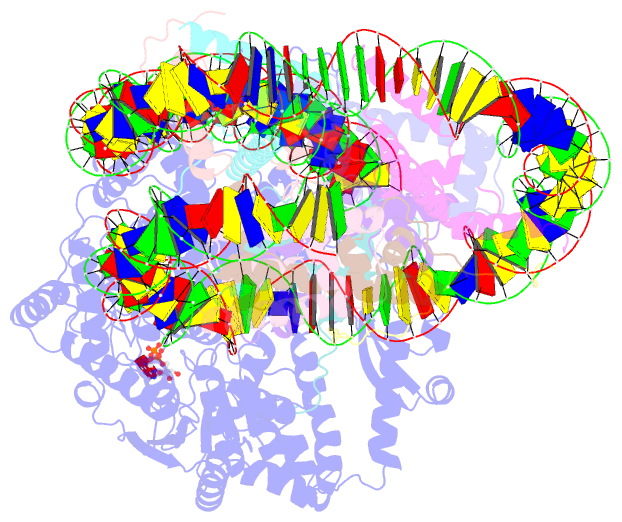
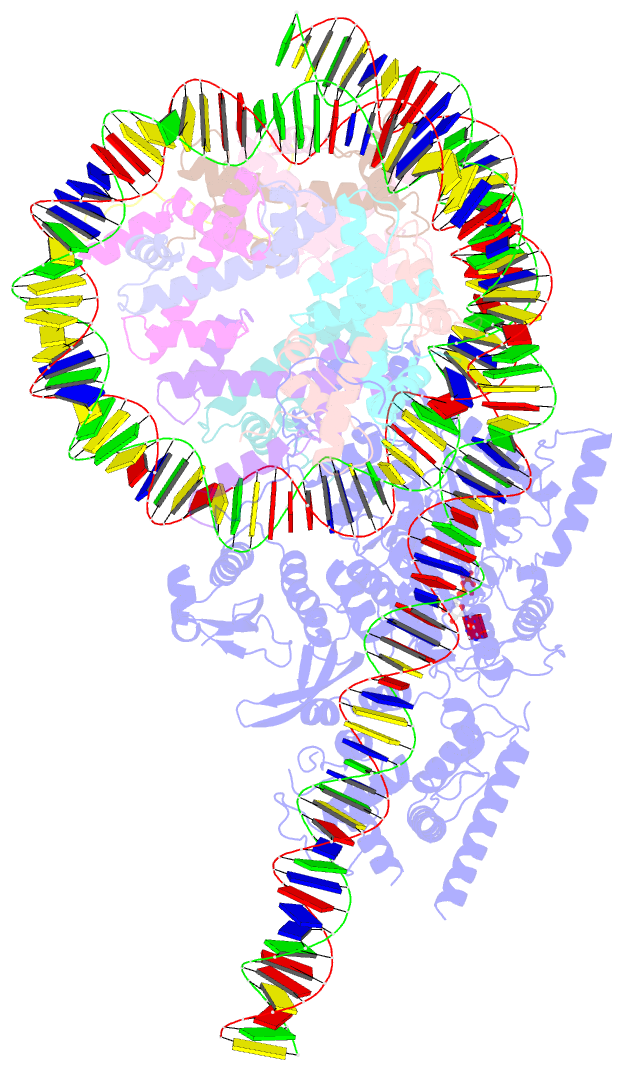
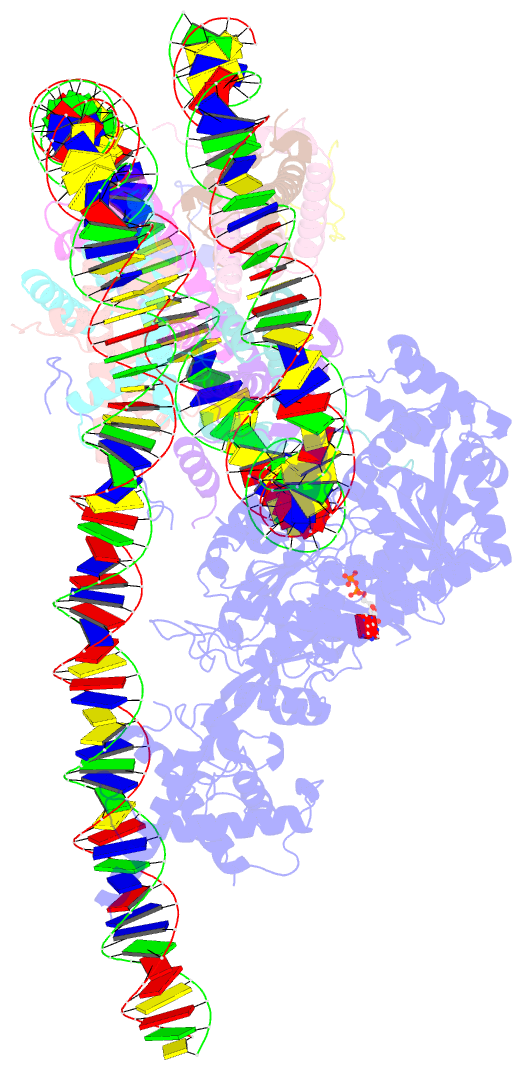
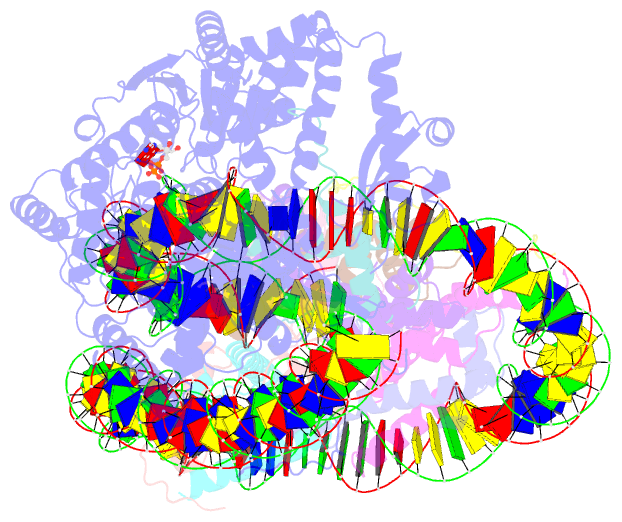
- Structure of a mononucleosome bound by one copy of chd1 with the dbd on the exit-side DNA.
- Reference
- Engeholm M, Roske JJ, Oberbeckmann E, Dienemann C, Lidschreiber M, Cramer P, Farnung L (2024): "Resolution of transcription-induced hexasome-nucleosome complexes by Chd1 and FACT." Mol.Cell, 84, 3423. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.08.022.
- Abstract
- To maintain the nucleosome organization of transcribed genes, ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers collaborate with histone chaperones. Here, we show that at the 5' ends of yeast genes, RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) generates hexasomes that occur directly adjacent to nucleosomes. The resulting hexasome-nucleosome complexes are then resolved by Chd1. We present two cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of Chd1 bound to a hexasome-nucleosome complex before and after restoration of the missing inner H2A/H2B dimer by FACT. Chd1 uniquely interacts with the complex, positioning its ATPase domain to shift the hexasome away from the nucleosome. In the absence of the inner H2A/H2B dimer, its DNA-binding domain (DBD) packs against the ATPase domain, suggesting an inhibited state. Restoration of the dimer by FACT triggers a rearrangement that displaces the DBD and stimulates Chd1 remodeling. Our results demonstrate how chromatin remodelers interact with a complex nucleosome assembly and suggest how Chd1 and FACT jointly support transcription by RNAPII.